Control method for downlink data reception of mobile communication terminal and mobile communication terminal
A technology for mobile communication terminals and downlink data, applied in wireless communication, error prevention/detection using return channels, digital transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as retransmission HARQ residues, errors, and reliability cannot be guaranteed, and achieve saving The effect of power loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
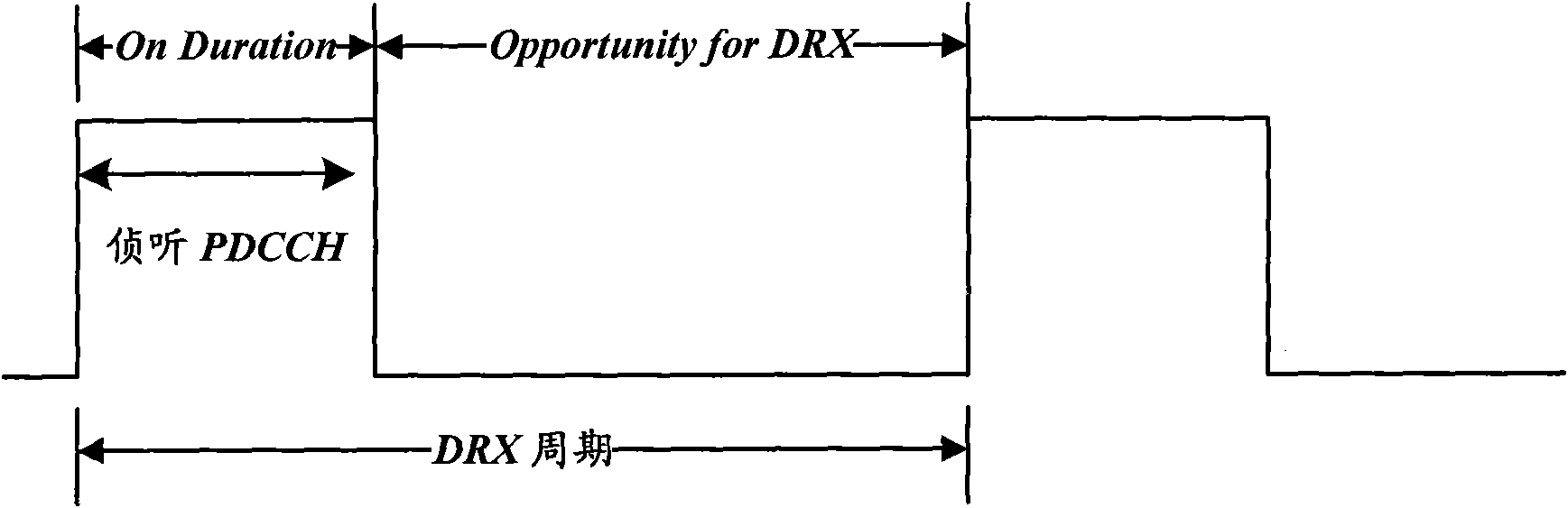
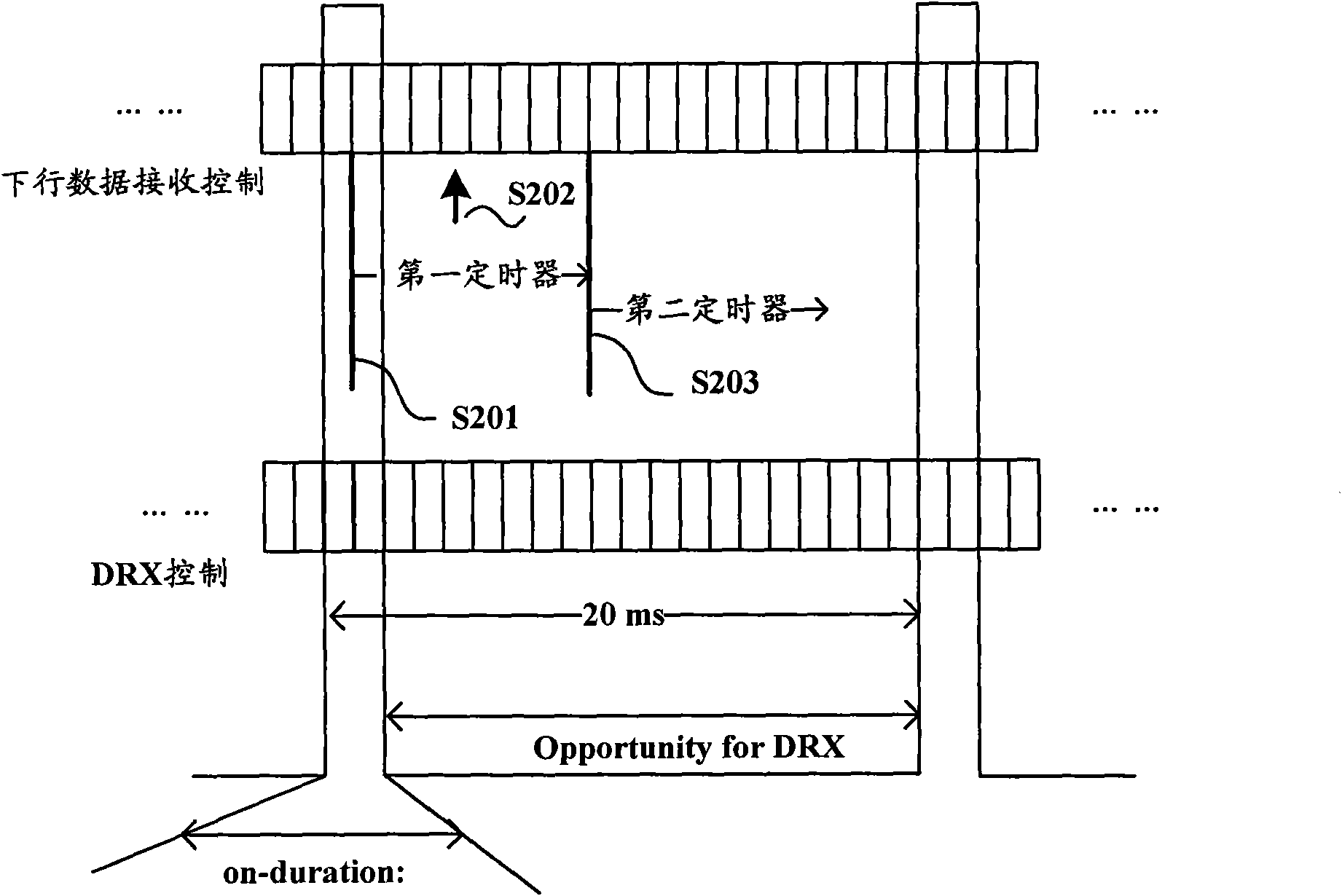
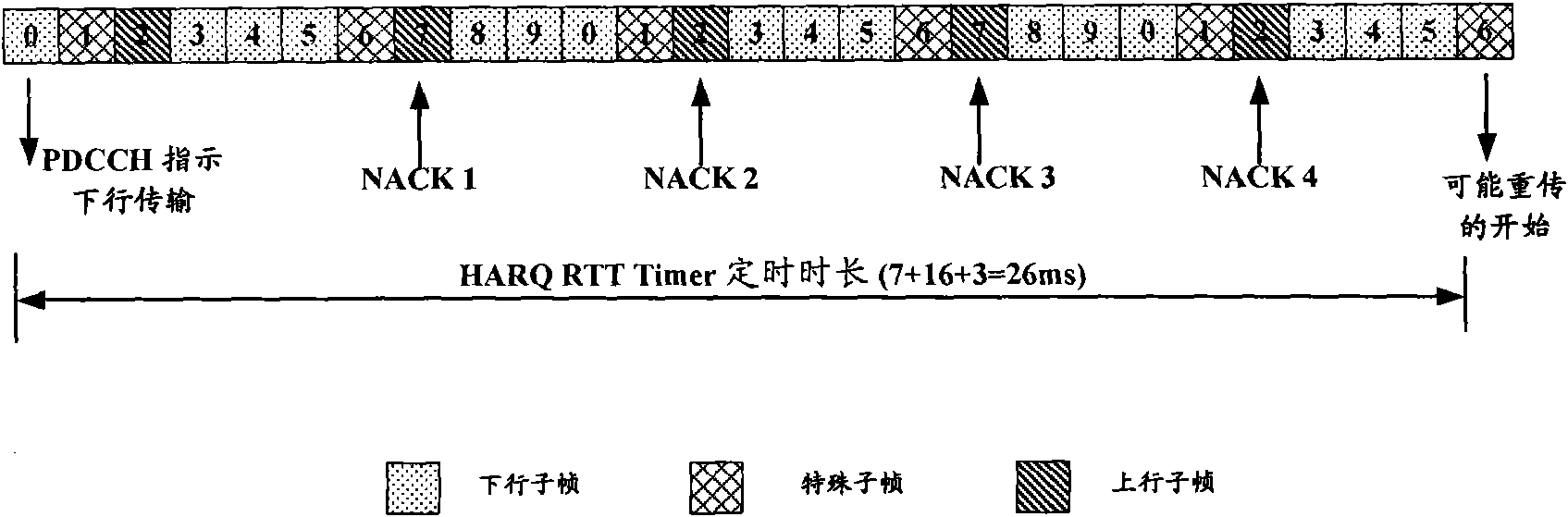
[0034] In the embodiment of the present invention, considering the use of the ACK / NACK repetition mechanism in the TDD system, the eNB makes a judgment after receiving the last ACK / NACK to decide whether to retransmit failed data or send new data. Since the mobile communication terminal starts the HARQ RTT Timer when it receives the downlink data transmission instruction, and then according to whether the downlink data is correctly received after the downlink data arrives, several consecutive uplink subframes, according to the configured retransmission times, feedback to the base station whether multiple Correctly receive the indication information ACK or NACK of the downlink data. The eNB will make a judgment after receiving the last ACK or NACK. If the judgment result is NACK, the downlink data will be retransmitted. Therefore, the optimal timing duration T1 of the HARQ RTT Timer is three parts The sum of time is calculated according to the following formula:
[0035] T1=kt+...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com