Green vegetable compound antistaling agent and matched antistaling method thereof
A technology for compound fresh-keeping of green leafy vegetables, which is applied in the supporting fields of formula and storage and fresh-keeping, can solve the problems of unseen compound preservative formula and fresh-keeping methods, toxic and harmful substance residues, and high capital investment, and achieves simple preparation and use methods Feasibility, suppression of breathing, effect of less investment in equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
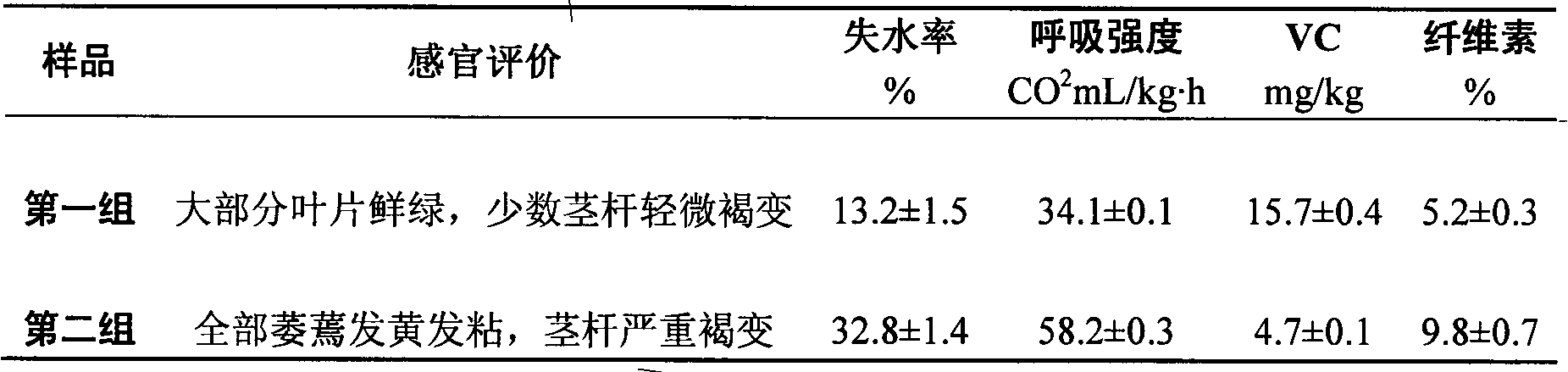
[0015] (1) Fresh-keeping effects of different treatments on celery under refrigeration
[0016] Taking celery as an example, select samples with consistent freshness and maturity, no disease and mechanical damage, and divide them into two groups: the first group is treated by the present invention, and the second group is a blank control without any treatment. The two groups of samples were put into storage at the same time, and stored in a mechanical cold storage at 1±0.5°C and a relative humidity of 90% for 15 days. The fresh-keeping effects of each group of treatments are shown in Table 1.
[0017] Table 1 Comparison of fresh-keeping effects of different treatments of celery
[0018]
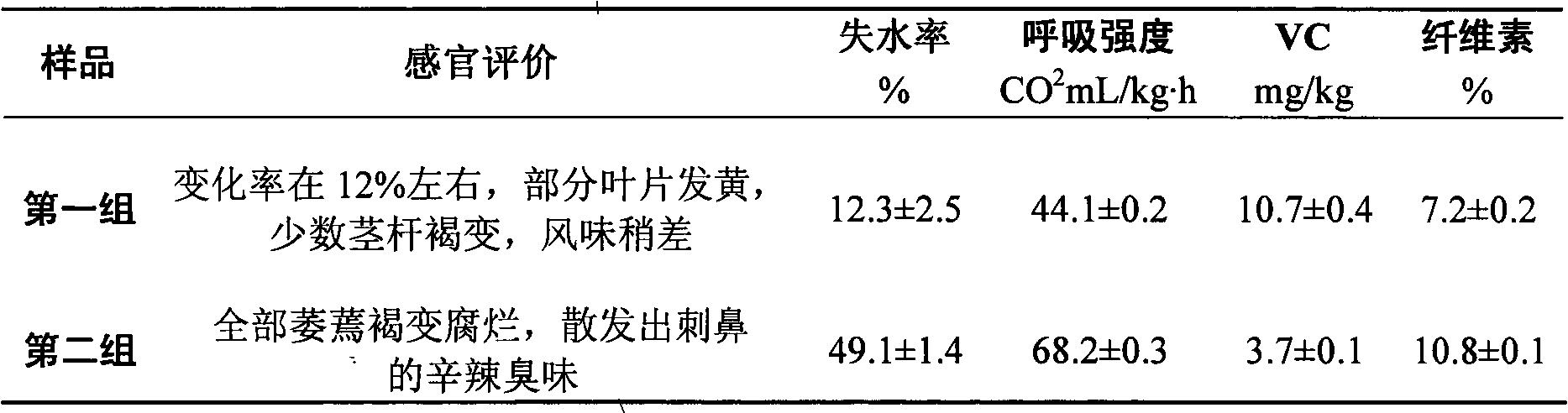
[0019] (2) Fresh-keeping effects of different treatments on celery at room temperature
[0020] Taking celery as an example, select samples with consistent freshness and maturity, no disease and mechanical damage, and divide them into two groups. The first group is processed by the presen...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Taking coriander as an example, select samples with consistent freshness and maturity, no disease and mechanical damage, and divide them into two groups. The first group is processed by the present invention, and the second group is a blank control without any treatment. The two groups of samples were put into storage at the same time, and stored in a mechanical cold storage at 2±0.5° C. and a relative humidity of 90% for 12 days. Table 3 shows the fresh-keeping effects of each group of treatments.
[0025] Table 3 Comparison of fresh-keeping effects of different treatments of coriander
[0026]
Embodiment 3
[0028] Taking leek as an example, select samples with consistent freshness and maturity, no disease and mechanical damage, and divide them into two groups. The first group is processed by the present invention, and the second group is a blank control without any treatment. The two groups of samples were put into storage at the same time, and stored in a mechanical cold storage at 5±0.5° C. and a relative humidity of 90% for 7 days. The fresh-keeping effects of each group of treatments are shown in Table 4.
[0029] Table 4 Comparison of fresh-keeping effects of different treatments on Chinese chives
[0030]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hole density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com