Noise source identification method adopting vibration speed measurement and partial near-field acoustical holography method
A near-field acoustic holography and recognition method technology, applied in the measurement of ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic waves, measuring devices, measuring propagation speed, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency, smaller sensor array than sound source, and complicated calculation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0101] The present invention is described in more detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing example:
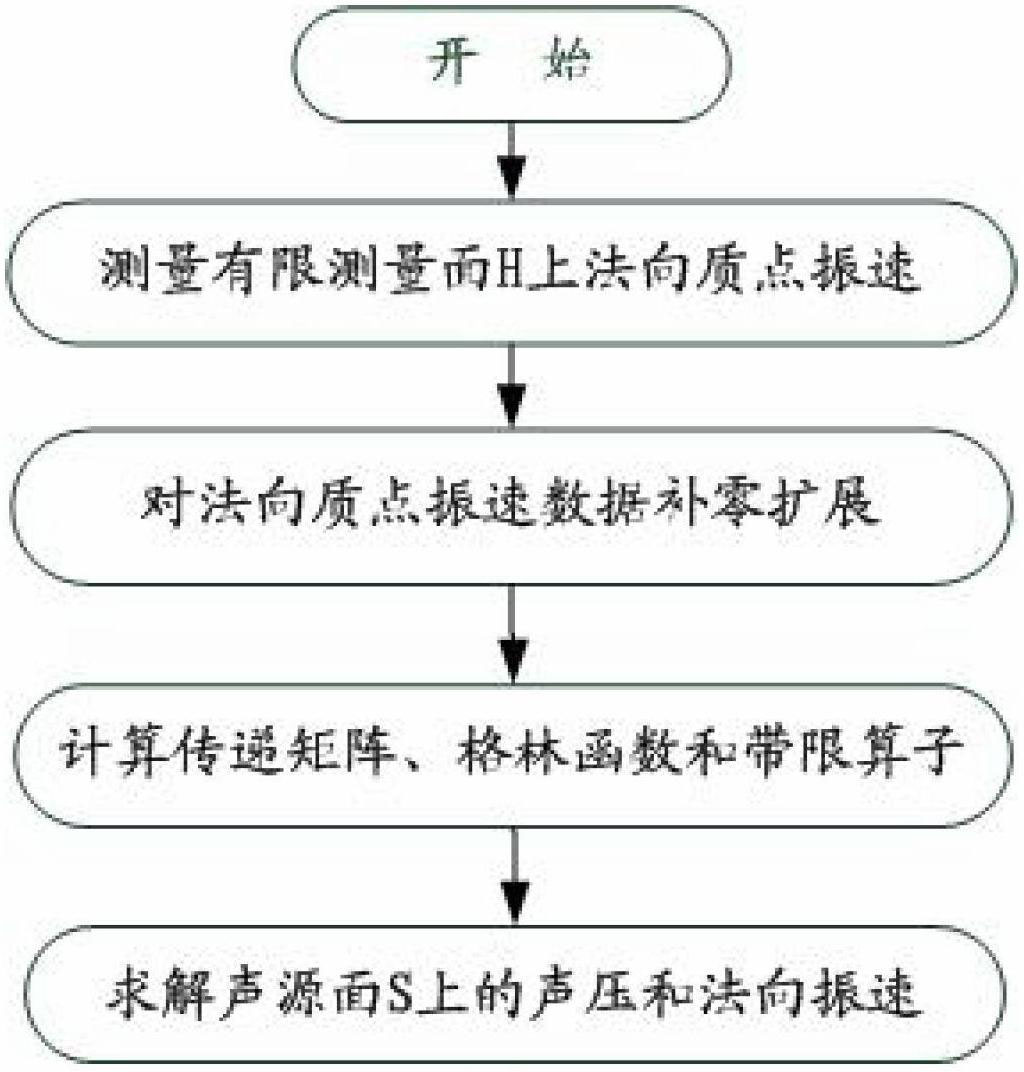
[0102] see figure 1 , in this embodiment, the distance from the sound source d is the measurement surface H, the measurement surface H can be obtained by zero-filling and extrapolation, and the measurement surface H+ can be obtained. The measurement points are distributed in a grid pattern on the measurement surface, and the distance between adjacent grid points The distance is less than half a wavelength.
[0103] The specific steps are:
[0104] a. Use single or multiple particle velocity sensors to scan on the measurement surface or use scanning sampling, and use a particle velocity sensor array to take a snapshot on the measurement surface to obtain normal particle velocity information on the measurement surface H;
[0105] b. Add zero to the normal particle vibration velocity on the measurement surface H to obtain the normal particle vibration velocity on t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com