Method for killing Laodelphax striatellus by utilizing pest taxis to plant
A planthopper and plant technology, applied in devices, applications, animal husbandry, etc. to capture or kill insects, can solve problems such as difficulty in fundamentally controlling insect pests, frequent use of chemical pesticides, and generation of pest resistance, and reduce Toxic transmission hazards, reduction of insect population base, and the effect of reducing the occurrence of hazards
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0012] Sorting 3 large fields with an area of 2000 square meters, respectively, planted corn seedlings, and planted bluegrass, bluegrass, and bermudagrass around it.
[0013] Rice seedlings were planted in paddy fields with a contiguous area of 2,000 square meters, and bluegrass bluegrass was planted at intervals around them.
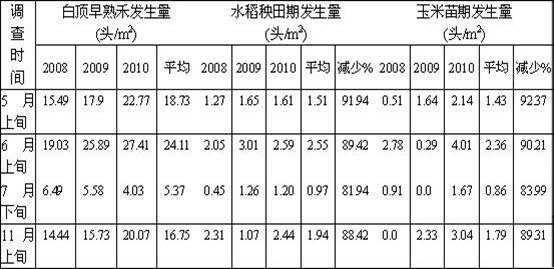
[0014] Field surveys revealed that the gray planthopper Laodelpax striutellus The feeding tendency of Falle'a to different host plants is quite different, especially when there are different host plants in the same area, adults of SBPH tend to choose to feed on the plants with strong feeding ability, resulting in different The occurrence of plant pests varies greatly, see Table 1 and Table 2 below for details.
[0015] Table 1 Comparison of occurrence of SBPH on rice, corn and host weeds
[0016]
[0017] (Adopt 5-point sampling method, evenly distribute points, survey 1 square meter at each point.)
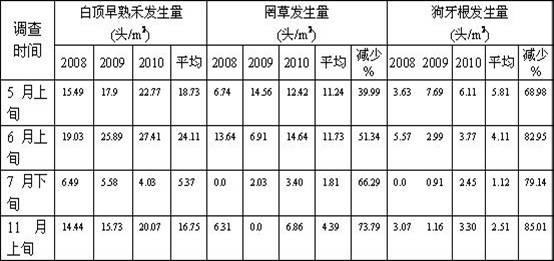
[0018] Table 2 Comparison table of oc...
Embodiment 2
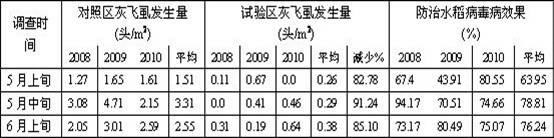
[0024] The implementation method for trapping and killing SBPH at the rice seedling stage to control viral diseases is as follows: the experimental area is rice seedling field with an area of more than 300 meters, planting trapping weeds - bluegrass bluegrass around the rice seedling field. Use medicine to kill, no need to use medicine to control rice seedlings. In contrast, the rice seedling fields in the control area were not planted with trapping weeds—Poa annua, and the rice seedling fields were not controlled with pesticides. The survey results showed that the incidence of SBPH in the test area was 82.78%-91.24% lower than that in the control area; the effect of preventing and controlling rice black-streaked dwarf and stripe leaf blight was 63.95%-79.81%, see Table 3 for details.
[0025] Table 3 The effect of planting and trapping plants to trap and kill SBPH in controlling viral diseases at rice seedling stage
[0026]
[0027] (Sampling at 5 points, evenly dist...
Embodiment 3
[0029] The implementation method of trapping and killing SBPH at the seedling stage of corn to control viral diseases is as follows: the experimental area is a corn seedbed with an area of more than 100 square meters, planting trapping weeds - bluegrass bluegrass around the corn seedbed, and concentrating after the detection of SBPH pests Use medicine to kill, no need to use medicine to control corn seedlings. In the control area, the trapping plant—Poa crimson bluegrass was not planted around the corn seedbed, and no pesticide was used to control the corn seedling stage. The survey results showed that the incidence of SBPH in the test area was 85.31%~91.69% lower than that in the control area, and the effect of preventing and controlling corn dwarf disease was 66.51%~80.55%. See Table 4 for details.
[0030] Table 4 The effect of planting trapping plants on corn seedbeds to control viral diseases by trapping and killing SBPH
[0031]
[0032] (Sampling at 5 points, ev...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com