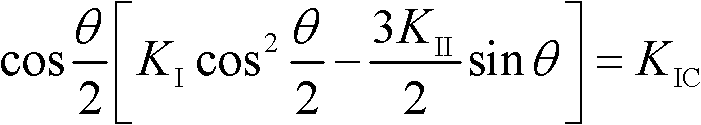Curved path cutting method of brittle base plate by laser cutting
A brittle material substrate, laser cutting technology, applied in the direction of laser welding equipment, welding equipment, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of low cutting precision, crack propagation path is easy to deviate from laser movement, etc., and achieve high cutting precision.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
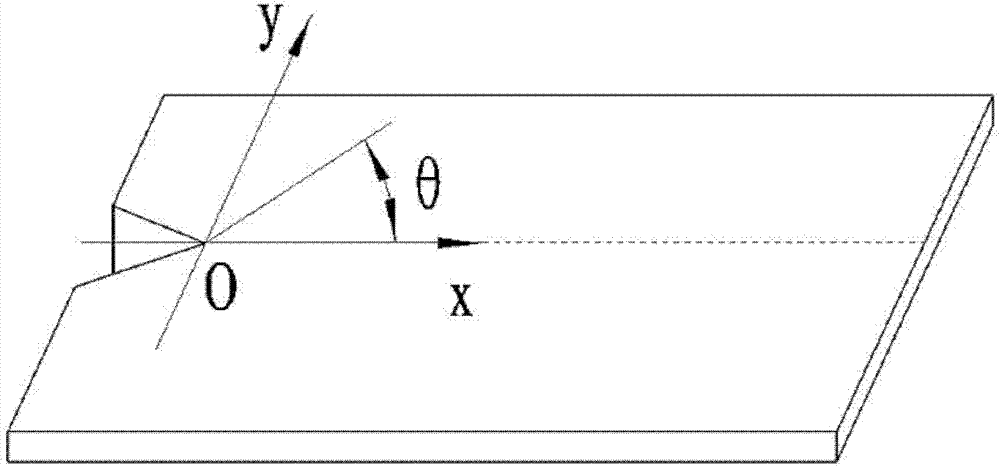
[0027] refer to figure 1 :
[0028] A curvilinear path cutting method for laser cutting a brittle material substrate, comprising the following steps:
[0029] 1. Create an initial crack on the substrate as a cutting path, and set sampling points on the cutting path based on experience; respectively obtain the cracking angle θ at each sampling point, and the cracking angle θ is the current expansion direction and the next moment the acute angle between the expansion directions;
[0030] 2. Obtain the current sampling point, the cracking angle θ obtained from the current sampling point and the fracture toughness K of the substrate IC , to calculate the stress intensity factor K from the current sampling point I , K II ;Calculated as follows:
[0031] cos θ 2 [ K I cos 2 θ 2 - 3 ...
Embodiment 2
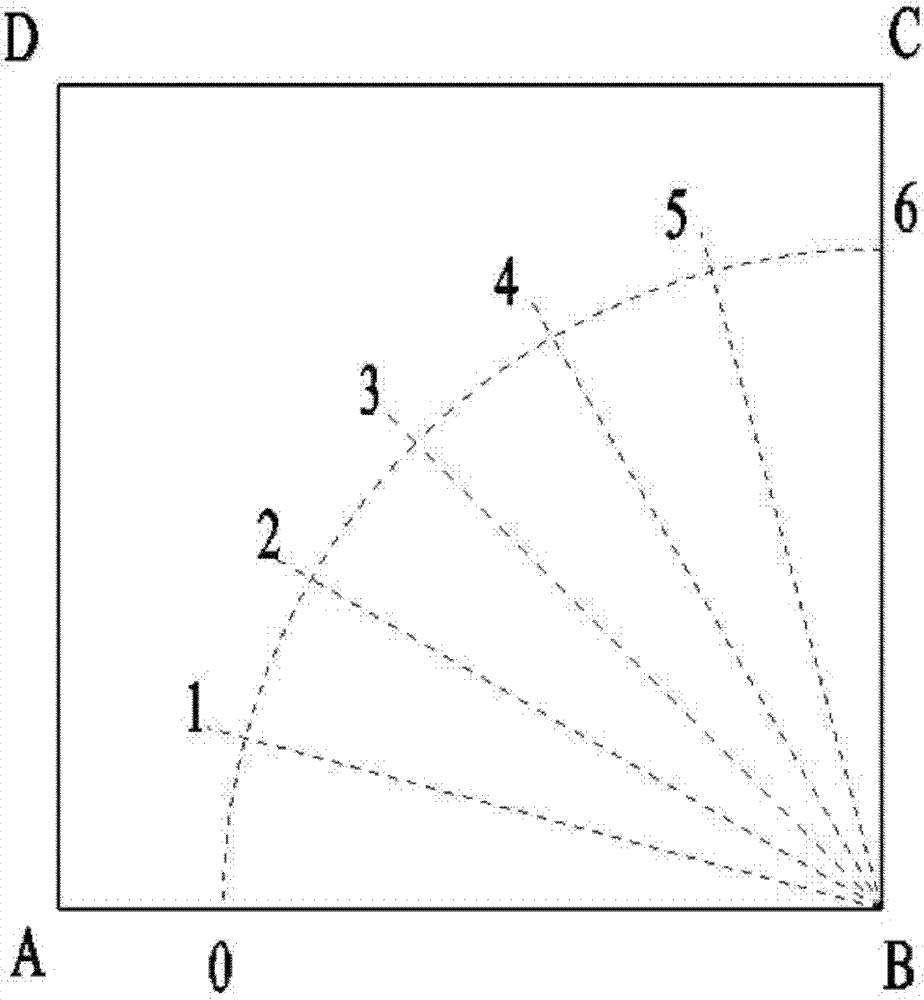
[0045] combine figure 2 and practical examples to further illustrate the invention:
[0046] This example demonstrates the application of the present invention through arc cutting on common white glass. The size of the liquid crystal glass is 100mm×100mm×1.1mm, and now an arc with a radius of 80mm is cut out on it, such as figure 2 shown. The calculated sampling points 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 are evenly distributed along the arc with an interval of 15°. The fracture toughness K of this liquid crystal glass is determined by experiments. IC At 0.7MPa·(mm) 1 / 2 to 0.8MPa·(mm) 1 / 2 between.
[0047] According to the maximum circumferential stress theory of brittle materials, curved cutting belongs to I and II composite fracture modes, and its fracture criterion and cracking angle θ prediction formula are as follows:
[0048] cos θ 2 [ K I cos 2 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| fracture toughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| fracture toughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com