sonos structure, sonos memory
A technology of substrate and convex surface, applied in the field of SONOS structure and SONOS memory, can solve the problems of erasure saturation and electron incomplete tunneling, etc., and achieve the effect of erasing saturation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
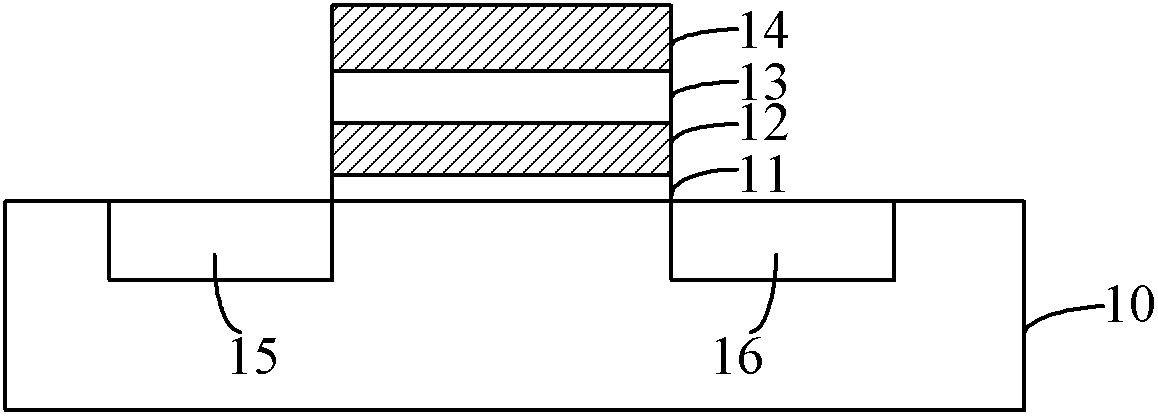
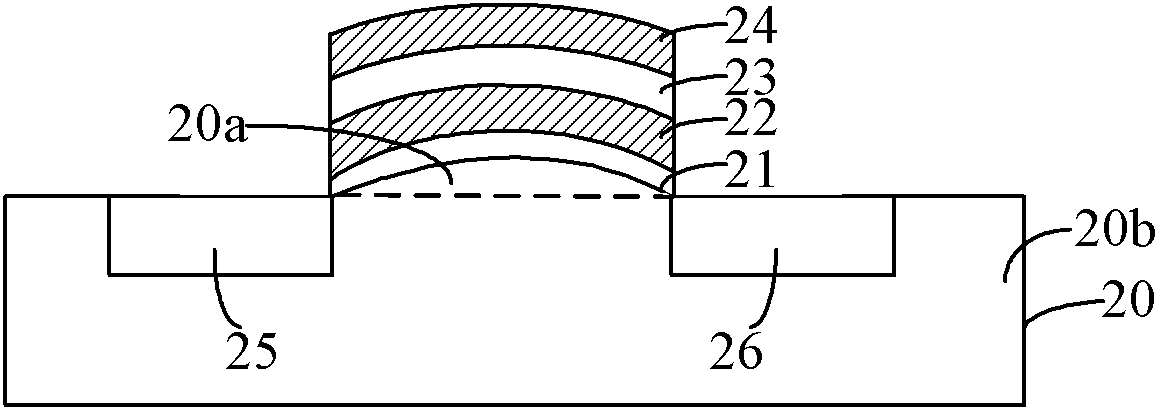
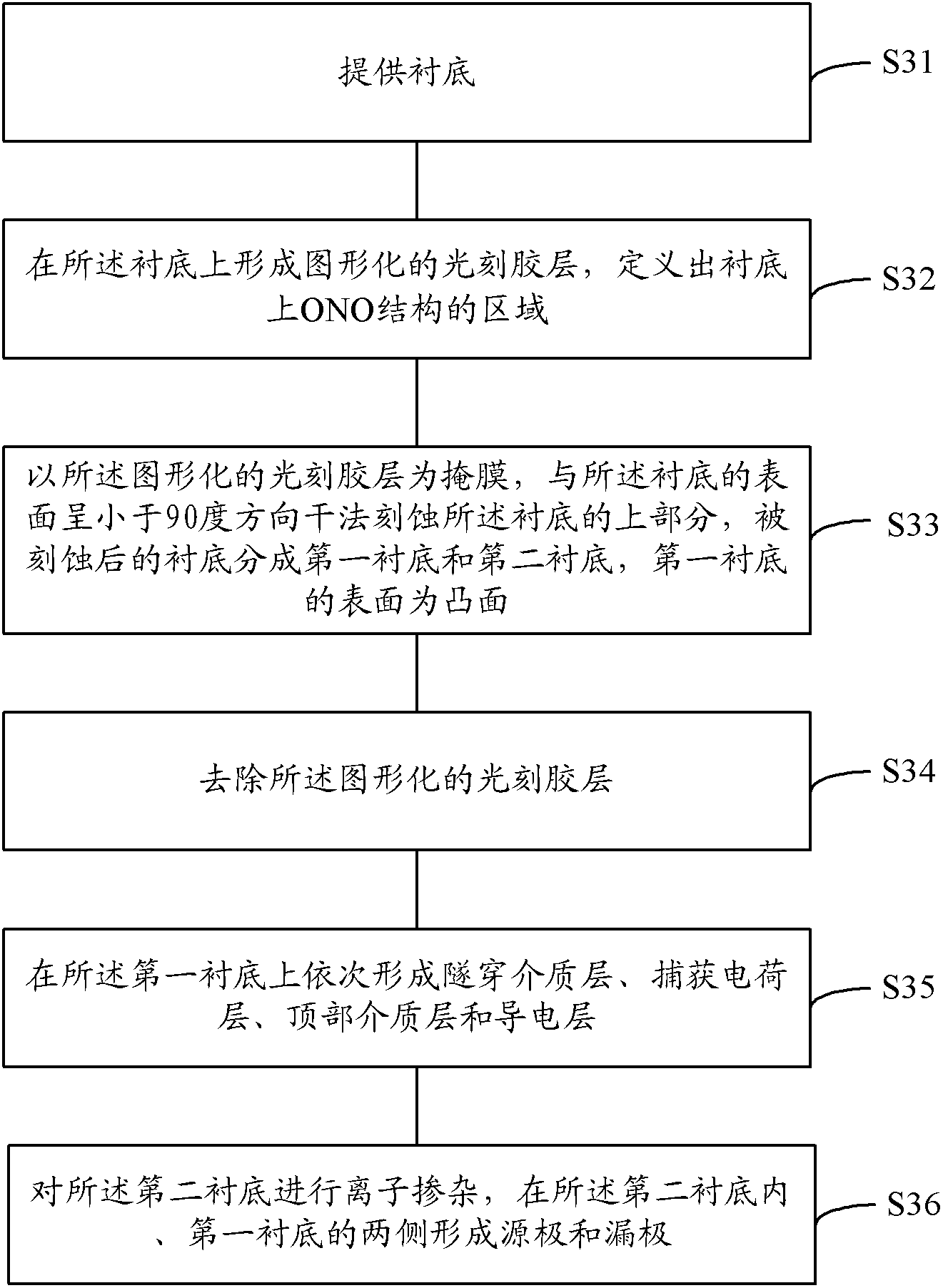
[0024] Based on the working principle of SONOS memory described above, SONOS memory uses FN tunneling effect (Fowler-Nordheim Tunneling) to erase: the strong field between the gate and the substrate makes the electrons in the trapped charge layer tunnel through the tunnel The tunneling dielectric layer enters the substrate. When the thickness of the tunneling dielectric layer is determined, the tunneling process is mainly determined by the electric field in the tunneling dielectric layer. The greater the electric field strength, the easier the tunneling occurs, that is, the trapping of the charge layer The easier it is for electrons to tunnel into the substrate. There are two tunneling processes in the SONOS structure: tunneling one, electrons tunnel from the gate through the top dielectric layer to the trapped charge layer, and tunneling two: electrons tunnel from the trapped charge layer through the tunneling dielectric layer to the substrate. In the traditional flat SONOS st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com