Microtubule-associated protein and coding genes and application thereof
A protein and gene technology, applied in the field of microtubule-binding protein and its coding gene and application, can solve problems such as abnormal chromosome separation and microtubule depolymerization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
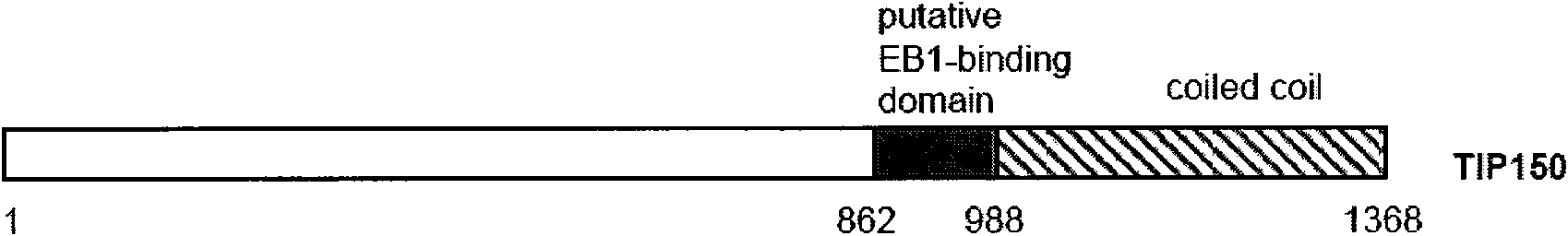
[0047] Example 1. Acquisition of the gene encoding microtubule-binding protein TIP150
[0048] Using the cDNA of human cervical cancer HeLa cells (Stratagene, Cat.No.937248) as a template, PCR amplification was carried out, and the primers used for PCR amplification were as follows:
[0049] Upstream primer: 5'-gcgaattctatgagcgtcccagtgg-3' (sequence 3 of the sequence listing);
[0050] Downstream primer: 5'-gcgtcgactcatctgggtgttgtgc-3' (SEQ ID NO: 4 in the Sequence Listing).
[0051] Digest the PCR product with EcoRI and SalI, connect the digested PCR product to the vector pMD18-T (TaKaRa Company) after the same digestion, transform the ligated product into Escherichia coli (E.coli) DH5α competent cells, and screen positive Cloning and extracting the plasmid, the recombinant plasmid containing the target fragment was obtained, which was named pMD-TIP150.
[0052] Sequencing was performed on pMD-TIP150, and the sequencing results showed that the human TIP150 gene has the nucl...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The construction of the expression vector of embodiment 2, TIP150 and EB1 and deletion mutant thereof
[0055] 1. Construction of GFP-TIP150
[0056] pMD-TIP150 was digested with restriction endonucleases EcoRI and SalI, and the digested product was ligated with pEGFP-C1 (Clontech, Cat. No. 6084-1) digested in the same way to obtain GFP-TIP150.
[0057] 2. Construction of MBP-TIP150
[0058] pMD-TIP150 was digested with restriction endonucleases EcoRI and SalI, and the digested product was ligated with pMAL-c2x (New England Biolabs, Cat. No. N8076S) digested in the same way to obtain MBP-TIP150.
[0059] 3. Construction of flag-TIP150
[0060] pMD-TIP150 was digested with restriction endonucleases EcoRI and SalI, and the digested product was ligated with p3XFLAG-myc-CMV-24 (Sigma, Cat. No. E6151) digested in the same way to obtain flag-TIP150.
[0061] 4. Construction of GST-EB1
[0062] Using the cDNA of human cervical cancer HeLa cells as a template, carry out PCR...
Embodiment 3
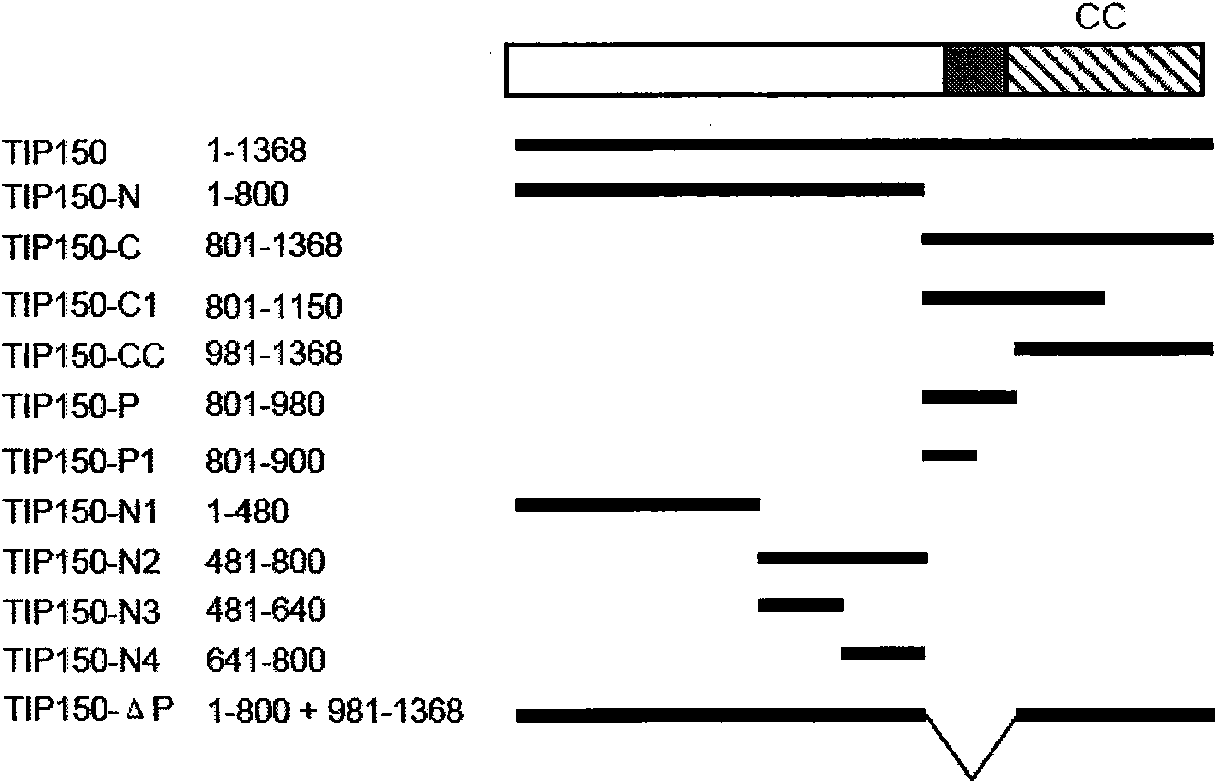
[0111] Example 3, Identification of the interaction region between TIP150 and EB1
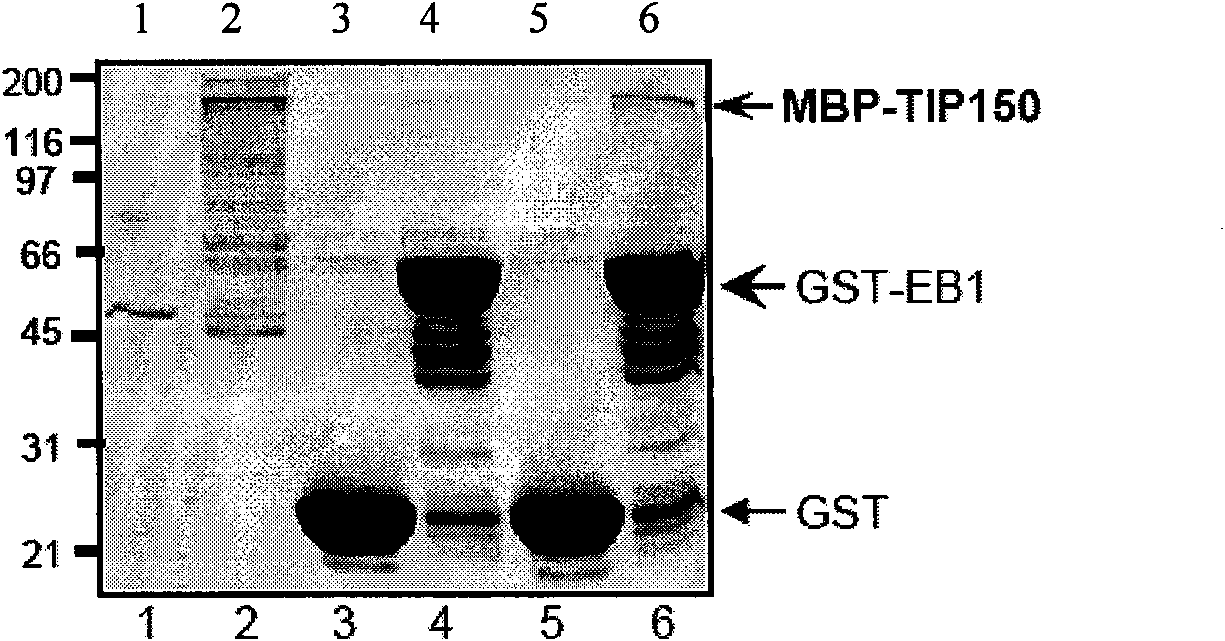
[0112] 1. In vitro pull-down detection of the interaction between TIP150 and EB1
[0113] MBP-TIP150 was expressed in Rossetta (DE) pLysS host bacteria at 30°C, and then purified with Amylose resin (New England Biolabs) according to standard procedures to obtain purified MBP-TIP150 fusion protein. GST-EB1 was expressed in Rossetta (DE) pLysS host bacteria at 30°C, and then purified with glutathione-Sepharose 4B (Amersham Biosciences) according to standard procedures to obtain purified GST-EB1 fusion protein. pMAL-c2x was expressed in Rossetta (DE) pLysS host bacteria at 30°C, and then purified with Amylose resin (New England Biolabs) according to standard procedures to obtain purified MBP protein. pGEX-6P-1 was expressed in Rossetta (DE) pLysS host bacteria at 30°C, and then purified with glutathione-Sepharose 4B (Amersham Biosciences) according to standard procedures to obtain purified GST pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com