Equalizing device and equalizing method in transmission diversity mode of LTE (long term evolution) system
A technology of transmit diversity and equalization device, applied in space transmit diversity, baseband system components, diversity/multi-antenna systems, etc., and can solve problems such as residual interference and system performance degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
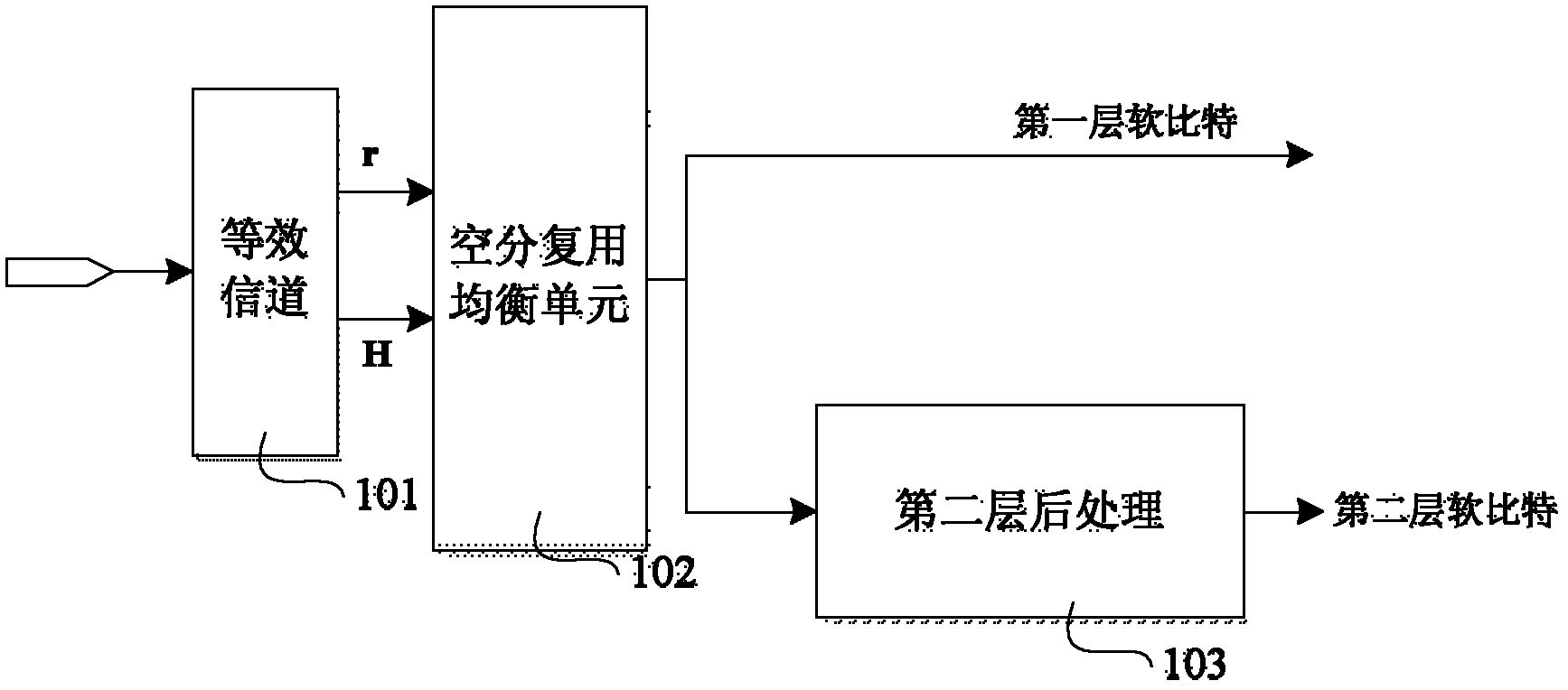
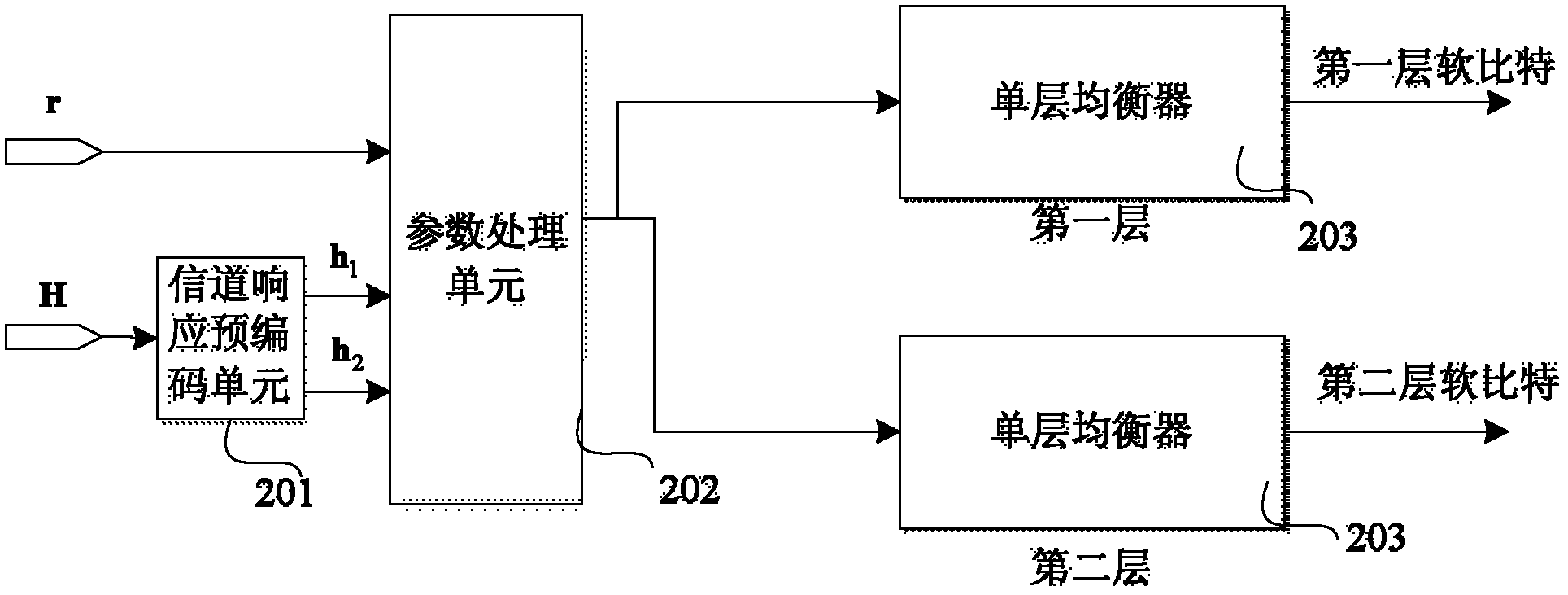
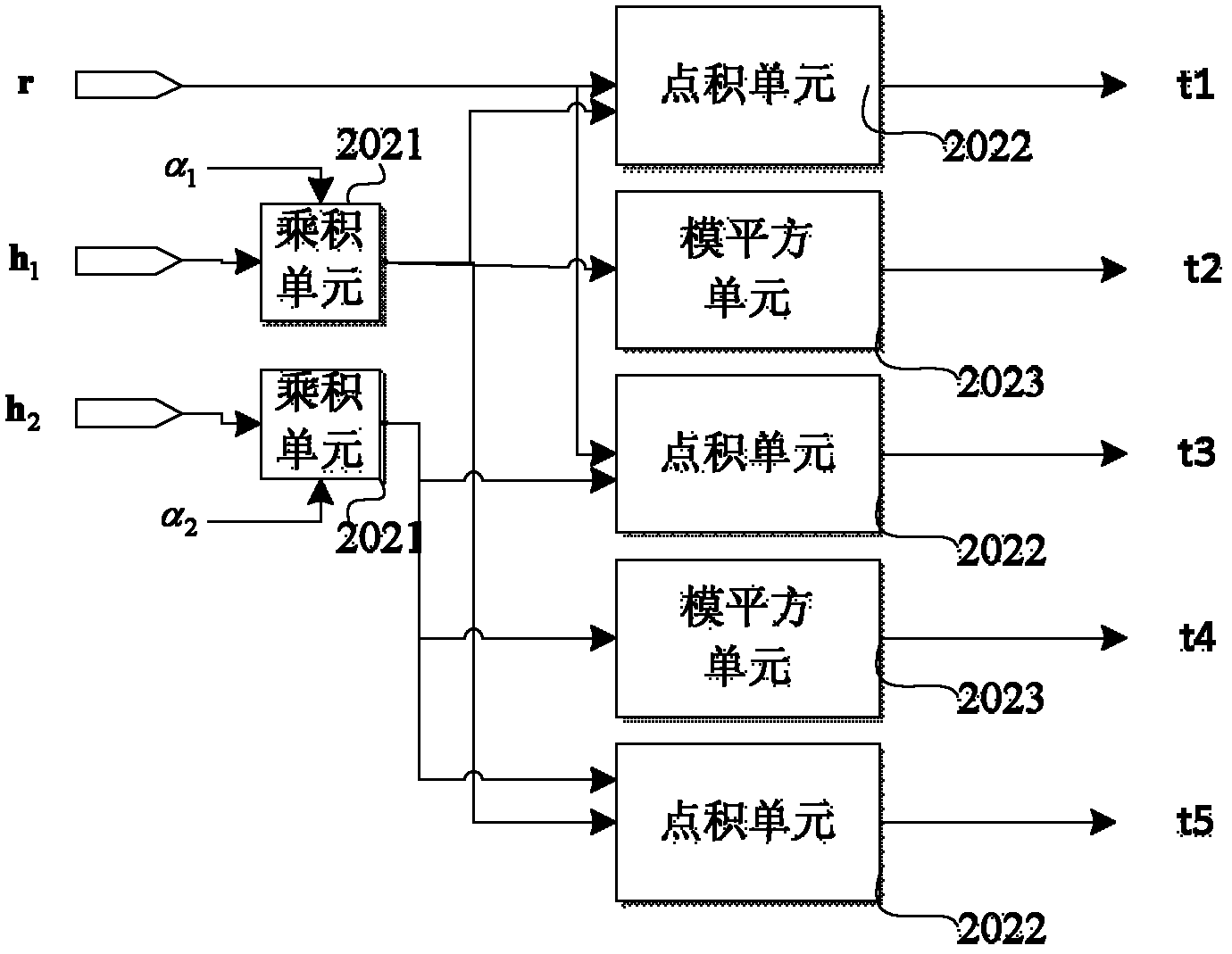
[0092] See attached figure 1 , In order to be applied in the transmit diversity mode of the long-term evolution LTE system, the structure diagram of an equalization device disclosed in the first embodiment of the present invention mainly includes: an equivalent channel unit 101, a space division multiplexing equalization unit 102, and a second layer processing Unit 103.
[0093] in figure 1 In the equivalent channel unit 101, based on the number of transmitting antennas and receiving antennas, the receiving antennas construct equivalent channels in pairs according to the two-antenna transmit diversity mode.
[0094] Assume that NR is the number of receiving antennas at the receiving end of the system, NT is the number of transmitting antennas at the transmitting end of the system, and NR and NT take a number greater than or equal to 1.
[0095] Take a group of transmitting antennas i and j as an example for description. The corresponding matrix structure of the data signal r sent ...
example 1
[0109] When there are two transmitting antennas and N receiving antennas, N is greater than or equal to 1.
[0110] The equivalent channel unit 101 constructs an equivalent channel based on two transmitting antennas and N receiving antennas, and the N receiving antennas receive the data signal r sent by the two receiving antennas as shown in equation (3).
[0111] r = r 0 ( 0 ) conj ( r 0 ( 1 ) ) · · · r N - 1 ( 0 ) conj ( r N - 1 ( 1 ) ) - - - ( 3 )
[0112] Among them, r(0) represents the signal of the 0th subcarrier, and r(n) represents the signal of the nth subcarrier. The equivalent channel response H corresponding to each group of equivalent channels is shown in equation (4).
[0113] H = h 00 ( 0 ) - h 01 ( 0 ) conj ( h 01 ( 1 ) ) conj ( h 00 ( 1 ) ) ...
example 2
[0116] When there are two transmitting antennas and the receiving antenna is a single antenna:
[0117] The equivalent channel unit 101 constructs an equivalent channel based on two transmitting antennas and a single antenna for receiving.
[0118] The data signal r received by the single antenna is shown in equation (5).
[0119] r = r ( 0 ) conj ( r ( 1 ) ) - - - ( 5 )
[0120] The corresponding equivalent channel response H is shown in equation (6).
[0121] H = h 00 ( 0 ) - h 01 ( 0 ) conj ( h 01 ( 1 ) ) conj ( h 00 ( 1 ) ) - - - ( 6 )
[0122] Among them, r(0) represents the signal of the 0th subcarrier, r(1) represents the signal of the 1st subcarrier; h 00 (1) Represents the channel response from the 0th transmitting antenna to a single antenna on the first subcarrier; h 00 (0) represents the channel response ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com