Method for producing 5'-guanylic acid
A technology of guanylic acid and guanylic acid synthase, which is applied in the field of 5’-guanylic acid production and can solve problems such as difficulty in decomposition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
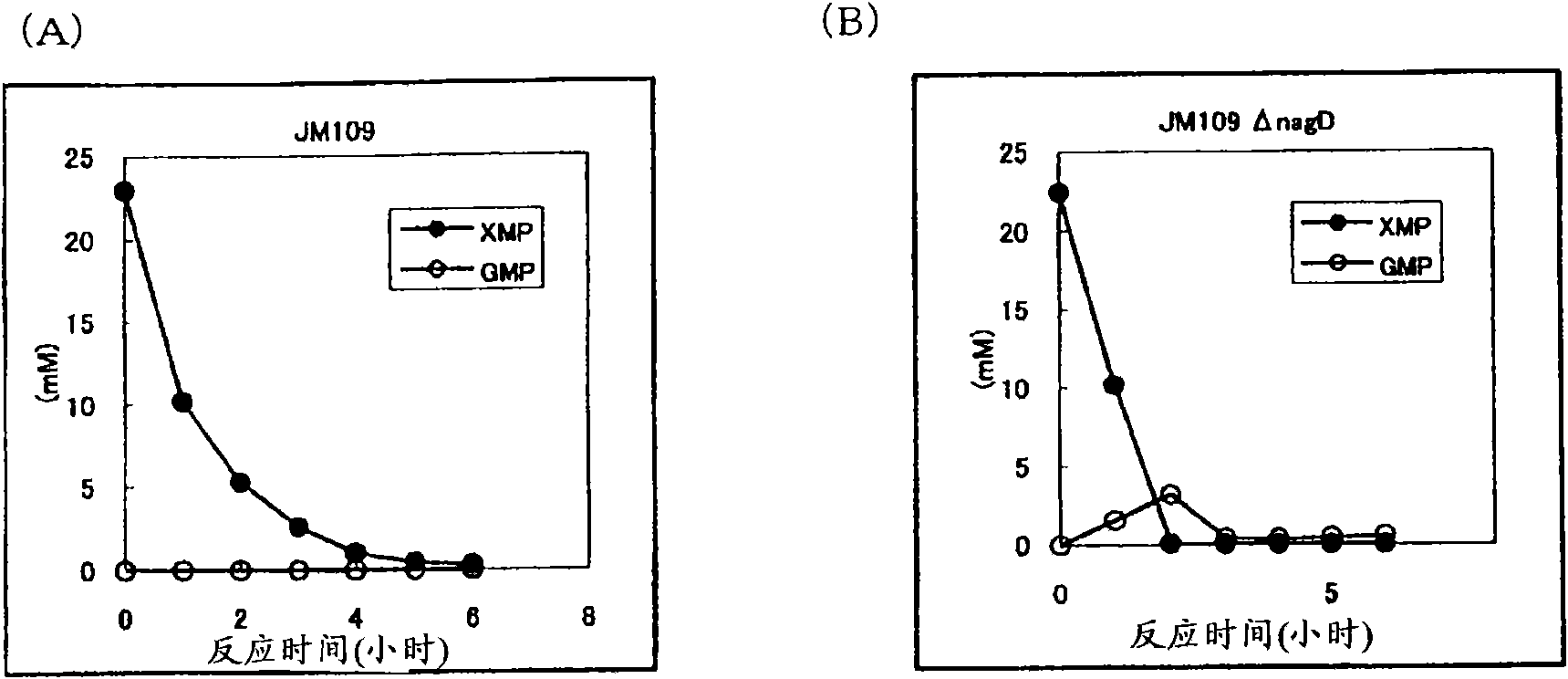
[0120] Construction of nagD gene disruption strain derived from JM109 strain
[0121] Using the Escherichia coli JM109 strain used as a host for conventional DNA cloning as a parent strain, a NagD protein non-producing strain was first constructed. The NagD protein is encoded by the nagD gene (GenBank Accession No. X14135 SEQ ID NO: 11).
[0122] The deletion of nagD gene was first developed by Datsenko and Wanner called "Red-driven integration (Red-driven integration)" method (Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA, 2000, vol.97, No.12, p6640- 6645) and λ phage-derived excision system (J.Bacteriol.2002Sep; 184(18):5200-3.Interactions between integrase and excisionase in the phage lambda excisive nucleoprotein complex. Cho EH, Gumport RI, GardnerJF.) to carry out . According to the "Red-driven integration" method, synthetic oligonucleotides in which a part of the gene of interest is designed on the 5' side and a part of the antibiotic resistance gene on the 3' side are used as primer...
Embodiment 2
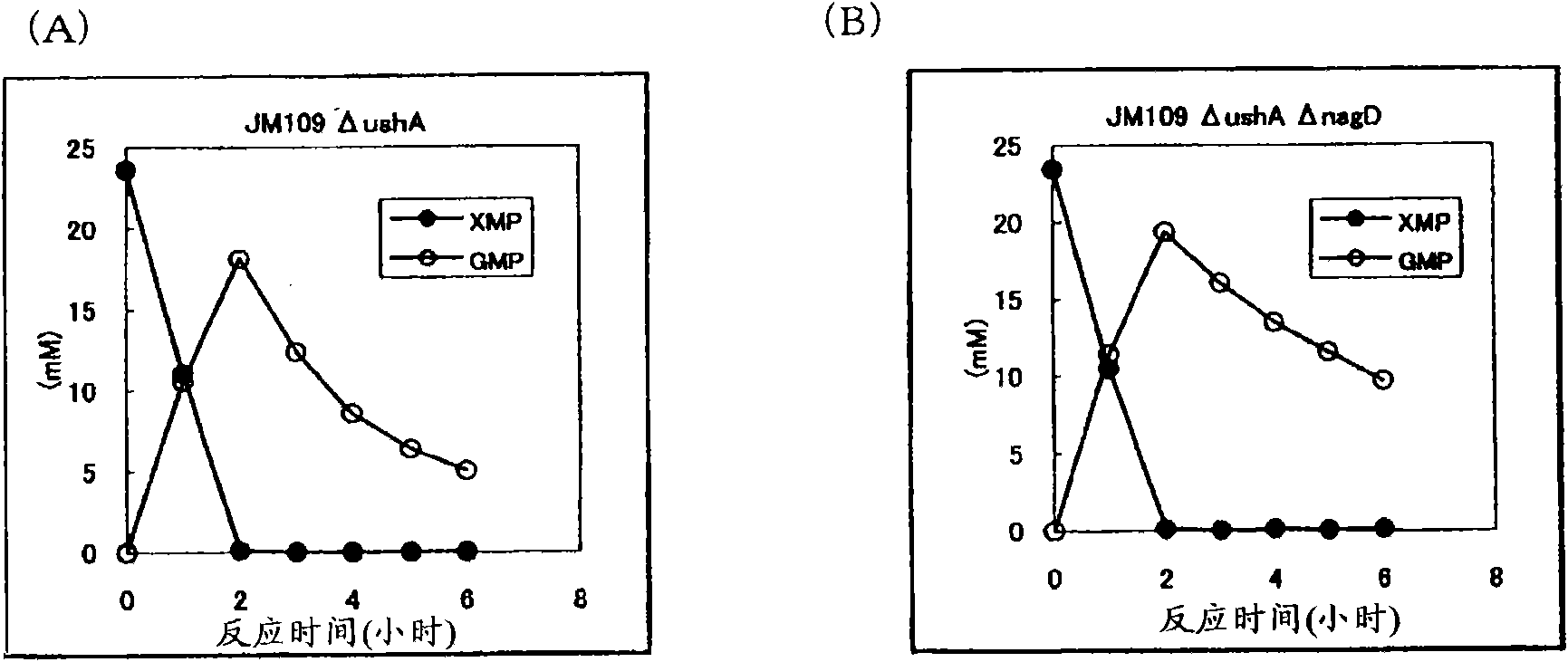
[0155] Construction of ushA gene disrupted strains derived from JM109 strain and JM109ΔnagD strain
[0156] Using the JM109 strain and the JM109ΔnagD strain obtained in Example 1 as parent strains, a UshA non-producing strain was constructed. UshA is encoded by the ushA gene (GenBank Accession No. X03895SEQ ID NO: 14). According to the aforementioned method for disrupting the nagD gene, the ushA gene was disrupted using the primers of SEQ ID NO: 21 and 22 as primers for disrupting ushA. Thus, JM109ΔushA and JM109ΔushAΔnagD were obtained.
[0157] Introduction of GMP synthetase expression enhanced plasmid pSTV29-Ptac-guaA into JM109ΔushA strain and JM 109ΔushAΔnagD strain
[0158] The GMP synthetase expression enhancing plasmid pSTV29-Ptac-guaA described in Example 1 was introduced into the JM109ΔushA strain and the JM109ΔushAΔnagD strain to obtain the JM109ΔushA / pSTV29-Ptac-guaA strain and the JM109ΔushAΔnagD / pSTV29-Ptac-guaA strain respectively.
[0159] Trans...
Embodiment 3
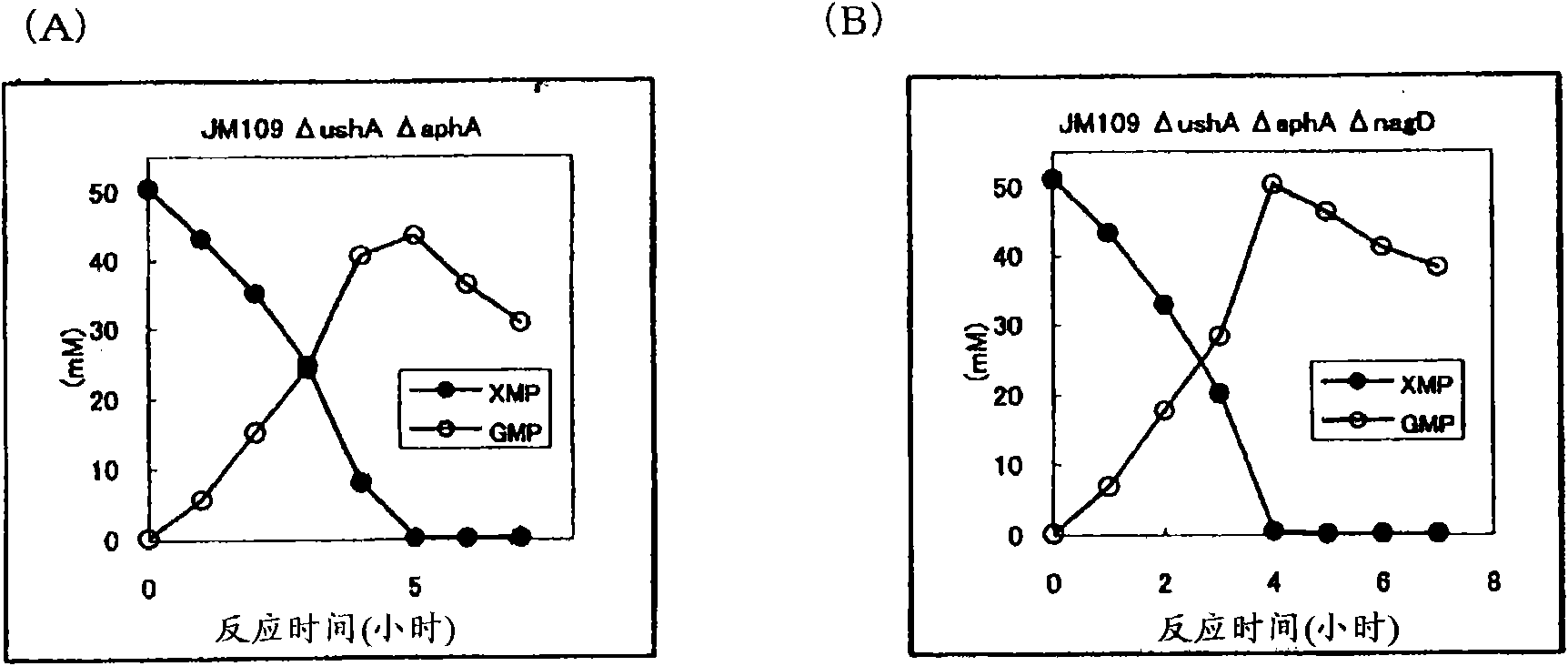
[0163] Construction of aphA gene disrupted strains derived from JM109ΔushA strain and JM109ΔushAΔnagD strain
[0164] Using the JM109ΔushA strain and the JM109ΔushAΔnagD strain obtained in Example 2 as parent strains, an AphA non-producing strain was constructed. AphA is encoded by the aphA gene (GenBank Accession No. X86971 SEQ ID NO: 17). According to the aforementioned nagD gene disruption method, using the primers of SEQ ID NO: 23 and 24 as primers for aphA disruption, aphA gene disruption was carried out. Thus, JM109ΔushAΔaphA and JM109ΔushAΔaphAΔnagD were obtained.
[0165] Introduction of GMP synthetase expression enhanced plasmid pSTV29-Ptac-guaA into JM109ΔushAΔaphA strain and JM109ΔushAΔaphAΔnagD strain
[0166] The GMP synthetase expression enhancing plasmid pSTV29-Ptac-guaA described in Example 1 was introduced into the JM109ΔushAΔaphA strain and the JM109ΔushAΔaphAΔnagD strain to obtain the JM109ΔushAΔaphA / pSTV29-Ptac-guaA strain and the JM109ΔushAΔaph...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com