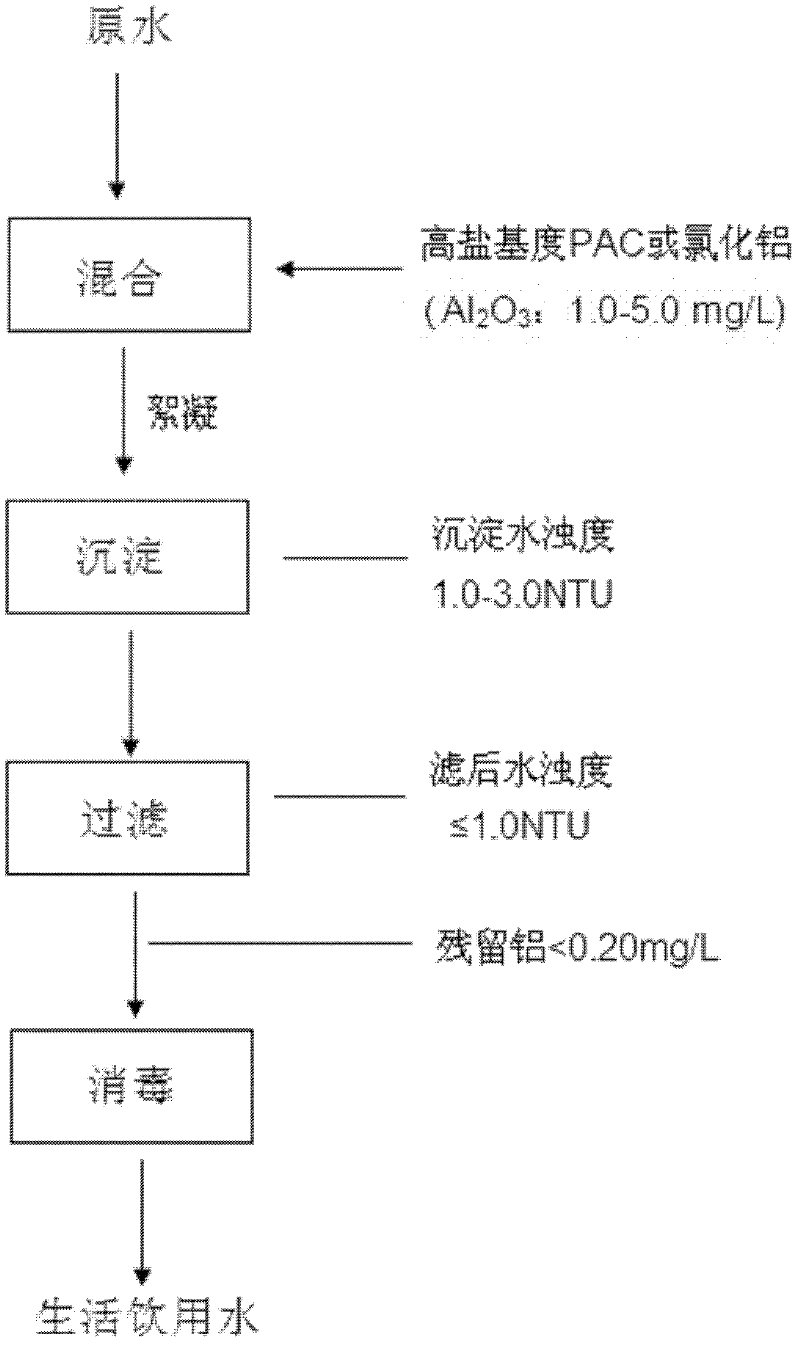
Application of high-basicity polyaluminum chloride in reduction of residual aluminum content of drinking water
A polyaluminum chloride and salinity technology, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve problems such as uncommon application, and achieve the effects of low economic cost and strong aluminum reduction effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] [Example 1] Effects of different coagulants on residual aluminum in purified water
[0040] In this example, different coagulants were used to carry out precipitation tests to study the influence of different coagulants on the residual aluminum content in purified water. The technical specifications of the coagulant used in the test are shown in Table 3. The test results of residual aluminum content are shown in Table 4. See Table 8 and Table 9 for economic costing and comparison.
[0041] Table 3 Test coagulant technical indicators
[0042]
[0043] Table 4 Effect of different coagulants on residual aluminum in purified water
[0044]
[0045] Raw water for the test: water from Shanghai Qingcaosha Reservoir, turbidity: 7.25NTU, alkalinity: 96mg / L, pH: 8.11, water temperature 23°C (indoor), GT value: 41304, stirring: 8 minutes, sedimentation: 15 minutes.
[0046] It can be seen from Table 4 that PAC, AC and AS coagulants all have the effect of reducing the r...
Embodiment 2
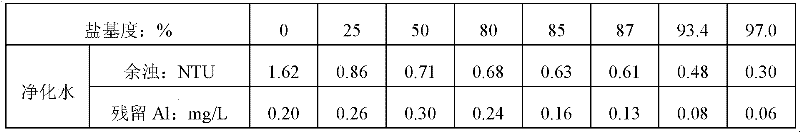
[0047] [Example 2] The impact of PAC with different salinity on residual aluminum in purified water
[0048] In this example, coagulation and sedimentation tests were further carried out with PACs of different basicity to study the effect of the basicity of PAC on the residual aluminum content of purified water. See Table 5 for the technical specifications of the coagulant used for the test, and Table 6 for the results. See Table 8 for economic costing and comparison.
[0049] Table 5 Technical index of coagulant used in test
[0050]
[0051] Table 6 Effect of PAC with different salinity on residual aluminum in purified water
[0052]
[0053] Raw water for the test: Dongjiang water distribution, turbidity: 17.4NTU, alkalinity: 38.0mg / L, pH: 8.32, water temperature 26°C, GT value: 35280, stirring: 8 minutes, precipitation: 10 minutes.
[0054] As can be seen from Table 6 and Table 8, compared with PAC with a basicity of 97.0% and a PAC with a basicity of 82.8%, the...
Embodiment 3
[0055] [Example 3] The influence of different raw water pH on residual aluminum in purified water
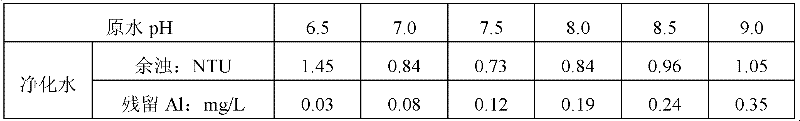
[0056] This embodiment further uses PAC with a basicity of 97.0% as a coagulant, and adjusts the raw water to different pHs with 0.5mol / L hydrochloric acid and 0.5mol / L sodium hydroxide aqueous solution to carry out coagulation and sedimentation tests to study the effect of the pH value of raw water on the residual water in purified water. The effect of aluminum content, the results are shown in Table 7.
[0057] Table 7 Effect of different raw water pH on residual aluminum in purified water
[0058]
[0059] Raw water for the test: Dongjiang water distribution, turbidity: 14.2NTU, alkalinity: 78.0mg / L, pH: 8.25, water temperature 26°C, GT value: 35280, stirring: 8 minutes, precipitation: 10 minutes.
[0060] It can be seen from Table 7 that the pH of raw water has an impact on the residual aluminum content of purified water, and as the pH increases, the residual aluminum ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com