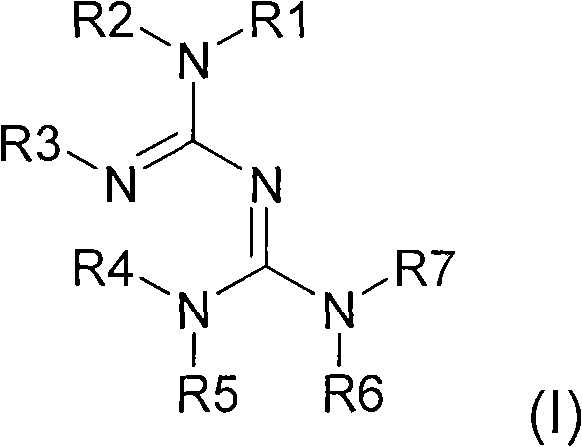
Modification of the surface chemistry of macromolecular species in the presence of a conjugated guanidine
A technology of macromolecular substances and substances, applied in the field of new macromolecular substances, can solve problems such as hindering the use, producing high, and damaging viscosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0267] Preparation of hyperbranched acrylic acid polymer (polymer P1)
[0268] 1.1 Synthesis of polyester polyol polymer
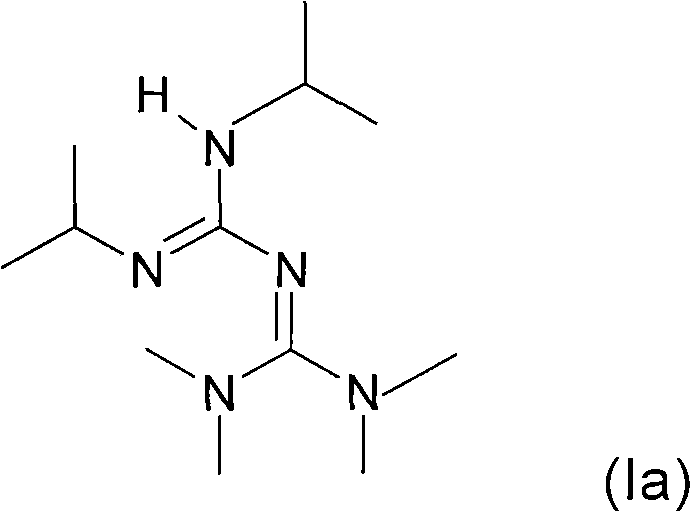
[0269] Put 126g of monomer AB2 into a 250ml jacketed reactor equipped with a mechanical stirring system and a condensation column. The medium is brought to 85° C. and 2.052 g of catalyst of formula (Ia) are added. The mixture was stirred (250 rpm) for 1 minute, then placed under -760 mmHg vacuum and stirred for 10 minutes.
[0270] 1.2 Functionalization and bridging of polyester polyol polymers (preparation of hyperbranched structures)
[0271] After 10 minutes of reaction in step 1.1, the reaction medium was brought to atmospheric pressure under nitrogen flow, the reaction temperature reached 116°C, and the temperature of the circulating fluid in the condensation column reached -20°C.
[0272] Then 51 g of MMA was gradually added to the medium. 0.820 g of catalyst of formula (Ia) and 0.380 g of BuOK (co-catalyst) were then added, using 50 mg of BH...
Embodiment 2
[0281] Synthesis of Acrylic Acrylic Hyperbranched Polymer (P2)
[0282] 2.1 Synthesis of polyester polyol polymer
[0283]Put 150g of monomer AB2 into a 250ml jacketed reactor equipped with a mechanical stirring system and a condensation column. The medium is brought to 85° C. and 2.44 g of catalyst of formula (Ia) are added. The mixture was stirred (250 rpm) for 1 minute, then placed under -760 mmHg vacuum and stirred for 10 minutes.
[0284] 2.2 Functionalization and bridging of polyester polyol polymers (preparation of hyperbranched structures)
[0285] After 10 minutes of reaction in step 1.1, the reaction medium is brought to atmospheric pressure under nitrogen flow, the reaction temperature reaches 116°C, and the temperature of the circulating fluid in the condensation column reaches -20°C.
[0286] Then 40.54 g of MMA and 12.88 g of hexanediol diacrylate (Sigma-Aldrich, Ref 411736, purity 95%) were gradually introduced into the medium. Then 0.977 g of catalyst o...
Embodiment 3
[0294] Synthesis of Hyperbranched Polymer of Acrylic Acid (Polymer P3)
[0295] 3.1 Synthesis of hyperbranched polymers with polyester polyol cores
[0296] 7.615 g of TMP (trimethylolpropane sold by Acros Organics, Ref 164650025, 98% pure) and 8.4 g of monomer AB2 were placed in a drop funnel equipped with a mechanical stirring system, condensation column and containing 117.6 g of monomer AB2 250ml jacketed reactor.
[0297] The medium was brought to 85°C and 0.137 g (Acros Organics, Ref 164650025, 98% pure) was added. The mixture was stirred (250 rpm) for 1 minute and then placed under vacuum at -760 mmHg. The mixture was subsequently stirred for 5 minutes and then placed again at atmospheric pressure.
[0298] 117.6 g of monomer AB2 contained in the dropping funnel were charged to the reactor and 1.915 g of catalyst of formula (Ia) were added again. The medium was stirred under vacuum (-760 mmHg) for 10 minutes.
[0299] 3.2 Polyester polyol bridging with diperoxid...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com