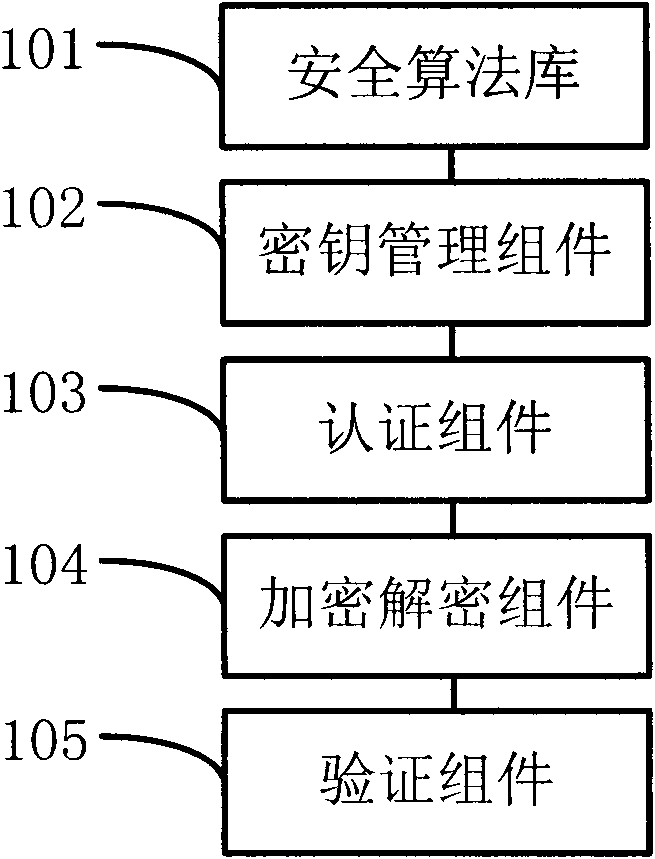
Set-top box-based secure information transmission system and method
A technology of information security and transmission method, applied in the field of information security transmission system based on set-top box, can solve the problems of heavy workload, low efficiency, difficult key management and distribution for developers, etc., to improve software reusability, ensure efficiency, guarantee safety effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
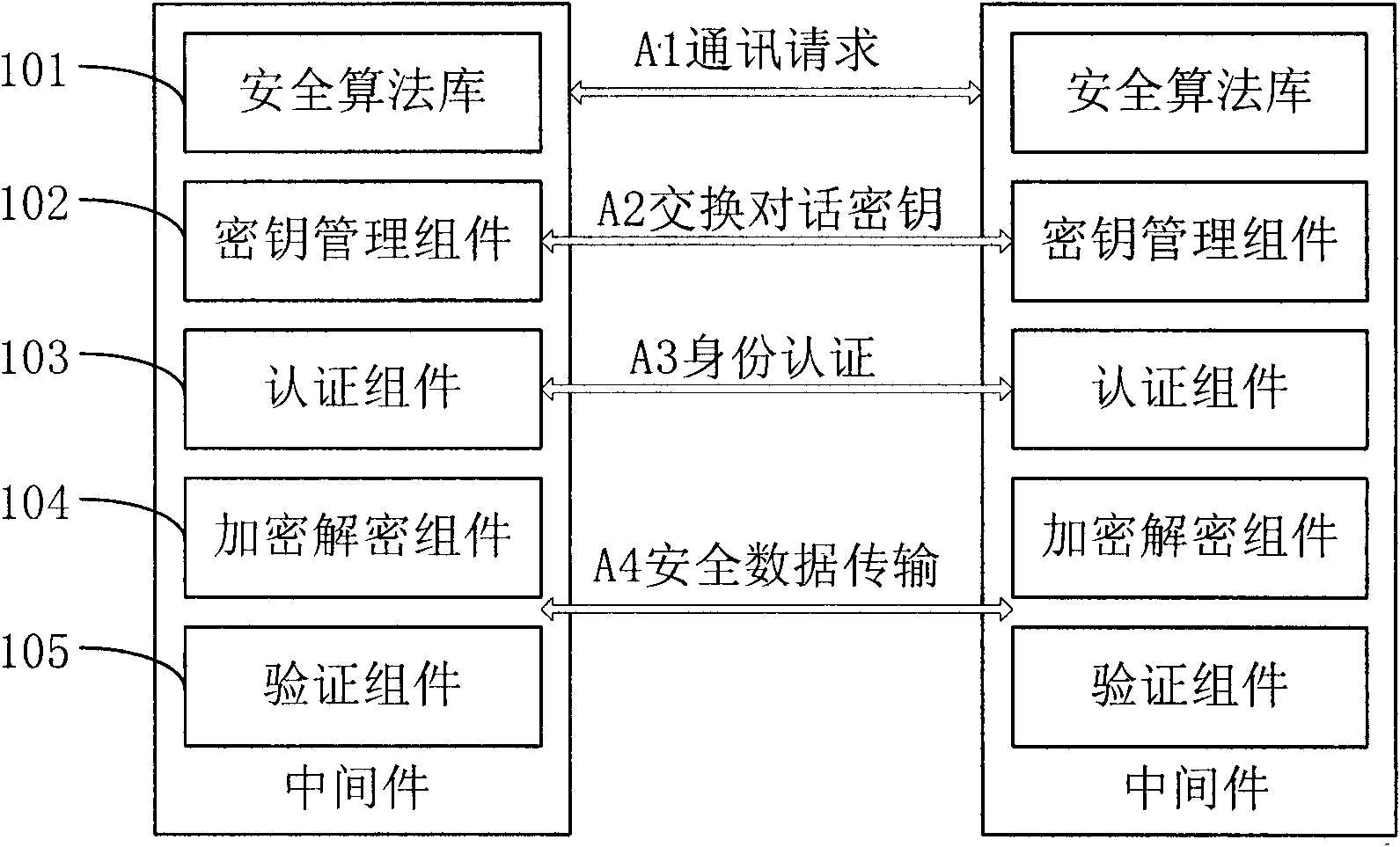
[0073] refer to figure 2 , is a schematic diagram of a communication process of an information security transmission system according to an embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, the information security transmission system of the present invention is provided in the form of middleware to provide services for upper-layer applications.
[0074] Such as figure 2 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0075] A1. The sender sends a communication request to the receiver;
[0076] A2. The key management components of the sender and the receiver interact with each other's session keys, that is, their respective public keys;
[0077] A3. The authentication components of the sender and the receiver respectively verify the identity of the other party;
[0078] A4. After knowing the other party's public key and confirming the identity of the other party, the sender and receiver use a mixture of symmetric and asymmetric algorithms to securely tra...
Embodiment 2
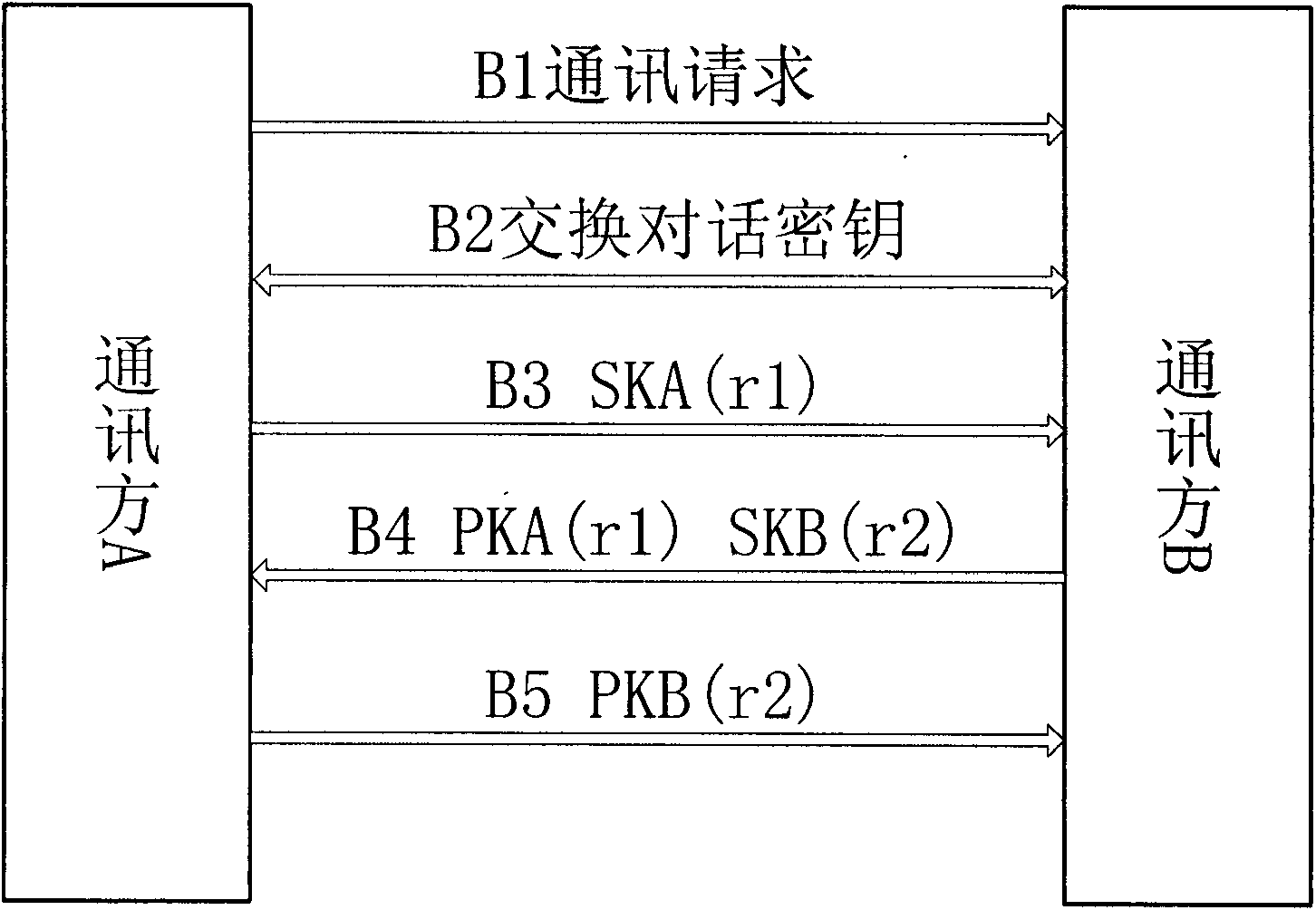
[0079] Embodiment 2, public key exchange and identity verification:
[0080] image 3 It is a flowchart of public key exchange and identity verification in Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0081] refer to image 3 , including the following steps:
[0082] B1. The communication party A sends a communication request to the communication party B;
[0083] B2. The two parties in the communication send their respective public keys to each other, that is, exchange the dialogue key;
[0084] B3. Communication party A generates a random number r1, encrypts r1 with its own private key SKA to obtain SKA(r1), and sends it to communication party B;
[0085] B4. After receiving the SKA(r1), the communicating party B decrypts the SKA(r1) into r1 with the public key PKA of the communicating party A, encrypts r1 into PKA(r1) with the public key PKA of the communicating party A, and generates a random number r2 , use your own private key SKB to encrypt r2 into SKB(r2), and send PK...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Embodiment 3, encryption process.
[0088] Figure 4 It is the encryption flowchart of Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0089] refer to Figure 4 , including the following steps:
[0090] The sender uses the DSA algorithm to calculate the digest A of the message M to be sent, and then adds its own identity and timestamp information T to prevent replay attacks;
[0091] Use your own private key SKA to encrypt and sign the summary A and timestamp information T to form signature information S=ESKA(A+T);
[0092] Generate a dynamic session key K, use K to encrypt the message itself M and signature information to form ciphertext C=EK(M+S);
[0093] Encrypt the session key K with the public key PKB of receiver B to obtain CK=EPKB(K);
[0094] Encapsulate the ciphertext C and the encrypted session key CK together to form a data envelope, and transmit the data envelope to the receiver B.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com