File access method and device of SD (Secure Digital) card
A file reading and file technology, applied in the direction of input/output to record carrier, instrument, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of discontinuity, resource occupation, memory address discontinuity, etc., to reduce resource occupation and improve speed Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
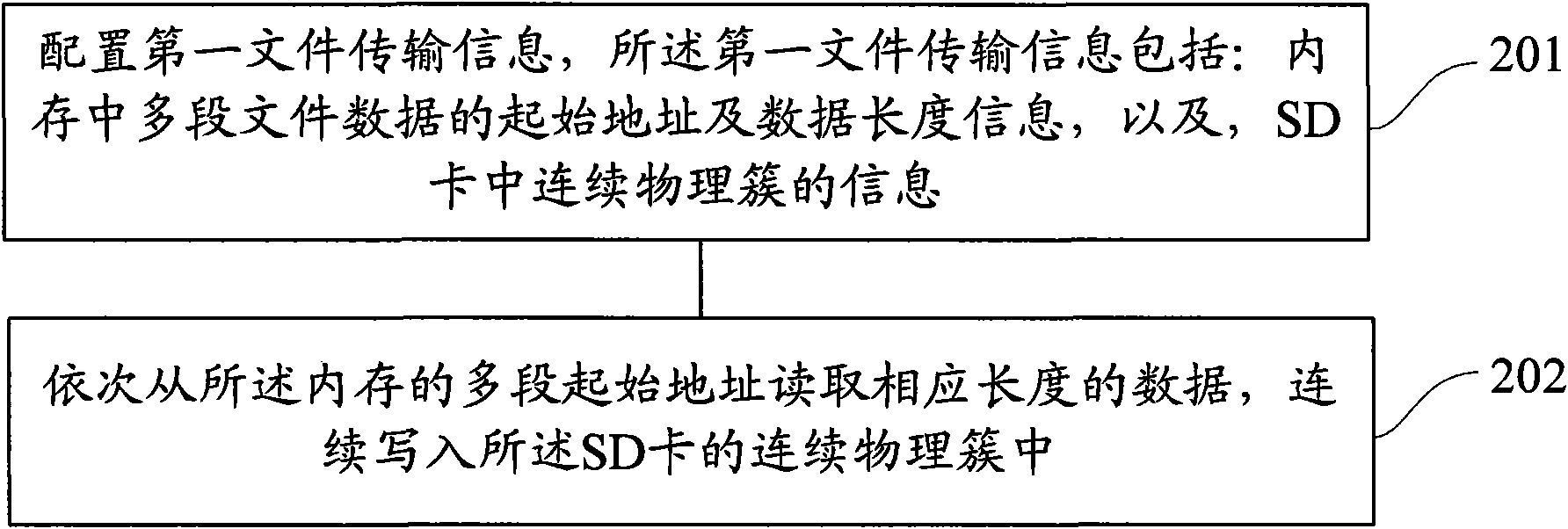
[0070] refer to figure 2 The flow chart of embodiment 1 of the file writing method of a kind of SD card shown, described file writes and relates to a DMA transfer process of writing file data in the continuous physical cluster of SD card from discontinuous memory address, this An embodiment may specifically include the following steps:
[0071] Step 201, configure the first file transfer information, the first file transfer information includes: the starting address and data length information of multiple pieces of file data in the memory, and the information of continuous physical clusters in the SD card;
[0072] Step 202, sequentially read data of corresponding lengths from multiple start addresses of the memory, and continuously write them into continuous physical clusters of the SD card.
[0073] In practice, the file has an end mark. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the step 202 may specifically include the following sub-steps:
[0074] Sub-step S11...
Embodiment 2
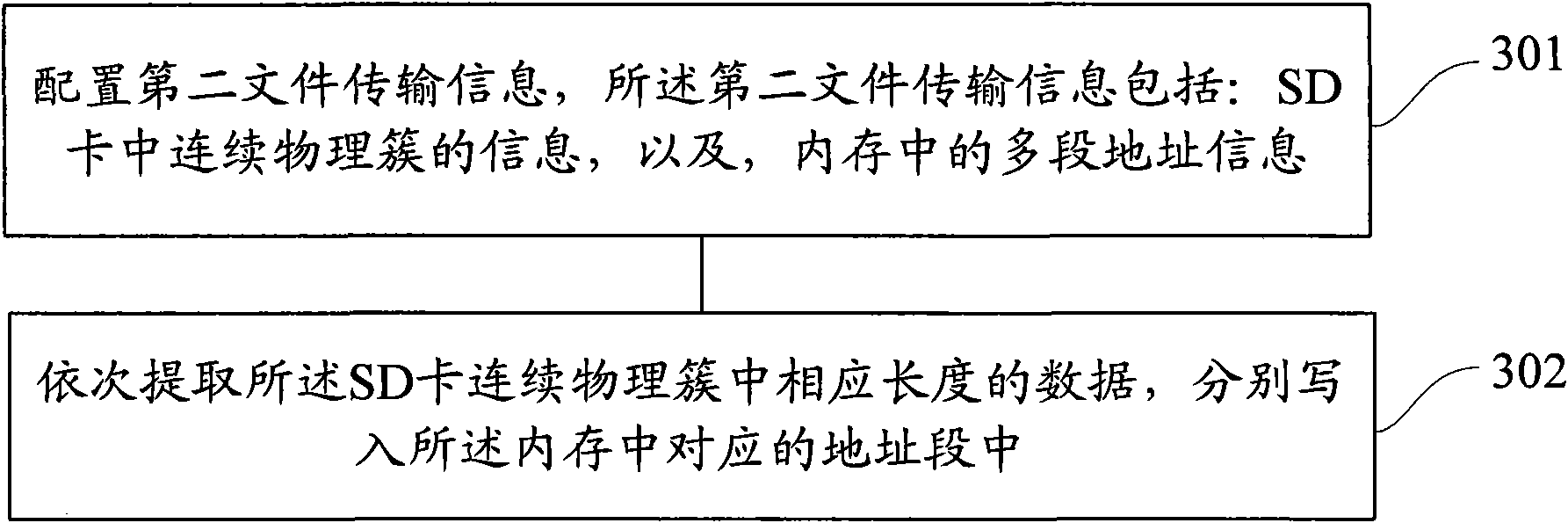
[0086] refer to image 3 The flow chart of Embodiment 1 of the file reading method of a SD card shown, the file reading involves a DMA transfer process of writing file data from a continuous physical cluster of the SD card to a discontinuous memory address, this implementation A specific example may include the following steps:
[0087] Step 301, configure the second file transfer information, the second file transfer information includes: information of continuous physical clusters in the SD card, and multi-segment address information in the memory;
[0088] Step 302, sequentially extracting data of corresponding lengths in continuous physical clusters of the SD card, and writing them into corresponding address segments in the internal memory.
[0089] In practice, the file has an end mark. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the step 302 may specifically include the following sub-steps:
[0090] Substep S21, according to the information of the first address s...
Embodiment 3
[0102] refer to Figure 4 A kind of flow chart of the file writing method embodiment 2 of SD card shown, described file writes and relates to a DMA transmission process of writing file data in discontinuous physical cluster group in SD card from continuous memory address, This embodiment may specifically include the following steps:
[0103] Step 401, configure the third file transfer information, the third file transfer information includes: continuous address segment information in the memory, and information of multiple physical cluster groups in the SD card;
[0104] Step 402, sequentially extracting data of corresponding lengths in continuous address segments of the internal memory, and writing them into corresponding physical cluster groups in the SD card respectively.
[0105] In practice, the file has an end mark. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the step 402 may specifically include the following sub-steps:
[0106] Substep S31, according to the n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com