Super-hydrophobic microstructure
A super-hydrophobic, micro-structure technology, applied in the field of micro-structure, can solve the problems of structural damage, lack of push-pull angle, insufficient construction, etc., and achieve the effects of low manufacturing cost, improved structural strength, and improved super-hydrophobic effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
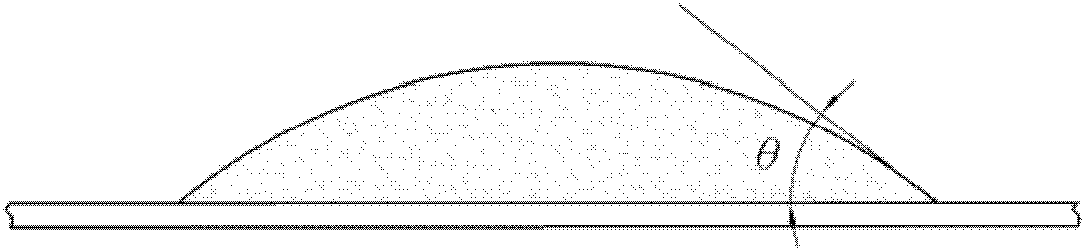
[0052]A superhydrophobic microstructure according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to related drawings, wherein the same components will be described with the same reference numerals.
[0053] Please refer to figure 2 As shown, it is a schematic diagram of a superhydrophobic microstructure 2 according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. The superhydrophobic microstructure 2 of the present invention can be used in the hydrophobicity, waterproofing or dustproofing of buildings, daily necessities, medical supplies or electronic products. For example, it can be applied to the waterproofing and hydrophobicity of building walls, or the hydrophobicity of urinals (so that urine is not easy to stick to the urinal), or the water repellency of car windshields, or the waterproofing of mobile phone screens. Here, the place of use and the objects that can be used are not limited. In addition, the present invention d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com