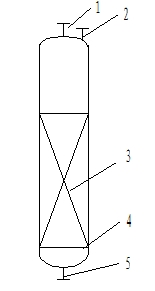Method for removing magnesium in seawater potassium extraction process
A seawater and removal technology, which is applied in the fields of potassium extraction from seawater and magnesium removal, can solve problems such as the quality decline of potassium products, and achieve the effects of low cost, easy availability of materials and simple technological process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
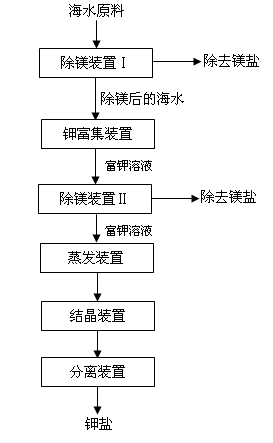
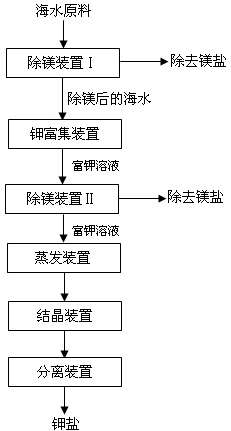
[0022] Before the potassium enrichment device, a magnesium removal device Ⅰ is installed, which is filled with a fixed bed type 2kgD113 macroporous cation exchange resin, and the filling capacity of the ion exchange resin is to treat 1m 3 The amount of seawater is 22kg, and the magnesium removal device II is installed in front of the evaporation device, which is filled with 2kg of C800 ion exchange resin of fixed bed type, and the filling capacity of the ion exchange resin is to treat 1m 3 Potassium-rich solution, the dosage is 30kg. The temperature of the seawater raw material is 20°C, and the seawater containing 1.27g / L of magnesium is passed into the magnesium removal device Ⅰ from bottom to top, and the superficial velocity of the fixed bed in the seawater into the magnesium removal device Ⅰ is 5m / h. 20L, the seawater is in contact with the ion exchange resin in the magnesium removal device Ⅰ, the magnesium content is reduced to 0.12g / L, and 90% of the magnesium in the sea...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Before the potassium enrichment device, a magnesium removal device Ⅰ is installed, which is filled with 2kg of D152 macroporous cation exchange resin of the moving bed type, and the filling capacity of the ion exchange resin is to treat 1m 3 The amount of seawater is 36kg, and the magnesium removal device II is installed in front of the evaporation device, which is filled with 2kg of C800 ion exchange resin of moving bed type, and the filling capacity of the ion exchange resin is to treat 1m 3 Potassium-rich solution, the dosage is 30kg. The temperature of the seawater raw material is 20°C, the seawater containing 1.27g / L of magnesium is passed into the magnesium removal device Ⅰ from bottom to top, and the superficial velocity of the fixed bed in the seawater into the magnesium removal device Ⅰ is 8m / h. 20L, the seawater is in contact with the ion exchange resin in the magnesium removal device Ⅰ, the magnesium content is reduced to 0.11g / L, and 90% of the magnesium in ...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Before the potassium enrichment unit, a magnesium removal unit Ⅰ is set, which is filled with 2kg of C800 ion exchange resin of fixed bed type, and the filling capacity of the ion exchange resin is to treat 1m 3 The amount of seawater is 50kg, and the magnesium removal device II is installed in front of the evaporation device, which is filled with 2kg of D152 macroporous cation exchange resin of fixed bed type, and the filling capacity of the ion exchange resin is to treat 1m 3 Potassium-rich solution, the dosage is 50kg. The temperature of the seawater raw material is 30°C, the seawater containing 1.27g / L of magnesium is passed into the magnesium removal device Ⅰ from bottom to top, and the superficial velocity of the fixed bed in the magnesium removal device Ⅰ is 10m / h. 20L, the seawater is in contact with the ion exchange resin in the magnesium removal device Ⅰ, the magnesium content is reduced to 0.12g / L, and 90% of the magnesium in the seawater is removed; the seaw...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com