Method and apparatus for controlling the size of a laser beam focal spot
A technology of laser beam and focal spot, applied in the field of size control, can solve problems such as large distances
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
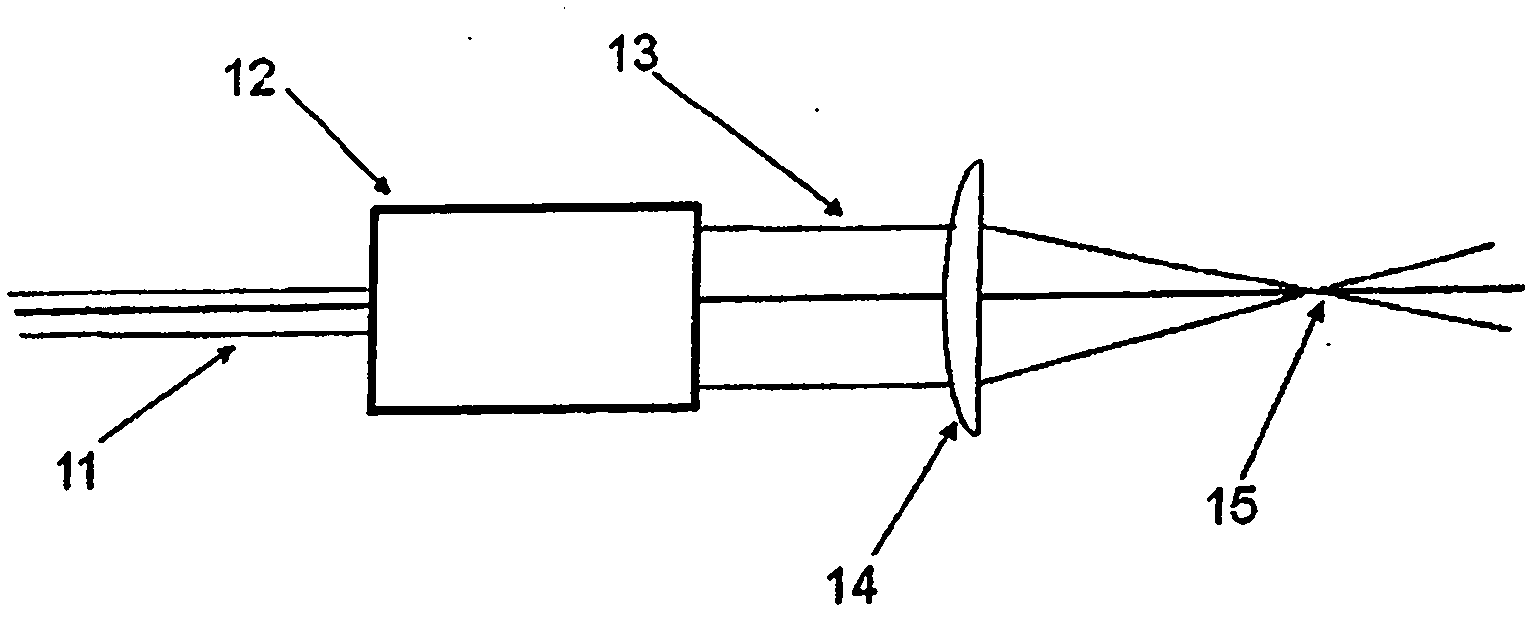
[0041] figure 1
[0042] figure 1 A standard method of conditioning a laser beam for direct write laser processing is shown. An input laser beam 11 generally having a smaller diameter passes through a transmission beam expander telescope 12 and becomes an output beam 13 with a larger diameter. The lens 14 then focuses the beam 13 into a small focal spot 15 whose diameter and distance from the lens 14 depends on the diameter and collimation of the laser beam 13 .
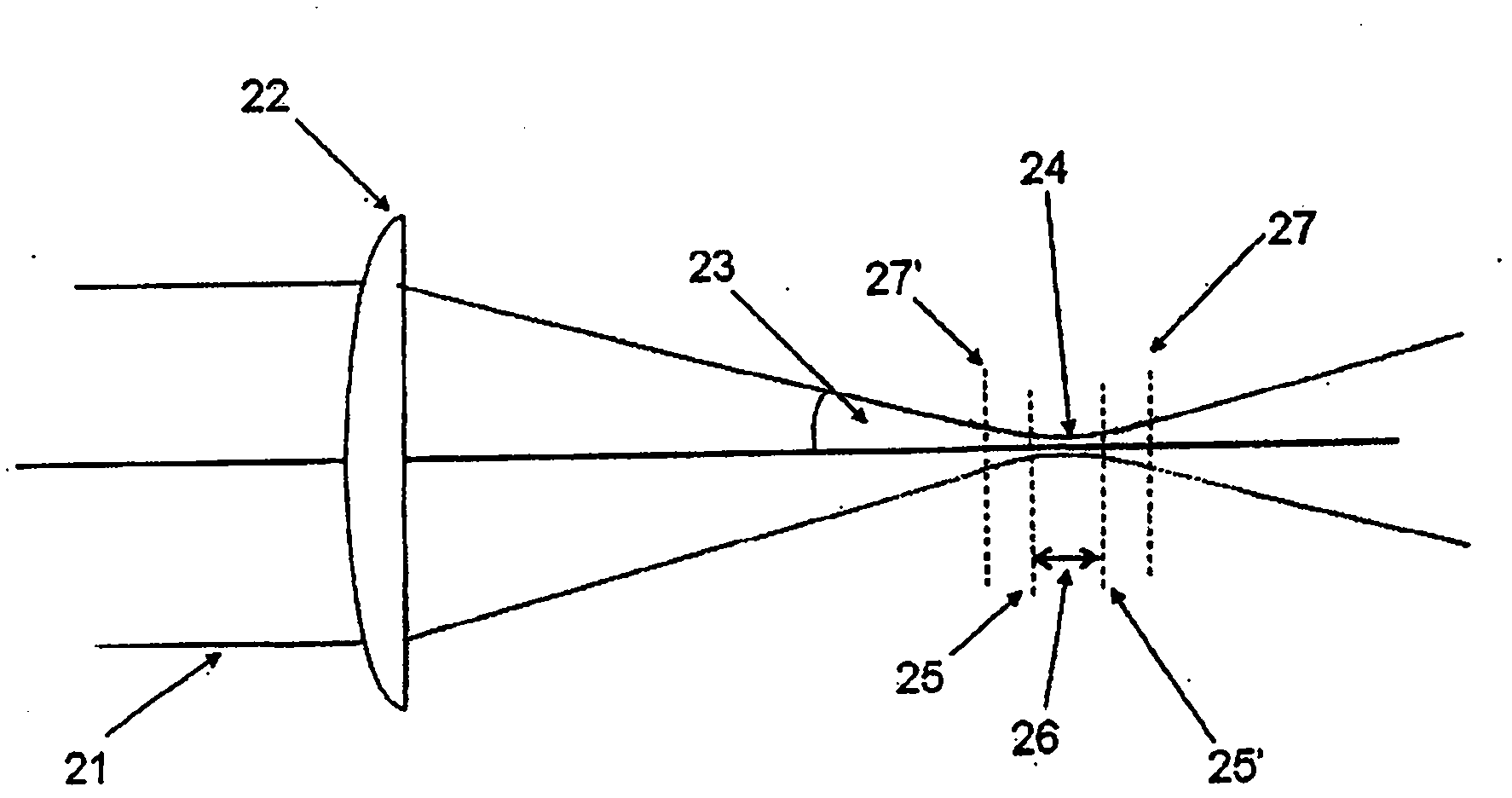
[0043] figure 2
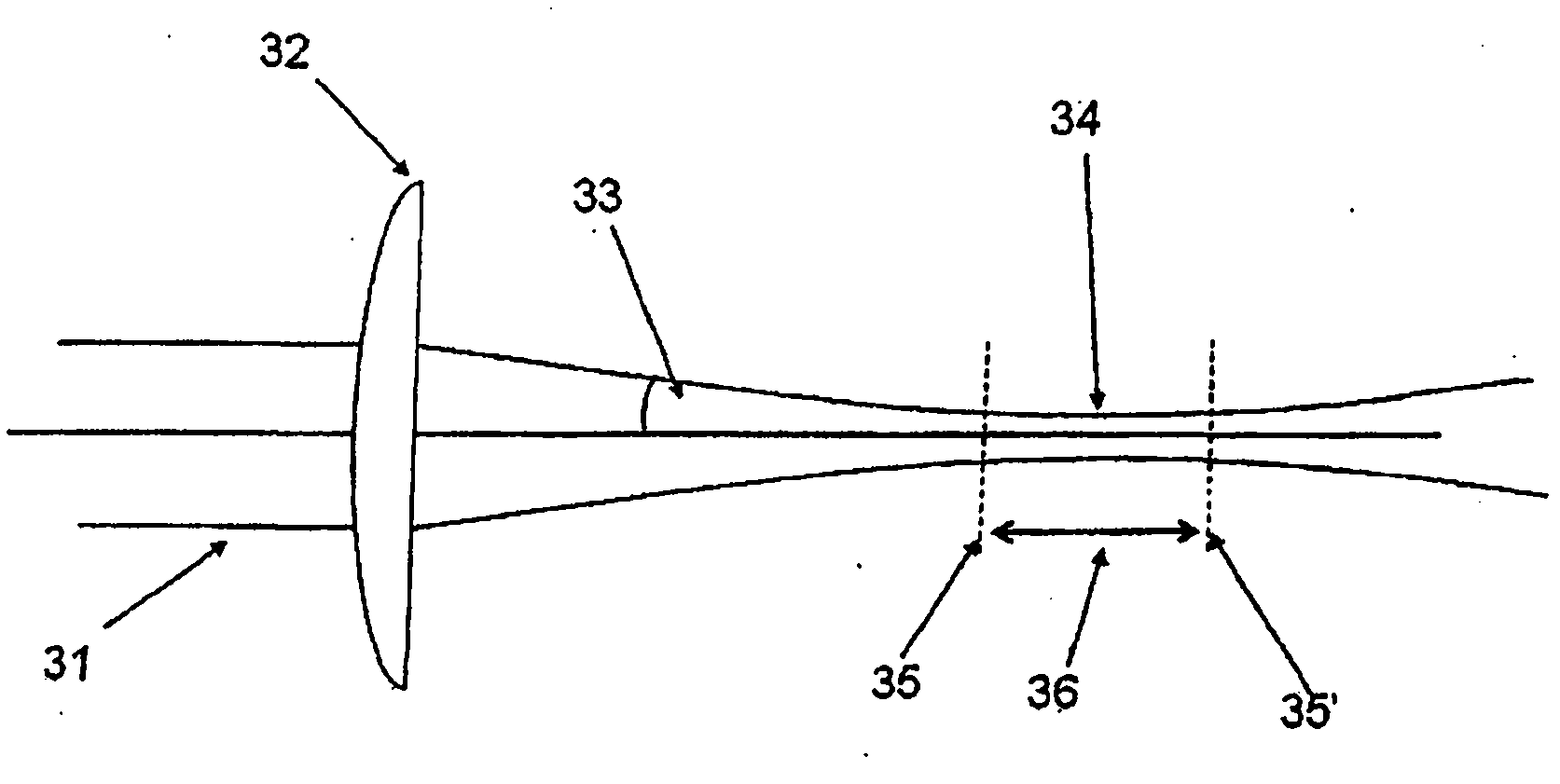
[0044] figure 2 Details of the laser beam near the focal spot are shown. The beam 21 is focused by a lens 22 such that the beam converges at a half angle 23 to a beam waist or focal point 24 before expansion. For the case where the beam entering the focusing lens 22 is collimated, the smallest diameter (d) of the beam in the waist region 24 is a function of the following parameters: laser wavelength (λ); quality of the laser beam relative to a fully diffraction-limited beam (M2); the d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com