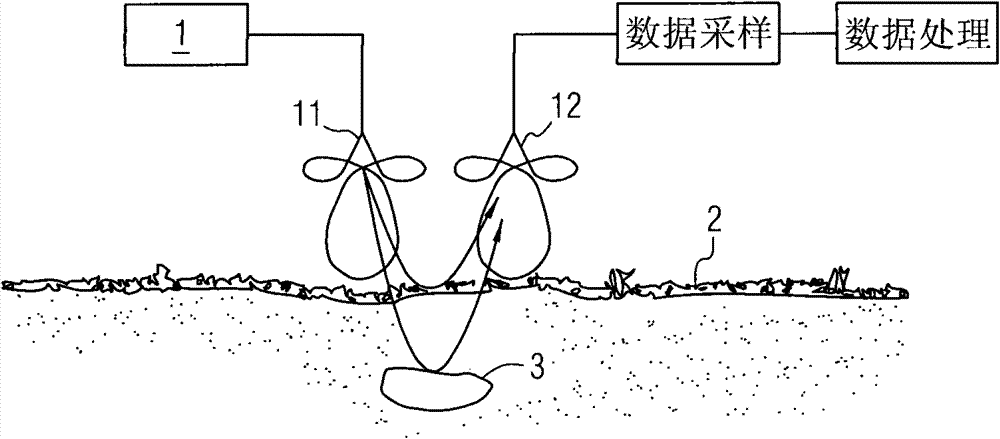
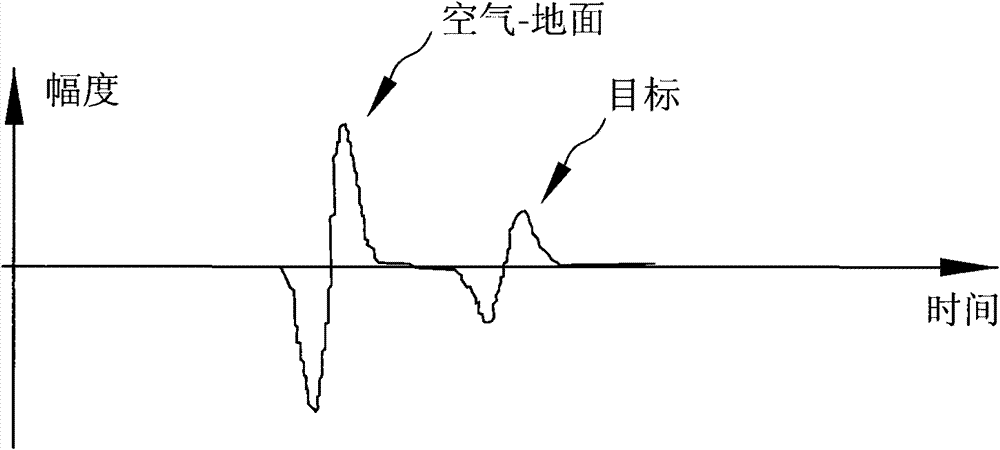
Method for measuring diameter of plant underground roots by using ground penetrating radar
A ground-penetrating radar and underground root technology, applied to measuring devices, using re-radiation, radio wave measurement systems, etc., can solve problems such as unrecognizable, quantitative research has not achieved complete success, and is limited to qualitative mapping, etc., to achieve strong correlation sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1 Measurement method
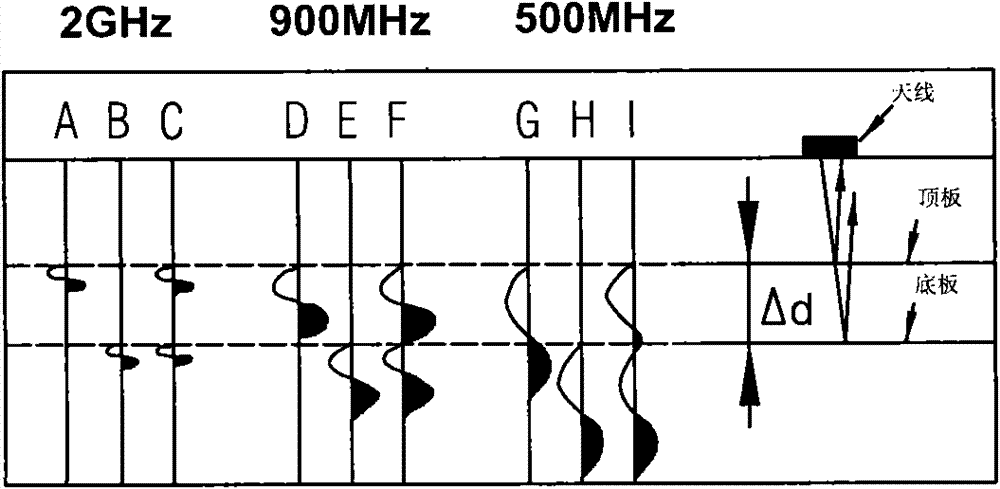
[0027] Theoretically speaking, the ability of GPR to identify the root diameter is related to the resolution of GPR. Resolution is a very important parameter to measure the detection effect of ground penetrating radar, which is defined as the ability to distinguish the smallest anomaly. The resolution of ground penetrating radar is closely related to the transmission frequency of the radar antenna. The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength and the stronger the resolution.
[0028] Such as figure 2 As shown, for a dielectric layer with a certain thickness underground, A-D-G in the figure represent the waveform records in the dielectric roof at high, medium and low frequencies (corresponding frequencies are 2GHz, 900MHz, 500MHz respectively); B-E-H represent 2GHz respectively , 900MHz, and 500MHz are the waveform records in the dielectric bottom plate; C-F-I represent the composite records in the top plate and the bottom pla...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2 Measurement of characteristic constant K
[0039] As can be seen from Example 1, in the method for measuring the diameter of the underground root according to the present invention, the diameter D of the underground root of the plant is proportional to the time parameter ΔT, therefore, the corresponding value of the underground root of a certain plant in a certain area can be obtained by the following method The characteristic constant K, and then obtain the diameter of the underground root of the plant in the area. The specific method is as follows:
[0040] This underground root after measuring in embodiment 1 is dug out, and the diameter D of this underground root that measures digging out 1 , the specific time parameter ΔT of the actually measured underground root of the plant calculated according to the method in Example 1 1 , the characteristic constant K=D corresponding to the underground root can be obtained 1 / ΔT 1 .
[0041] That is to say, in t...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3 Verification test
[0044] see Figure 5 , shown in this embodiment is the correlation diagram between the time parameter ΔT obtained by detecting underground roots at different depths and the actual root diameter, wherein the frequency of the corresponding radar wave is 2 GHz.
[0045] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the correlation analysis results of the time parameter ΔT and the actual root diameter show that there is a very significant correlation between ΔT and the actual root diameter, and the coefficient of determination R 2 The value of 0.868, the root mean square error (RMSE) is 3.816mm.
[0046] Figure 6 Shown are the time parameters ΔT and Figure 5 The relationship diagram between the estimated root diameter value and the actual root diameter obtained by the characteristic constant K, such as Figure 6 As shown, the similarity between the estimated root diameter value and the measured root diameter value from the radar antenna measurement dat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com