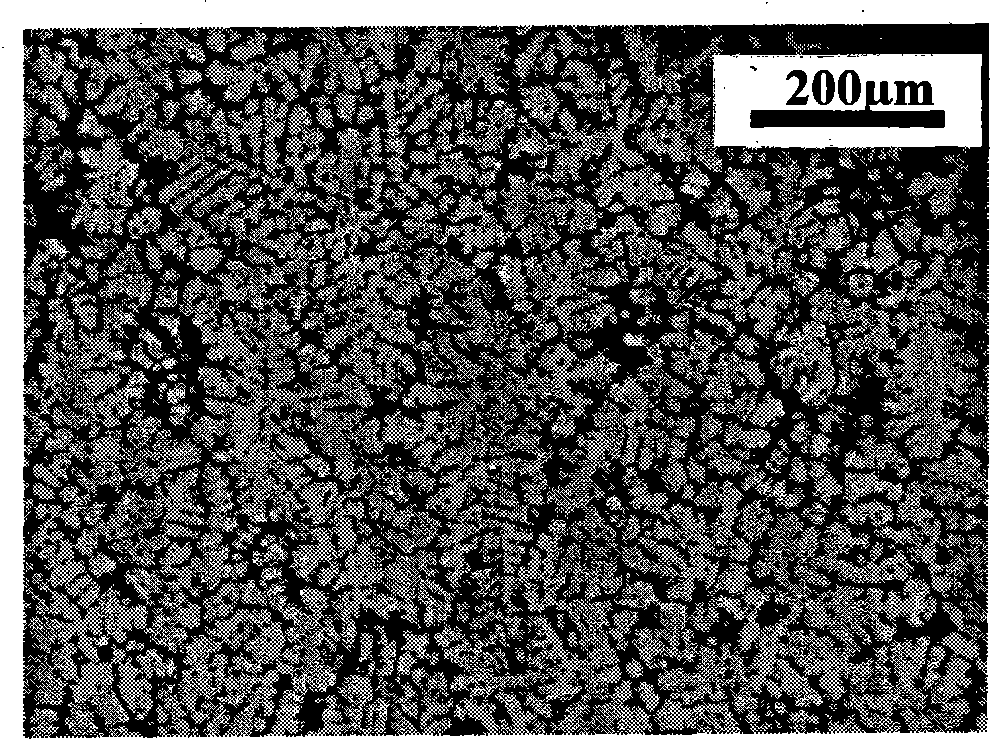
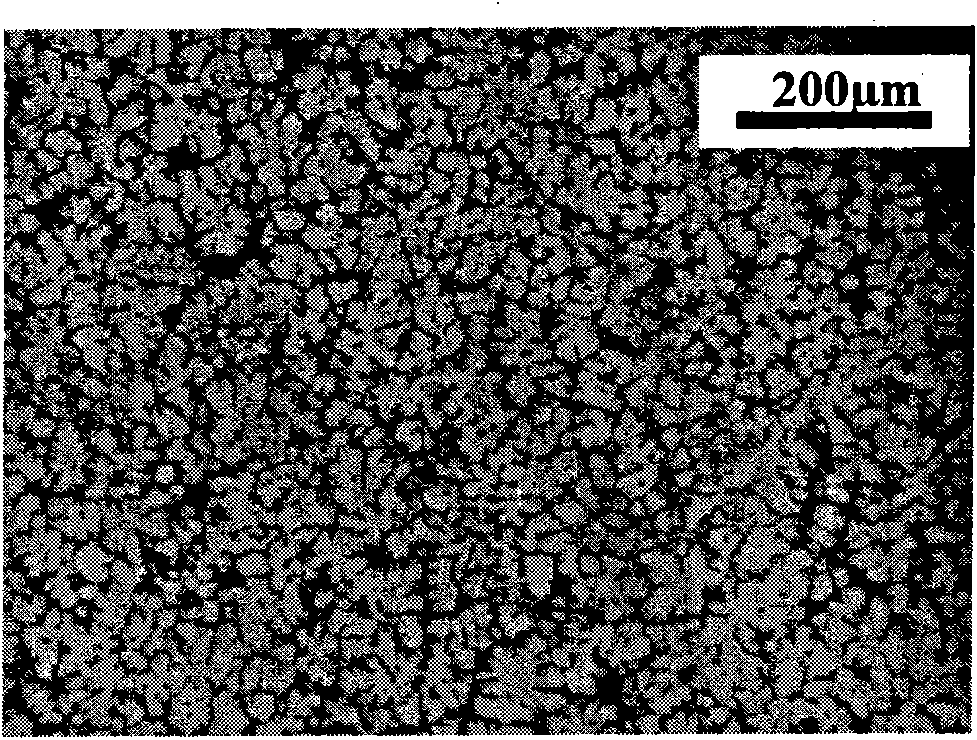
Method for preparing zinc-titanium intermediate alloy
An intermediate alloy and alloy liquid technology, applied in the field of metal alloy materials, can solve the problems of long reaction time and low titanium content in zinc-titanium alloy, and achieve the effects of short production cycle, complete reaction and reduced oxidation loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Ingredients according to the following mass proportions: 94% pure zinc, 6% pure titanium; use an intermediate frequency induction furnace to melt pure zinc to about 740°C in a graphite clay crucible, then rapidly increase the power of the induction furnace, and will account for 1.5% of the total mass of raw materials The pure titanium is pressed into the pure zinc melt with a bell jar, and the heating is continued for 4 minutes. The power of the induction furnace is appropriate to rapidly raise the melt temperature to 780°C within the above time and completely melt the pure titanium into the molten zinc. Next, the remaining pure titanium is divided into two batches (2%, 2.5% respectively) and pressed into the alloy liquid with a bell jar. During the process of pressing the pure titanium and within 6 minutes after pressing, the appropriate induction furnace power is maintained to control the melt. The temperature is around 840°C. After the pure titanium is completely me...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Ingredients according to the following mass proportions: 97% pure zinc, 3% pure titanium; use an intermediate frequency induction furnace to melt pure zinc to about 730°C in a graphite clay crucible, then rapidly increase the power of the induction furnace, and will account for 1% of the total mass of raw materials The pure titanium is pressed into the pure zinc melt with a bell jar, and the heating is continued for 5 minutes. The power of the induction furnace is appropriate to rapidly raise the melt temperature to about 760°C within the above time and completely melt the pure titanium into the molten zinc. Next, the remaining pure titanium is pressed into it with a bell jar, and the appropriate induction furnace power is maintained during the process of pressing the pure titanium and within 5 minutes after the pressing, and the temperature of the melt is controlled at about 810°C. After the pure titanium is completely melted within the above heating time, stop heating...
Embodiment 3
[0028]Ingredients according to the following mass ratios: 90% pure zinc, 10% pure titanium; use an intermediate frequency induction furnace to melt pure zinc to about 740°C in a graphite clay crucible, and then rapidly increase the power of the induction furnace to account for 1% of the total mass of raw materials The pure titanium is pressed into the pure zinc melt with a bell jar, and the heating is continued for 4 minutes. The power of the induction furnace is appropriate to rapidly raise the melt temperature to about 780°C within the above time and completely melt the pure titanium into the molten zinc. Next, the remaining pure titanium is divided into three batches (2%, 3%, 4%) into the alloy liquid with a bell jar, and the appropriate induction furnace power is maintained during the process of pressing the pure titanium and within 10 minutes after the pressing. Control the melt temperature at around 850°C. After the pure titanium is completely melted within the above he...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com