Intracranial lesion computerized tomography (CT) body surface simple positioning method
A positioning method and body surface technology, applied in patient positioning for diagnosis, computerized tomography scanner, echo tomography, etc., can solve the problems of delaying rescue time, increasing treatment costs, expensive equipment, etc., and achieve good prognosis and recovery , shorten the positioning time, reduce the effect of tissue damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
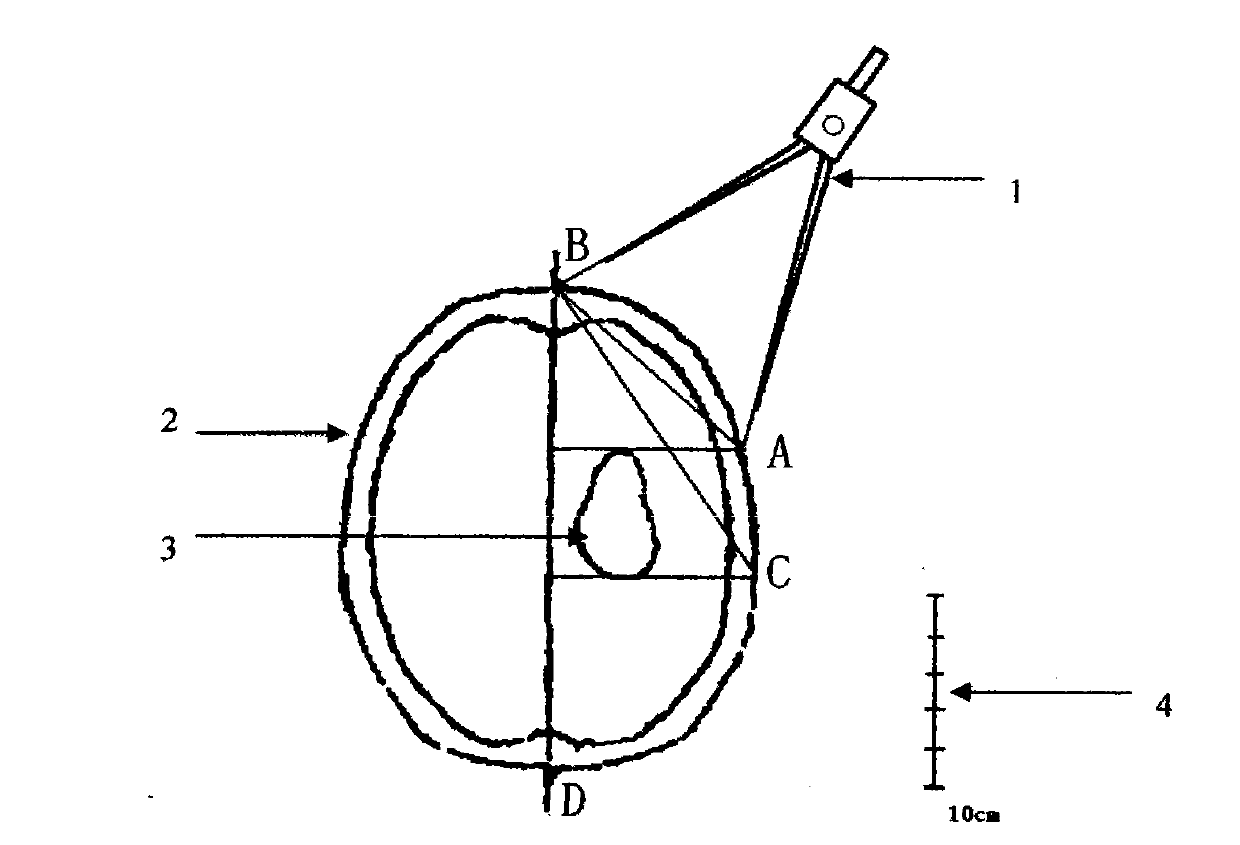
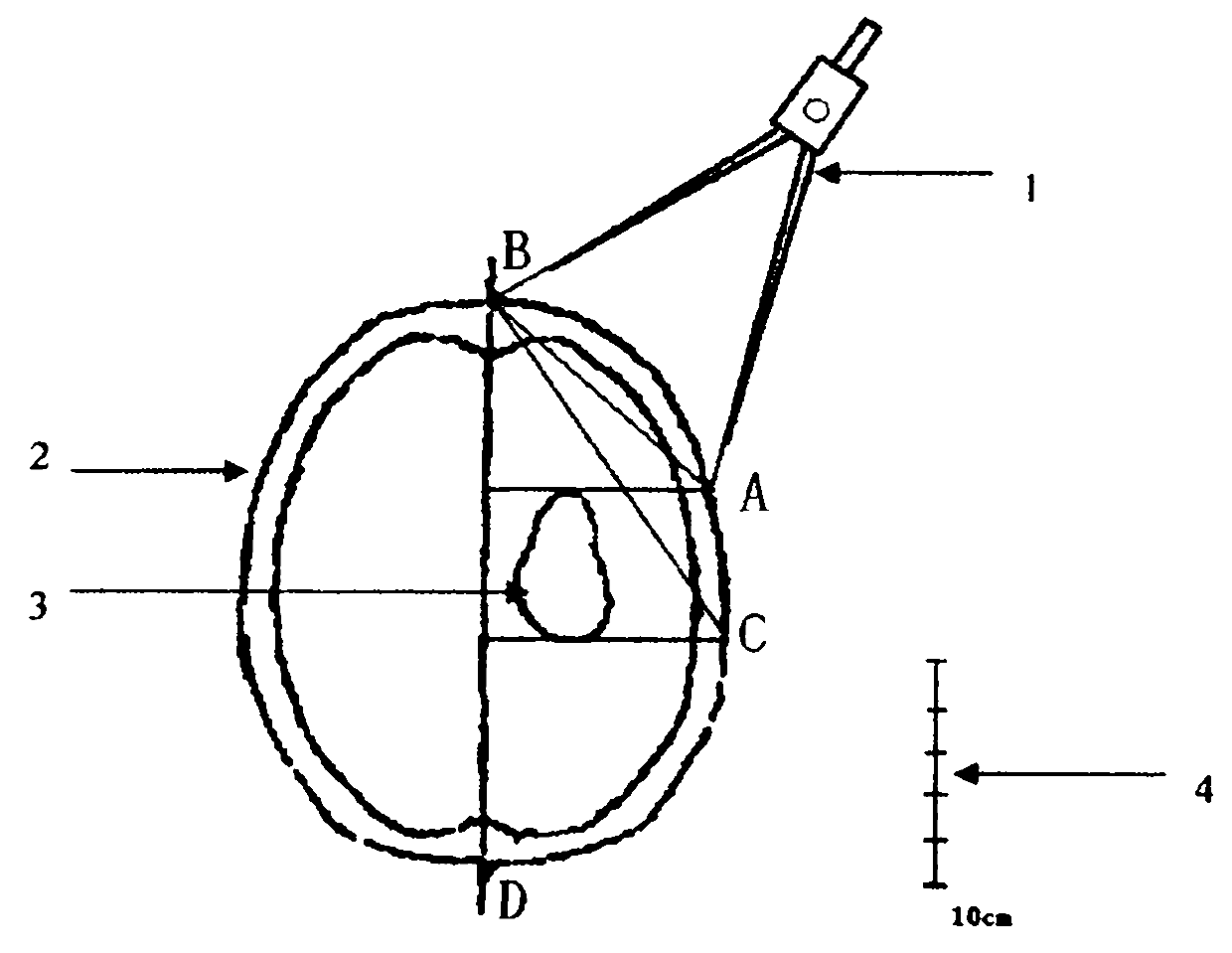
[0012] In the figure, firstly mark the intersection points B and D of the midline and the scalp on the CT axial map (2) at the largest level of the lesion, and then mark the lesion (3) the anterior and posterior boundaries after avoiding important structures and functional areas For projection points A and C, use the compass (1) to measure the BA straight-line distance and the BC straight-line distance respectively, and use the scale (4) to calculate their actual distance.
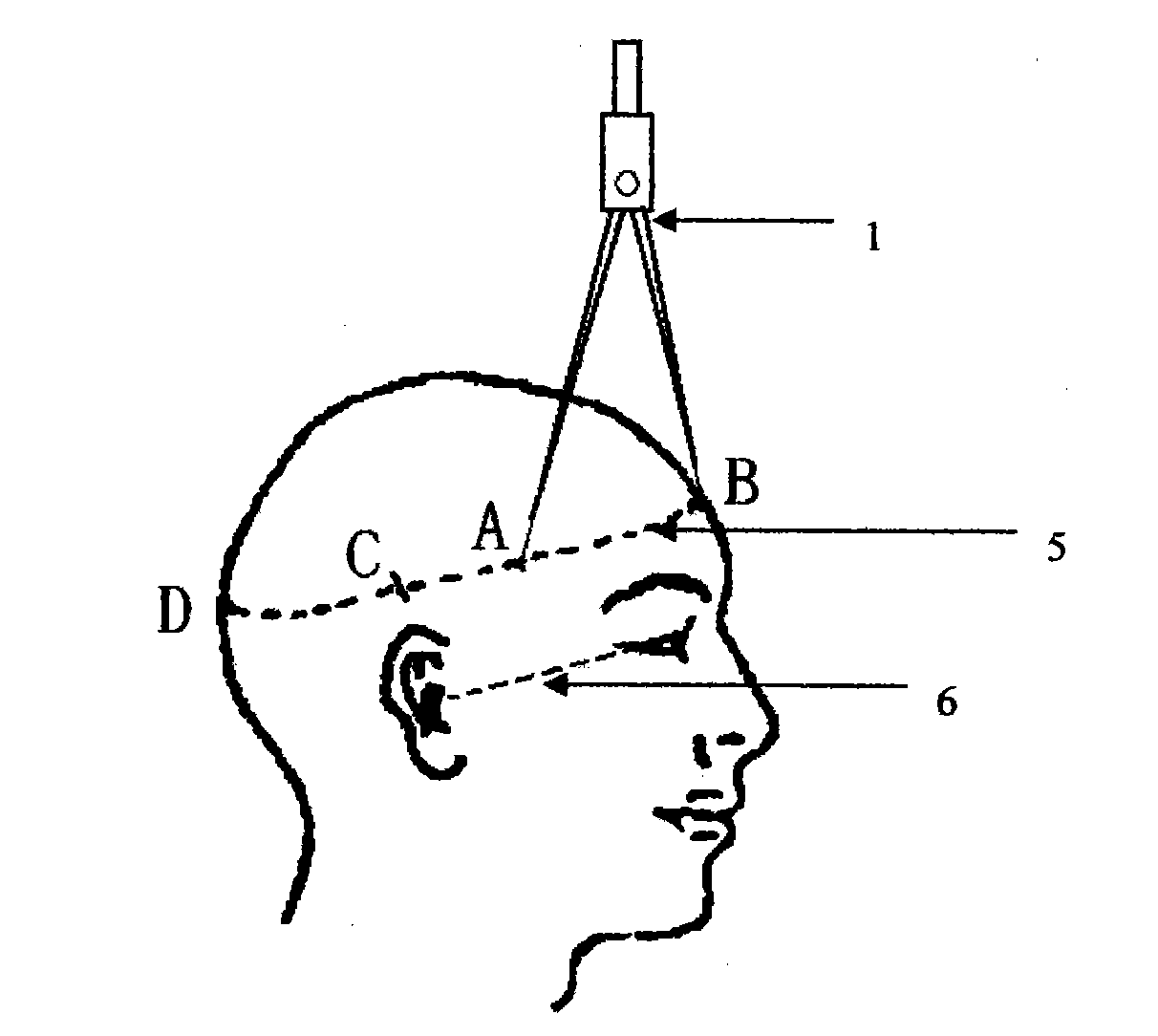
[0013] The ear canthus line (6) is selected as the baseline for head CT axial radiography, and the arc line (5) parallel to the baseline (6) is marked on the scalp body surface where the CT axial map (2) of the largest lesion range is located. Draw the midline (ie sagittal line) BD on the scalp. Use the calculated BA and BC distances to mark points A and C on the arc line (5) on the side where the lesion is located. These two points are the projection of the anterior and posterior boundary of the intracra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com