Fusion polypeptides and uses thereof
A technology of fusing polypeptides and combining polypeptides, which is applied in the field of molecular biology and can solve the problems of no research on methods to improve the activity of ligases, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0383] The construction of embodiment 1-plasmid and the production of fusion polypeptide
[0384] This example describes the construction of plasmids for the production in E. coli of fusion polypeptides comprising T4 DNA ligase (ligase) or E. coli ligase (LigA) fused to various DNA-binding polypeptides, as shown in the table below listed in 1. The orientation of polypeptides comprising ligase activity and DNA-binding activity relative to each other is indicated by an order wherein the polypeptides are described by the name of the fusion polypeptide, e.g. p50-ligase refers to a fusion polypeptide whose comprising a p50 DNA-binding polypeptide fused to the N-terminus of a T4 DNA ligase polypeptide (optionally via a linking polypeptide), whereas ligase-p50 refers to a fusion polypeptide comprising a T4 DNA-binding polypeptide fused to the N-terminus of a p50 DNA-binding polypeptide Enzyme polypeptide (again, optionally via linker polypeptide).
[0385] Table 1: Ligase-DNA bindi...
Embodiment 2-T4
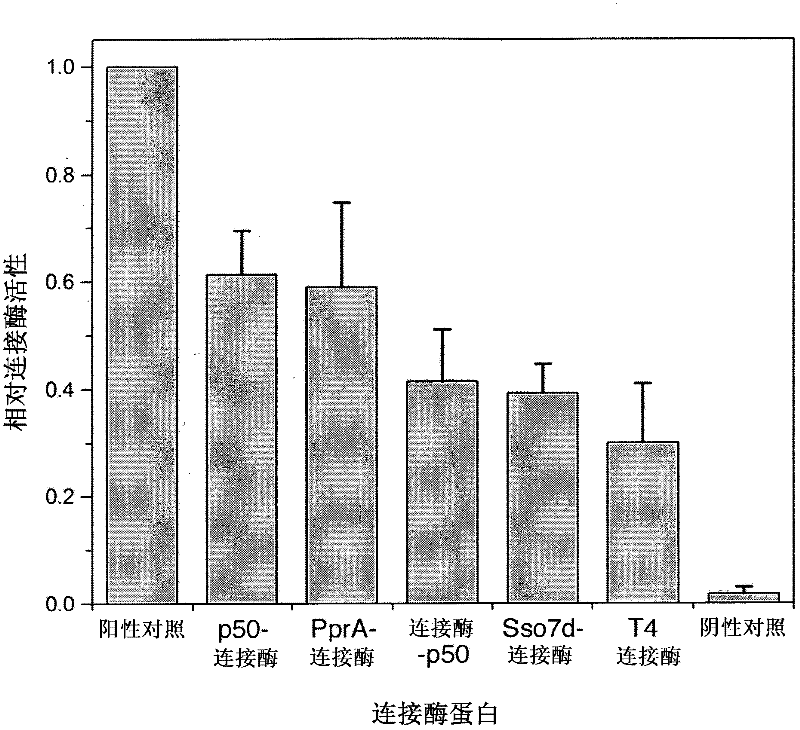
[0404] The analysis of the connecting activity of embodiment 2-T4DNA ligase fusion protein
[0405] Gel-Based Activity Assays
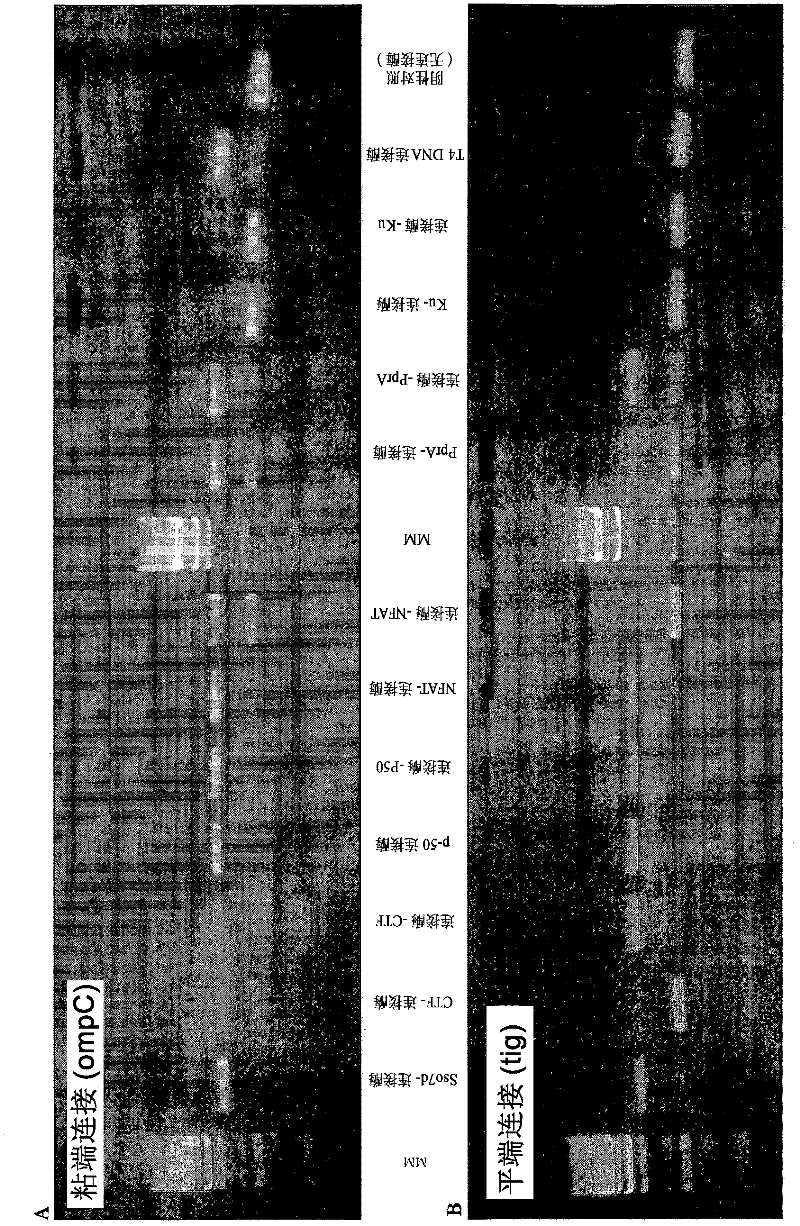
[0406] For sticky-end ligation, by amplifying plasmid pCA24N-ompC with the aid of primers pCA24N.for (5'-GATAACAATTTCACACAGAATTCATTAAAGAG-3' [SEQ ID No. 19]) and pCA24N.rev (5'-CCCATTAACATCACCATCTAATTCAAC-3' [SEQ ID No. .20]), to generate a 1,277bp PCR product. The PCR product was cleaved with the aid of the restriction enzyme Spel, resulting in two linear fragments of very similar size (638bp and 639bp). The two products of the cleavage reaction were co-purified and incubated in the presence or absence of the various ligase proteins. 150 ng of substrate DNA was incubated with 20 pmol of enzyme for 10 min at 16°C. The reaction was terminated by heating to 65°C for an additional 15 minutes. Ligase activity was determined by purifying samples using QiagenMinElute columns and then running them on agarose gels. Activity was measured as the appearance...
Embodiment 3
[0414] Example 3-Analysis of the linking activity of Escherichia coli LigA fusion protein
[0415] Gel-Based Activity Assays
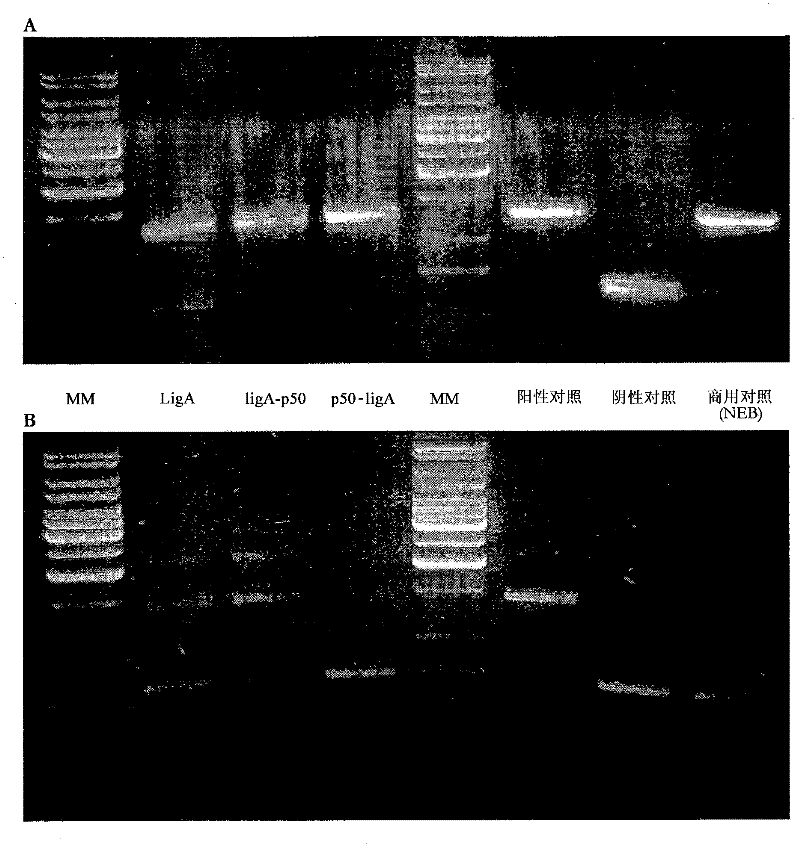
[0416] For sticky-end ligation, 170 ng of Spel-digested ompC substrate (as described in Example 2) was incubated with 20 pmol of each LigA enzyme for 17 hours at 16°C. Reactions were heat-killed (65°C, 15 minutes) and then run on agarose gels. In addition to LigA-p50 and p50-LigA fusion polypeptides, native LigA ligase and three control samples were assayed.
[0417] Positive control - commercially available T4 DNA ligase (Fermentas)
[0418] Negative control - no ligase added
[0419] · Commercial control - 1 μl E. coli LigA (New England Biolabs)
[0420] For blunt-end ligation, 120 ng of SfiI / SmaI-digested tig substrate (as described in Example 2) was incubated with 20 pmol of each enzyme for 17 hours at 16°C. Reactions were heat killed (65°C, 15 minutes) and then run on an agarose gel.
[0421] result
[0422] The sticky-end and blunt-end lig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com