Method for discriminating Laves phase and carbide phase in high Nb iron nickel base high temperature alloy
A high-temperature alloy, iron-nickel-based technology, applied in the preparation of test samples, measuring devices, and material analysis by optical means
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
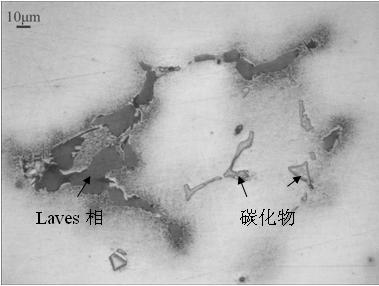
[0024] After grinding and polishing the GH4169 as-cast alloy sample, expose the polished sample surface to a box-type resistance furnace at a furnace temperature of 500°C for 1 hour, and then air-cool to ensure that the polished sample surface is not polluted. After the sample was cooled, it was directly observed under a metallographic microscope. The tissue of the sample after being treated at 500°C for 1 hour is as follows: figure 2 shown. It can be seen that after heat dyeing at 500°C for 1 hour, the Laves phase in the sample has turned reddish brown, and the carbides have a certain luster, surrounded by a coating film.
Embodiment 2
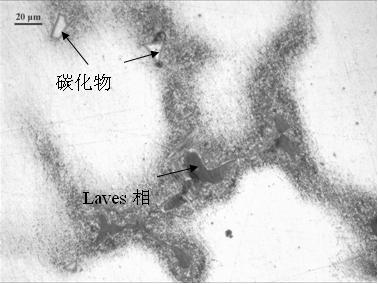
[0028] After the GH4169G alloy as-cast sample was ground and polished, the surface of the polished sample was exposed to a box-type resistance furnace at a furnace temperature of 520 ° C for 60 minutes, and the sample was directly observed under a metallographic microscope after cooling. The tissue of the sample after being treated at 520°C for 60 minutes is as follows: Figure 4 As shown, it can be seen that after heat dyeing at 520°C for 60 minutes, the Laves phase in the sample has turned brown, while the carbides have a certain luster.
Embodiment 3
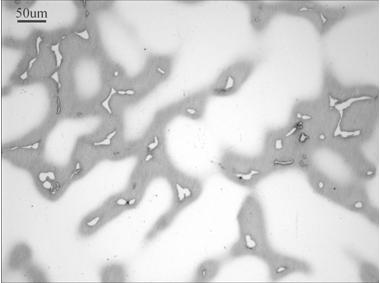
[0032] The Thermo-Span as-cast alloy sample was homogenized at 1120°C for 20 hours. After the sample was ground and polished, the surface of the polished sample was exposed to a box-type resistance furnace at a furnace temperature of 450°C for 80 minutes. After the sample was cooled, Observe directly under a metallographic microscope. The tissue of the sample after being treated at 450°C for 80 minutes is as follows: Figure 6 As shown, it can be seen that after heat dyeing at 450°C for 80 minutes, the Laves phase in the sample has turned reddish brown, and the carbides have a certain luster.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com