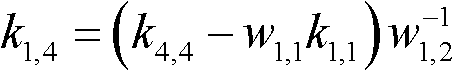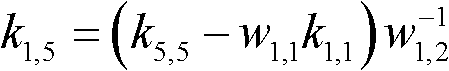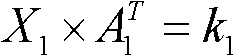Graded group key management method based on line geometry
A technology of group key and management method, applied in the field of group key management, can solve the problems of inability to know specific paths, insufficient scalability, inability to know subgroup ancestors and subgroups, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0194] Such as figure 1 As shown, a group communication system with hierarchical access control includes a central controller CC, a subgroup V i , subgroup controller SC i , CC and each SC i They are interconnected through the Internet, where i=1, 2, . . . , 7.
[0195] The group's hierarchical access structure is as follows figure 2 As shown, all high-level nodes can derive the keys of their direct or indirect descendant nodes, while low-level nodes cannot derive the keys of their ancestor nodes. Nodes without direct or indirect superior-subordinate relationship cannot derive each other's key. Sibling nodes also cannot export each other's keys.
[0196] Such as image 3 As shown, the system selects the finite field F, and all operations are based on the finite field F; at the same time, the pseudo-random number generator is selected as f(.,.); for the same initialization input (seed), the pseudo-random number generator Should have the same output sequence; initializat...
Embodiment 2
[0310] When the relationship between subgroups changes, such as Figure 5 Shown: V 6 to leave the group, and V 8 to be used as V 2 A new subgroup of is added.
[0311] Step 1, such as Figure 6 Shown, SC 6 Send a leave request to CC, and CC deletes V after receiving the request 6 The private vector Z of 6 ; CC randomly selects a private vector Z ∈ F N , sent to V through a secure channel 8 The subgroup controller of V 8 After the subgroup controller receives Z, it will be stored secretly;
[0312] CC reassigns the number of the current subgroup controller: SC 1 ~ SC 5 remain unchanged, the corresponding private vectors are Z 1 ~ Z 5 ; while SC 7 became SC 6 , the corresponding private vector becomes Z 6 ;V 8 The corresponding number is SC 7 , and the corresponding private vector is Z 7 . At this time, the private vector saved by CC is Z i (i=1, 2, ..., 7); at this time, the hierarchical relationship of the group is as follows Figure 7 shown;
[0313] Ot...
Embodiment 3
[0328] Such as Figure 8 As shown, a group communication system with hierarchical access control includes a central controller CC, a subgroup V i , subgroup controller SC i , the CC and each SC are interconnected through the Internet, where i=1, 2, . . . , 5.
[0329] The group's hierarchical access structure is as follows Figure 9 As shown, all high-level nodes can derive the keys of their direct or indirect descendant nodes, while low-level nodes cannot derive the keys of their ancestor nodes. Nodes without direct or indirect superior-subordinate relationship cannot derive each other's key. Sibling nodes also cannot export each other's keys.
[0330] Such as Figure 10 As shown, the system selects the finite field F, and all operations are based on the finite field F; at the same time, the pseudo-random number generator is selected as f(.,.), for the same initialization input (seed), the pseudo-random number generator Should have the same output sequence; initialize m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com