Solar cell panel
A technology for solar panels and photovoltaic cells, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of lack of anti-ultraviolet performance, large space for improving the conversion efficiency of components, and reducing the utilization efficiency of sunlight.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
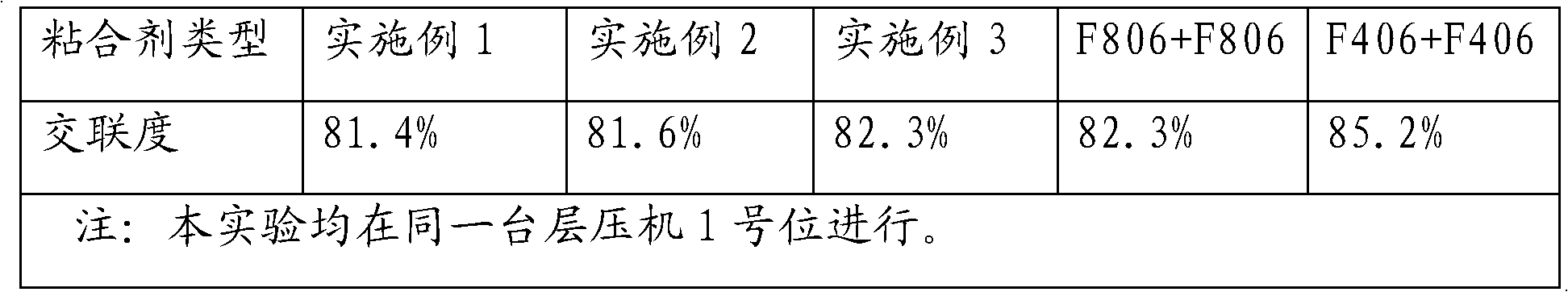
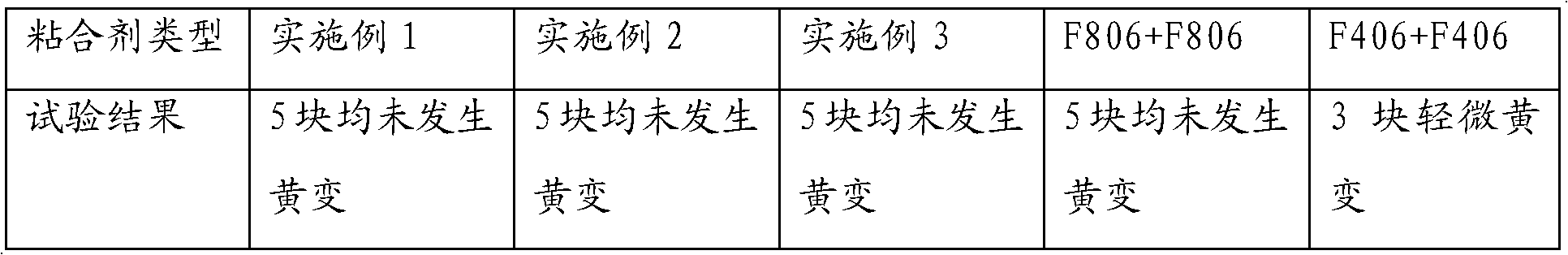
[0016] A solar cell panel is sequentially composed of a glass plate, a first adhesive layer, a photovoltaic cell, a second adhesive layer and a back sheet, the first adhesive layer bonds the glass plate and the photovoltaic cell into one, and The adhesive has no effect on ultraviolet rays in sunlight, that is, the energy of ultraviolet rays passing through the adhesive does not change. The second adhesive layer bonds the other side of the photovoltaic cell sheet to the back sheet, wherein the second adhesive contains a UV cutoff agent that is impenetrable to ultraviolet rays, and the UV cutoff agent is a titanium oxide-cerium oxide composition. The molar ratio of them is 1:5, they account for 20 wt% in the adhesive, and the thickness is 300 nanometers.
[0017] The main raw material of the above-mentioned two-layer adhesive is EVA material.
Embodiment 2
[0019] A solar cell panel is sequentially composed of a glass plate, a first adhesive layer, a photovoltaic cell, a second adhesive layer and a back sheet, the first adhesive layer bonds the glass plate and the photovoltaic cell into one, and The adhesive has no effect on ultraviolet rays in sunlight, that is, the energy of ultraviolet rays passing through the adhesive does not change. The second adhesive layer bonds the other side of the photovoltaic cell sheet to the back sheet, wherein the second adhesive contains a UV cutoff agent that is impenetrable to ultraviolet rays, and the UV cutoff agent is a titanium oxide-cerium oxide composition. The molar ratio of them is 5:1, they account for 40 wt% in the adhesive, and the thickness is 20 nanometers.
[0020] The main raw material of the above-mentioned two-layer adhesive is EVA material.
Embodiment 3
[0022] A solar cell panel is sequentially composed of a glass plate, a first adhesive layer, a photovoltaic cell, a second adhesive layer and a back sheet, the first adhesive layer bonds the glass plate and the photovoltaic cell into one, and The adhesive has no effect on ultraviolet rays in sunlight, that is, the energy of ultraviolet rays passing through the adhesive does not change. The second adhesive layer bonds the other side of the photovoltaic cell sheet to the back sheet, wherein the second adhesive contains a UV cutoff agent that is impenetrable to ultraviolet rays, and the UV cutoff agent is a titanium oxide-cerium oxide composition. The molar ratio of them is 1:1, they account for 30 wt% in the adhesive, and the thickness is 150 nm.
[0023] The main raw material of the above-mentioned two-layer adhesive is EVA material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com