Method for modeling dynamic multi-document abstracts
A modeling method, multi-document technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems that affect the comprehensiveness of abstracts, abstract fragments from the same subtopic, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
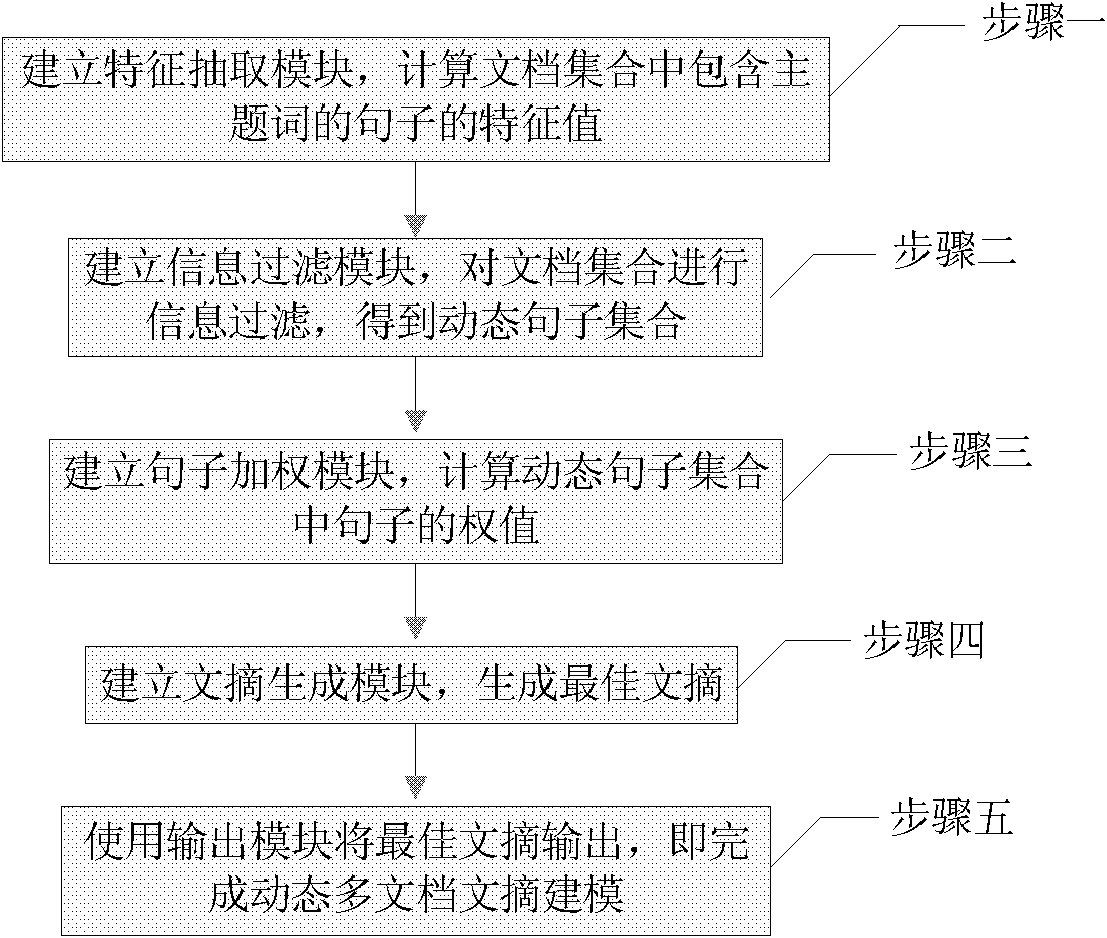
[0037] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this implementation mode, the specific steps of the dynamic multi-document summarization modeling method of this implementation mode are:
[0038] Step 1, set up a feature extraction module, calculate the feature value of the sentence that contains the subject word in the document collection; the feature value of the sentence is the historical redundancy feature value of the sentence, the significance feature value of the sentence, the time feature value of the sentence, The length feature value of the sentence and the position feature value of the sentence, and the document collection is composed of the current document collection and the historical document collection;
[0039] Step 2. Establish an information filtering module to perform information filtering on the document collection to obtain a dynamic sentence collection;
[0040] Step 3, establish a sentence weighting module to calculate the weight of s...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0044] Specific embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further description of step 1 in a dynamic multi-document summarization modeling method described in specific embodiment 1. In step 1, a feature extraction module is established to calculate the topics contained in the document collection. The method of the feature value of the sentence of the word is:
[0045] Step 11, calculate the weight Wgt(w) of the subject term w: Wgt(w)=TF(w)*IDF(w)*ISF(w); wherein TF(w) is the term frequency of the subject term w, IDF( w) is the inverse document frequency of the keyword w, and ISF(w) is the inverse sentence frequency of the keyword w;
[0046] Steps 1 and 2, calculating the historical redundancy feature value NWgt(s) of the sentence s:
[0047] NWgt ( s ) = Σ i = 1 m ( Σ ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0056] Specific embodiment three: this embodiment is a further description of step 2 in a dynamic multi-document summarization modeling method described in specific embodiment 1. In step 2, an information filtering module is established to perform a set of candidate documents Information filtering, the method of obtaining the dynamic sentence set is as follows: first, according to the historical redundancy feature value of the sentence s, sort all the sentences in the sentence set of the current document set from high to low, delete the first 50 sentences sorted, and get the dynamic collection of sentences.
[0057] The information filtering module of this embodiment processes the original sentence set, and filters the historical information in the current document set. The schematic diagram of the document set after filtering is as follows Figure 8 As shown, the sentences with large historical information in the original sentence set are filtered out, so that the remaining s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com