RNA interference mediated inhibition of proprotein convertase subtilisin Kexin 9 (PCSK9) gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
A nucleotide and double-stranded nucleic acid technology, applied in DNA/RNA fragments, gene therapy, genetic engineering, etc., can solve the problem of RNAi activity reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0711] The synthetic methods used for RNA comprising certain siNA molecules of the present invention follow the procedures described in the following references: Usman et al., 1987, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 109, 7845; Scaringe et al., 1990, Nucleic Acids Res., 18, 5433; and Wincott et al., 1995, Nucleic Acids Res. 23, 2677-2684 Wincott et al., 1997, Methods Mol. Bio., 74, 59, and utilize common nucleic acid protection and coupling Groups such as dimethoxytrityl at the 5'-end, and phosphoramidite at the 3'-end. In a non-limiting example, the small-scale synthesis was performed on a 394 Applied Biosystems, Inc. synthesizer using a 0.2 μmol scale protocol, a 7.5-minute coupling step for alkylsilyl protected nucleotides and a 2'-O-methylated nucleotides use a 2.5-minute coupling step. Table V summarizes the amount of reagents and contact time used in the synthesis cycle. Alternatively, synthesis on a 0.2 μmol scale can be performed on a 96-well plate synthesizer, such as that produced ...
Embodiment 1
[0824] Example 1: Tandem synthesis of siNA constructs
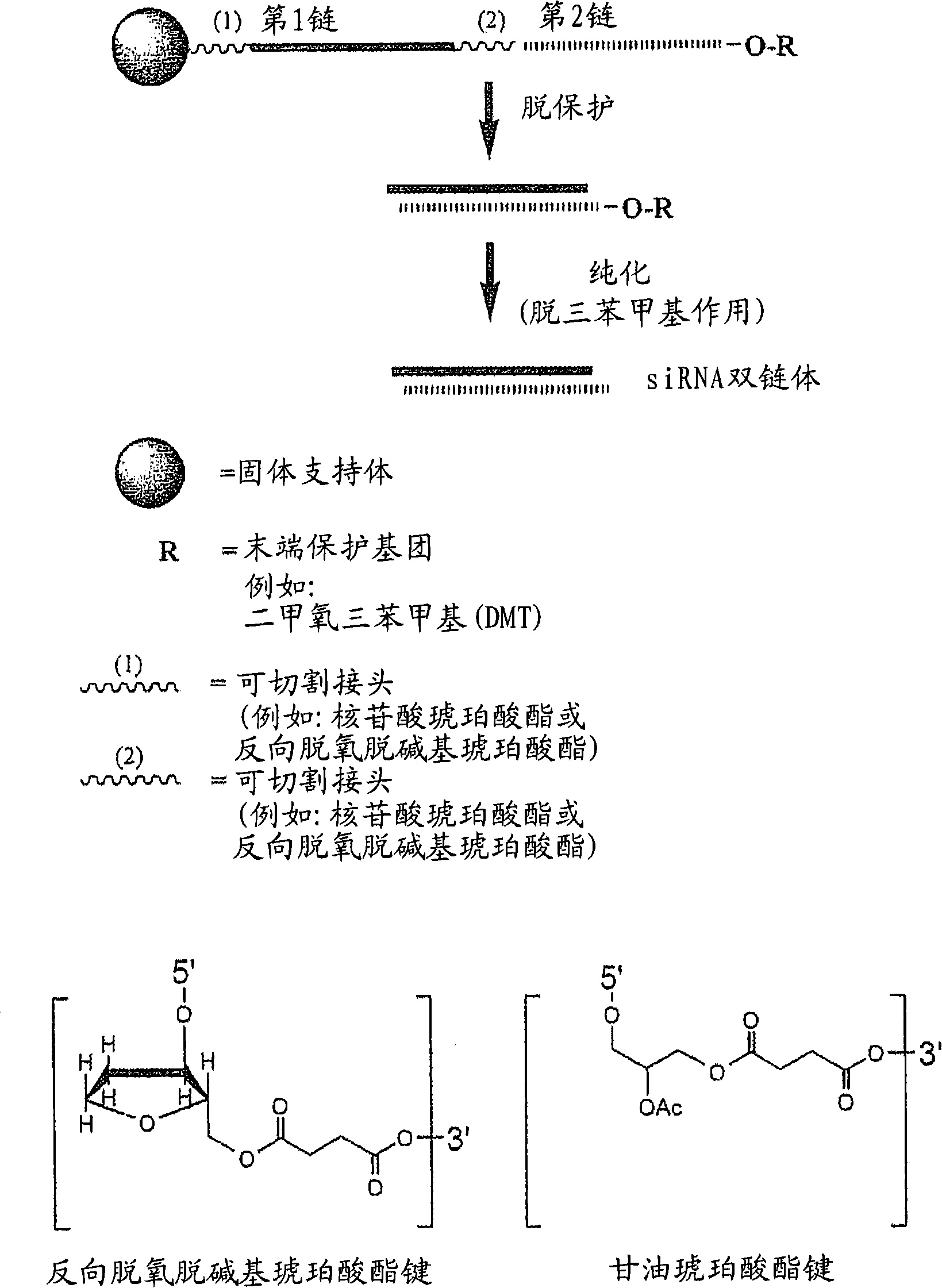
[0825] Exemplary siNA molecules of the invention are synthesized in tandem using cleavable linkers such as succinyl-based linkers. Tandem synthesis as described herein is followed by a single-step purification process that provides RNAi molecules in high yield. This method is highly compliant with siNA synthesis, supports high-throughput RNAi screening, and can be easily adapted to multi-column or multi-porous synthesis platforms.
[0826] Among them, the 5′-terminal dimethoxytrityl (5′-O-DMT) remains intact (trityl-dependent synthesis) of siNA oligonucleotides (oligo) and their complements. Glycolic acid is deprotected as described above. After deprotection, the siNA sequence strands are allowed to hybridize spontaneously. This hybridization produces a duplex in which one strand has retained the 5'-O-DMT group and the complementary strand contains a terminal 5'-hydroxyl group. The newly formed duplex behaves as a single ...
Embodiment 2
[0830] Example 2: Identification of potential siNA target sites in any RNA sequence
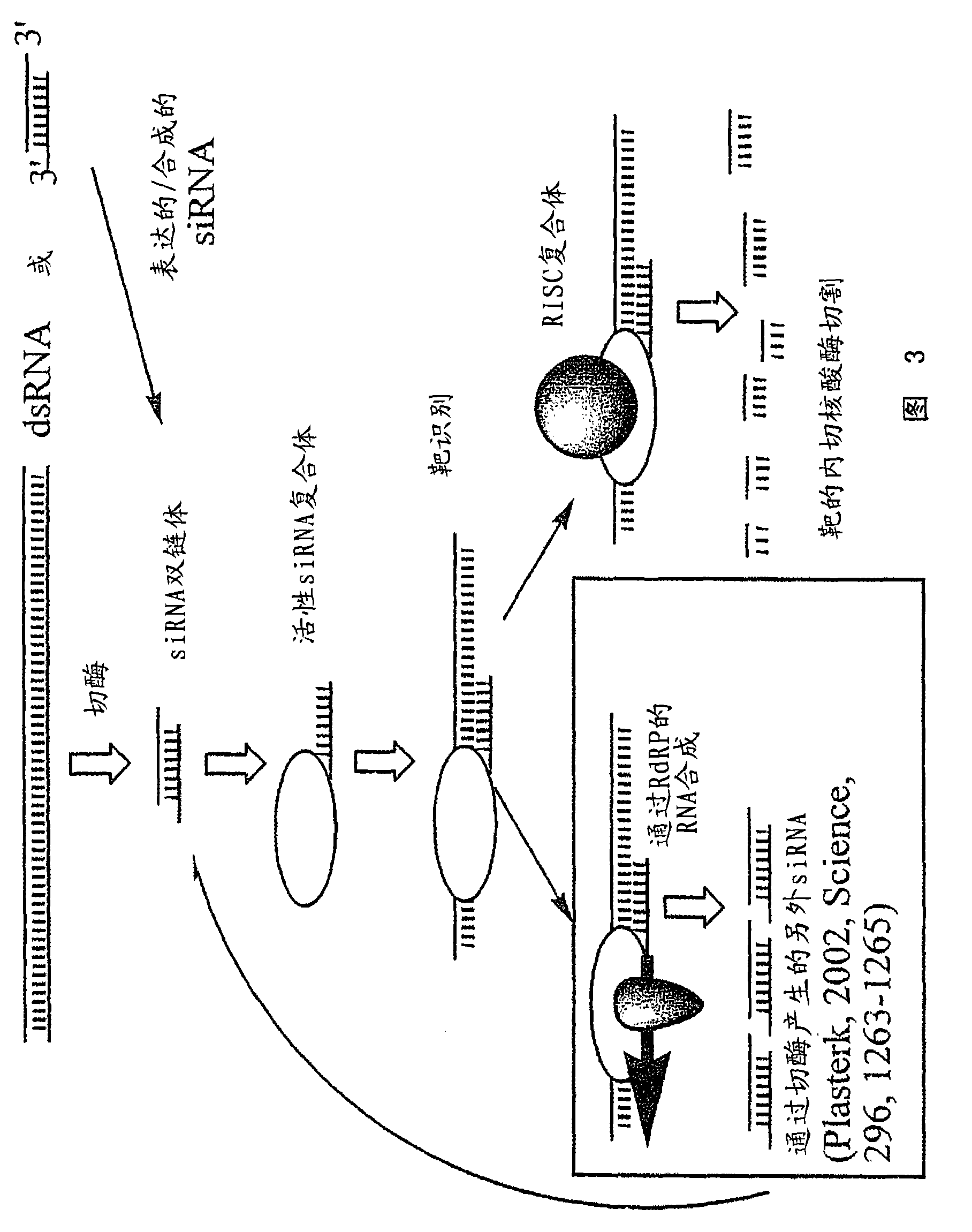
[0831] For example, by using a computer folding algorithm to screen a target RNA target sequence of interest, such as a human mRNA transcript (for example, any sequence mentioned herein by Genbank accession number). In a non-limiting example, sequences derived from databases, such as Genbank genes or RNA gene transcripts, are used to generate siNA targets that have complementarity with the target. Such sequences can be obtained from a database, or can be determined experimentally as known in the art. Known target sites, such as those determined to be effective target sites based on studies using other nucleic acid molecules such as ribozymes or antisense, or those targets known to be related to diseases, traits or conditions, such as those that contain mutations or Those sites that are missing can be used to design siNA molecules that target those sites. Various parameters can be used to dete...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com