Method for recycling platinum from waste platinum crucibles
A technology of platinum crucible and ammonium chloroplatinate, which is applied in the field of metal recovery and can solve problems such as difficulties in platinum recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
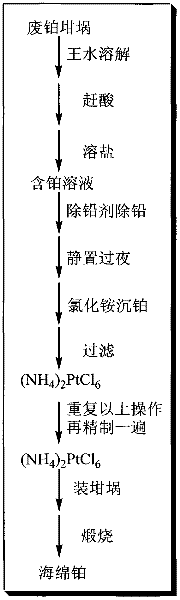
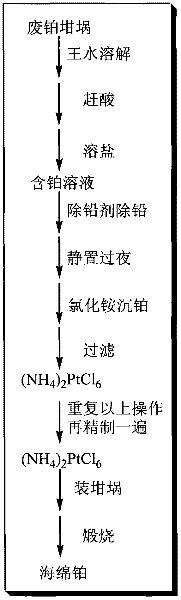
[0024] The steps of the inventive method are:
[0025] (1) Put 105 g of spent platinum crucible in a 4000 mL beaker, add excess aqua regia (V hydrochloric acid: V nitric acid = 3:1) and place it on an electric furnace to heat and dissolve. After the platinum waste is completely dissolved, continue heating, concentrate the volume to 500mL, add hydrochloric acid to catch the nitrate until there is no yellow smoke. After diluting with deionized water, heat the dissolved salt.
[0026] (2) Dilute the platinum-containing solution obtained in (1) with water to 2000 mL, add 10 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid under stirring, continue stirring and let stand overnight. Filter with a Buchner funnel and rinse the funnel with deionized water. The filter residue is impurities such as insoluble matter and lead sulfate.
[0027] (3) Dilute the filtrate obtained in (2) with water to 2500 mL, heat to boil, add 950 mL of 25% ammonium chloride solution to precipitate platinum. Stand still, s...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The process of the inventive method is:
[0032] 105g waste platinum crucible is placed in 4000mL beaker, the 10mL vitriol oil in embodiment 1 is changed into 25g anhydrous sodium sulfate, all the other conditions are all the same, get sponge platinum 103.91g, productive rate 98.96%, sampling analysis, platinum content ≮99.99%.
Embodiment 3
[0034] The process of the inventive method is:
[0035] Put 105g of waste platinum crucible in a 4000mL beaker, change 10mL of concentrated sulfuric acid in Example 1 to 31g of potassium sulfate, and keep the rest of the conditions unchanged to obtain 72.15g of platinum sponge, with a yield of 68.71%. Sampling and analysis showed that the platinum content≮99.99 %.
[0036] Compared with the existing technology, for platinum recovery from waste platinum crucible containing impurities such as lead, niobium, silicon, sodium, etc., after being dissolved in aqua regia, concentrated sulfuric acid or water-soluble sulfate is used to pre-remove lead to reduce chlorination. The repeated times of ammonium platinum precipitation can not only shorten the refining cycle of platinum, reduce the amount of reagents, reduce the cost of purification, but also improve the purity of platinum sponge.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com