Methods and systems for producing granules of biomass in the treatment of wastewater
A technology of biomass particles and biomass, which is applied in energy wastewater treatment, natural water treatment, biological water/sewage treatment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
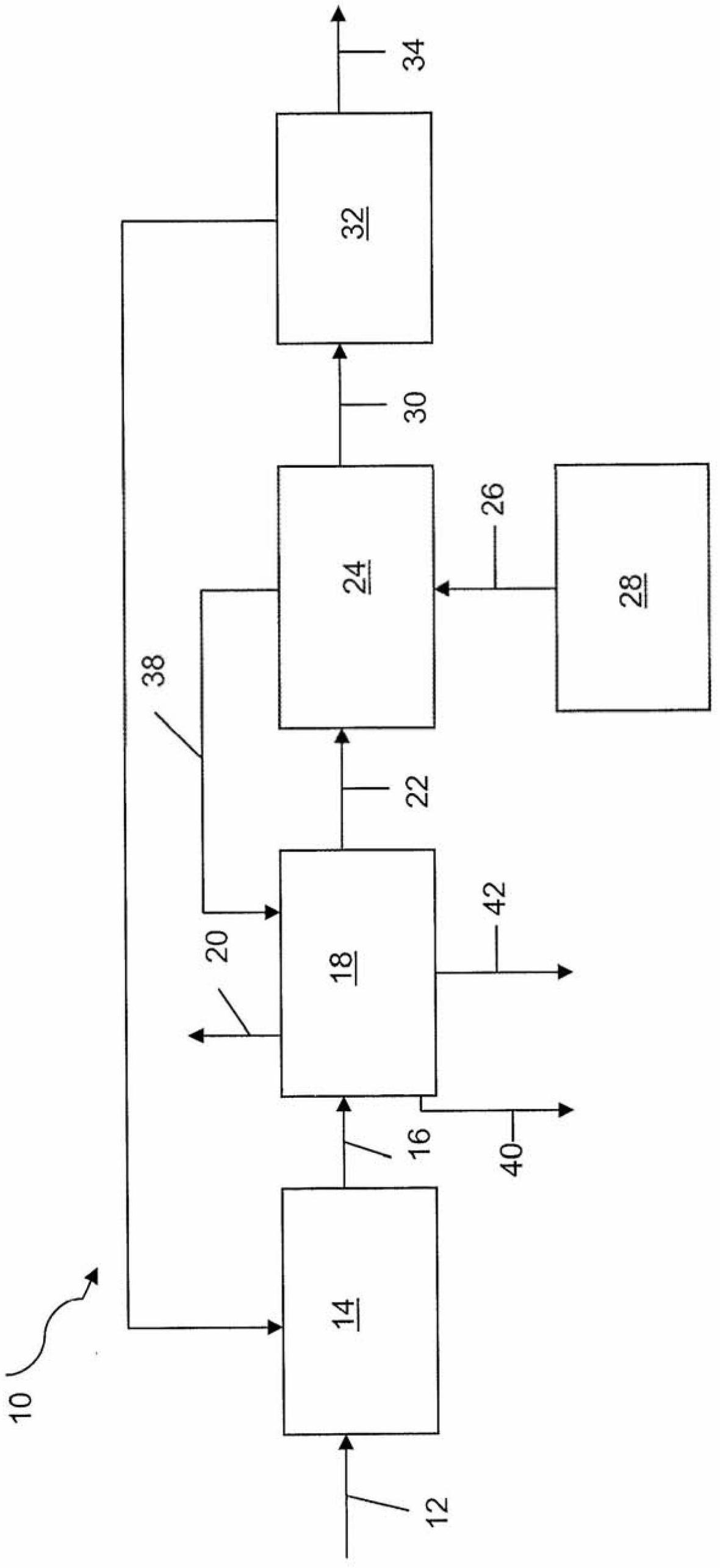
[0036] The method and system of one embodiment of the invention were demonstrated in a laboratory pilot plant. The anaerobic zone was configured as a 10 L upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor (UASB) with overflow recirculation. The reactor was maintained at 38°C and pH 6.8.
[0037] Wastewater streams from a purified terephthalic acid manufacturing process containing varying amounts of TOC were fed to a UASB with an upflow velocity of 2.2 m / hr. A portion of the water withdrawn from the top of the UASB reactor was recirculated and another portion was fed into the aerobic zone configured as three aeration tanks in series. Air is fed into each cell. Spent sludge was recirculated back into the UASB from the bottom of the last aeration tank, and the amount of sludge transferred was calculated as the ratio of recirculated spent activated sludge solids to solids in the UASB. In additional trials to establish baseline growth yields, waste sludge was not transferred back to the U...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The method and system of one embodiment of the invention were also demonstrated in a commercial scale pilot plant. The anaerobic zone was configured as a Biothane EGSB reactor with a reactor volume of 851 cubic meters. The reactor was maintained at 38°C and a pH range of 6.8 to 7.0.
[0043] Wastewater streams from a purified terephthalic acid manufacturing process containing various amounts of TOC were fed to a reactor with an upflow velocity of 2.6 m / hr. A portion of the water drawn from the top of the reactor is recirculated and another portion is fed to the aerobic tank. The spent sludge was transferred from the bottom of the aeration tank back into the anaerobic reactor and was calculated as the ratio of recirculated spent activated sludge solids to solids in the anaerobic reactor. In two additional baseline experiments, no waste sludge was transferred back to the anaerobic reactor.
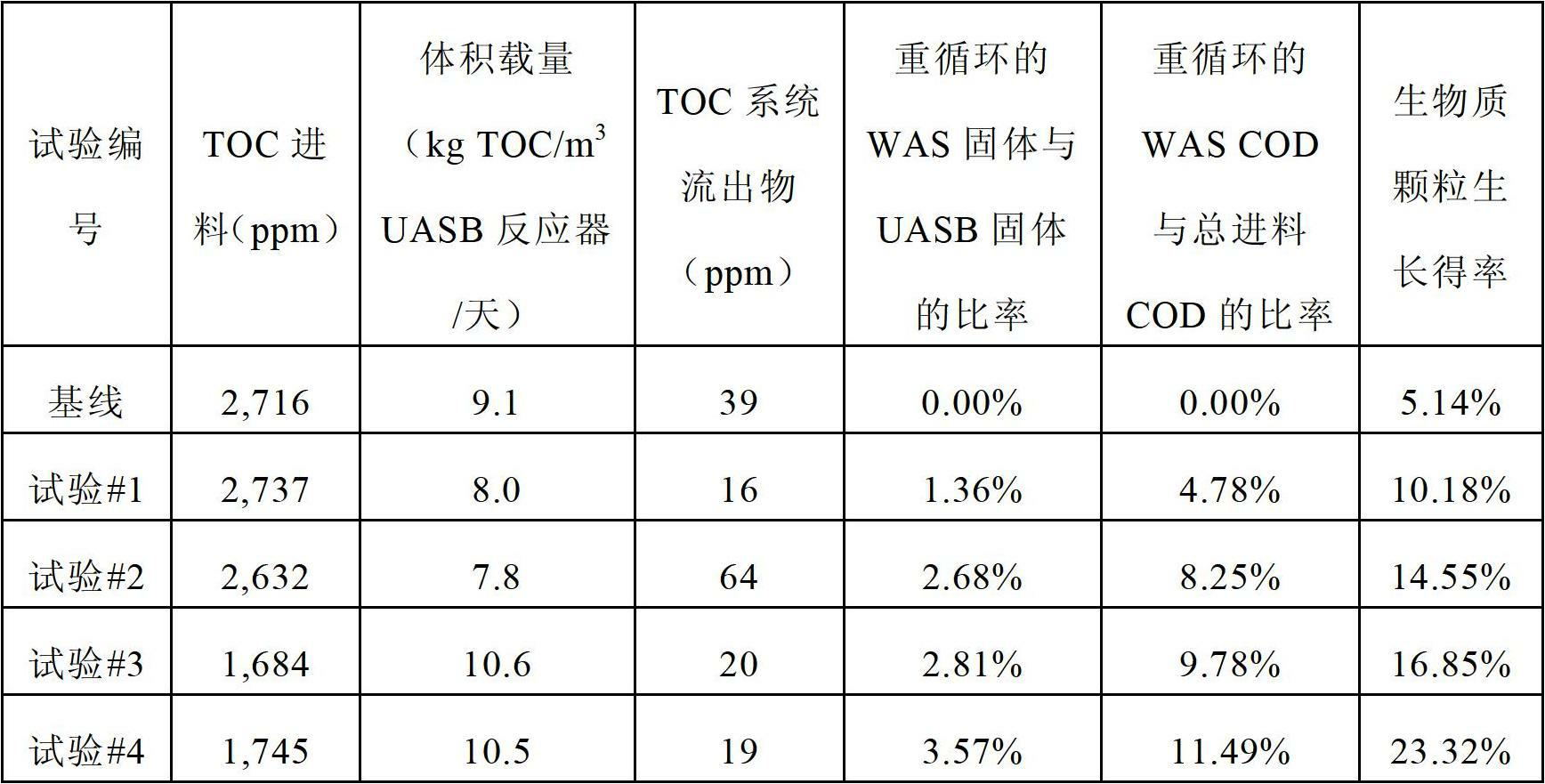
[0044] The results shown in Table 2 demonstrate that the process of the presen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com