Rotating electrical machine and its manufacturing method
A technology for rotating electrical machines and rotating shafts, which is applied in the manufacture of stator/rotor bodies, electric components, electrical components, etc. It can solve the problems of increased amplitude of fundamental wave components and difficulty in achieving small and high output, and achieves increased amplitude and small size High output effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
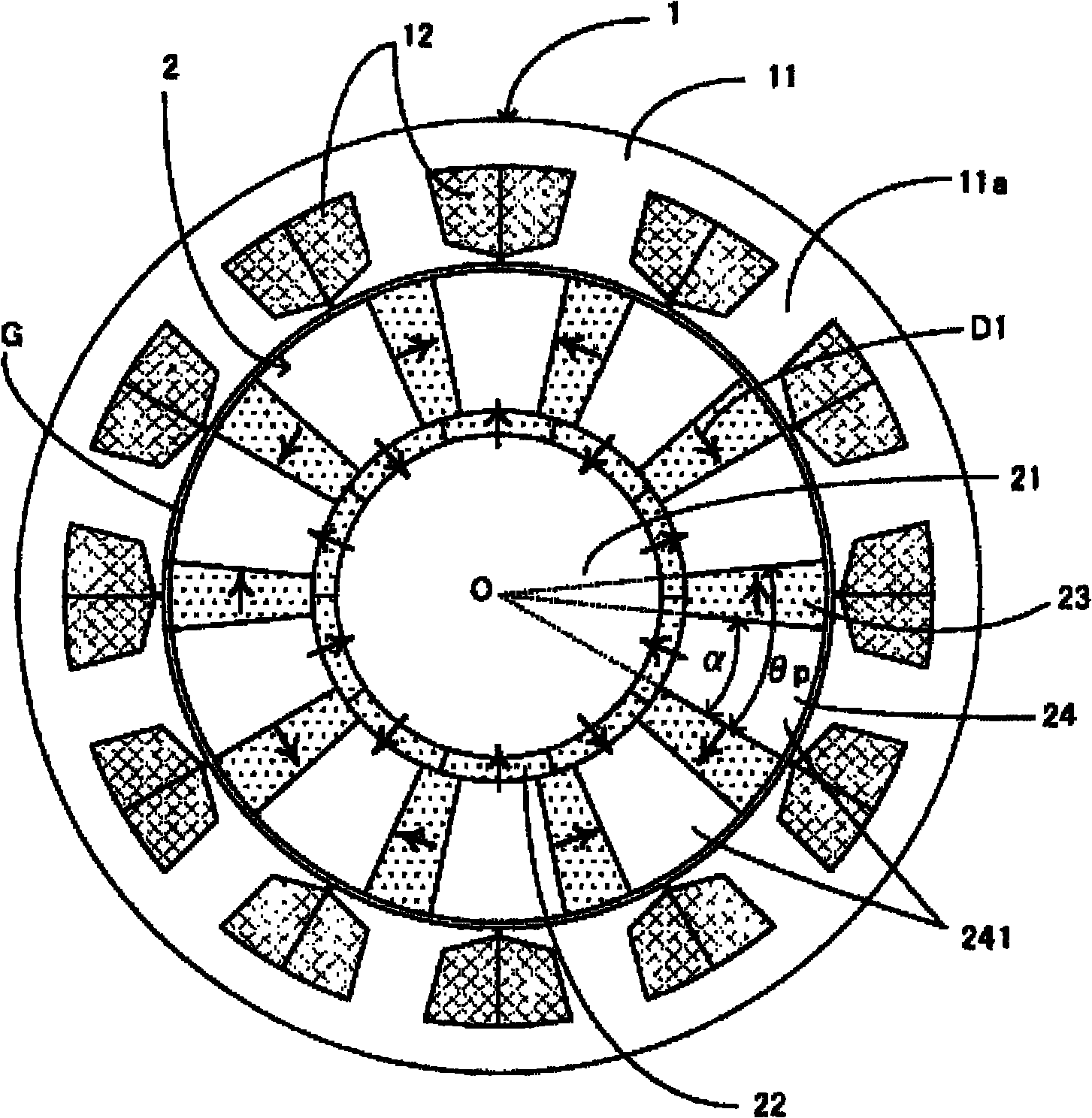
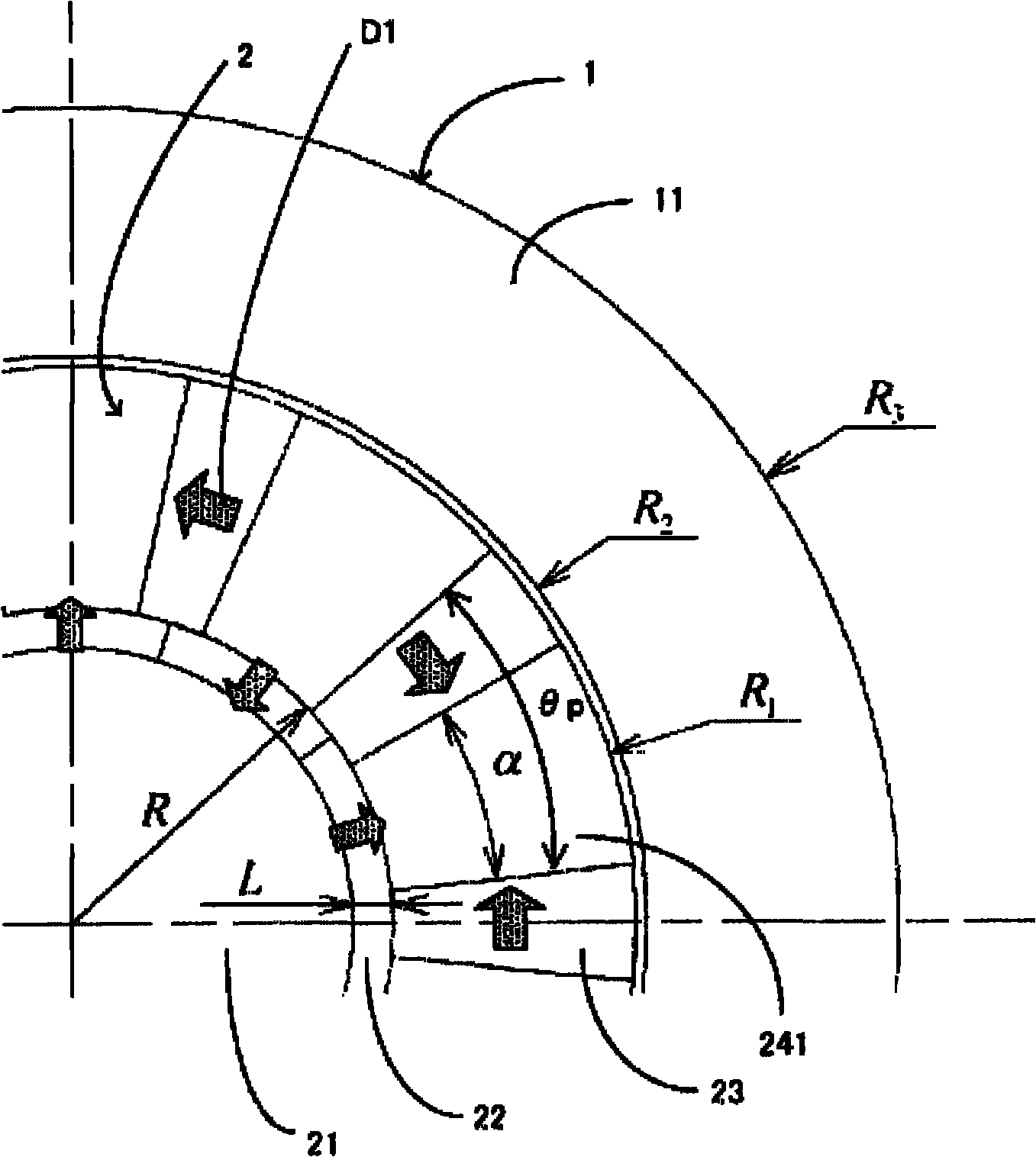
[0043] In the rotating electric machine according to the first embodiment of the present invention, the permanent magnets used in the rotor are arranged by an arrangement method called MMASPM (Magnetic Mate rial Attached Surface Permanent Magnet) arrangement. use figure 1 This arrangement will be specifically described.
[0044] figure 1 It is a cross-sectional view of the rotating electric machine according to the first embodiment. figure 1 The "O" shown indicates the axis of rotation of the rotor. figure 1 A cross section of the rotating electrical machine when the rotating electrical machine is cut perpendicular to the rotation axis O direction is shown. figure 1 The "G" shown is the air gap that exists between the rotor and stator. figure 1 The shown one-way arrow D1 indicates the magnetization direction of the permanent magnet.
[0045] exist figure 1 Among them, the rotating electric machine according to the first embodiment includes a stator 1 and a rotor 2 . The...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0085] refer to Figure 9 ~ Figure 11A , Figure 11B , the rotating electric machine according to the second embodiment including the rotor in consideration of manufacturability and mechanical strength will be described. Figure 9 It is a cross-sectional view of the rotating electric machine according to the second embodiment. Figure 10 yes Figure 9 A cross-sectional view of the rotor core shown. Figure 11 is Figure 9 Cutaway view of the rotor shown. Figure 11B is in Figure 11A Figures of end caps are added to the structure shown. Figure 9 ~ Figure 11A , Figure 11B The "O" shown indicates the axis of rotation of the rotor. Figure 9 A cross section of the rotating electrical machine when the rotating electrical machine is cut perpendicular to the rotation axis O direction is shown. Figure 10 shows a cut perpendicular to the direction of rotation axis O Figure 9 The section of the rotor core when the rotor core is shown. Figure 11A , Figure 11B shows the ...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0104] refer to Figure 12 ~ Figure 14A , Figure 14B , a rotating electric machine according to a third embodiment including a rotor in consideration of manufacturability and mechanical strength will be described. Figure 12 It is a cross-sectional view of the rotating electric machine according to the third embodiment. Figure 13 yes Figure 12 A cross-sectional view of the rotor core shown. Figure 14A yes Figure 12 Cutaway view of the rotor shown. Figure 14B is in Figure 14A Figures of end caps are added to the structure shown. Figure 12 ~ Figure 14A , Figure 14B The "O" shown indicates the axis of rotation of the rotor. Figure 12 A cross section of the rotating electrical machine when the rotating electrical machine is cut perpendicular to the rotation axis O direction is shown. Figure 13 shows a cut perpendicular to the direction of rotation axis O Figure 12 The section of the rotor core when the rotor core is shown. Figure 14A , Figure 14B shows th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com