Ladle working liner and preparation method thereof
A technology of working lining and ladle, applied in metal processing equipment, manufacturing tools, casting equipment, etc., can solve the problems of iron infiltration in brick joints, easily damaged working lining bricks, and asynchronous working lining life.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
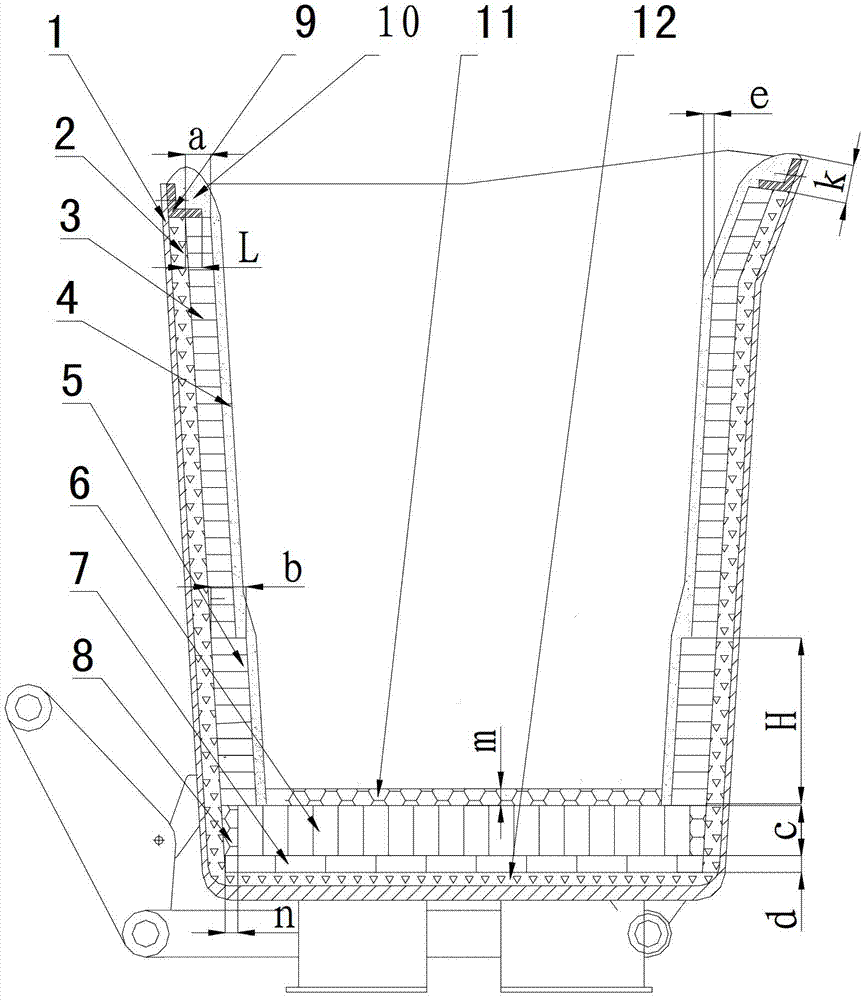
[0052] like figure 1As shown, a ladle working lining, the ladle working lining is installed in the ladle shell 1, the ladle wall permanent lining 2 and the ladle bottom permanent lining 12, the ladle working lining is laid on the inner wall of the ladle shell 1 and the cladding wall is permanently Lining 2, ladle bottom permanent lining 12 is laid on the bottom of ladle shell 1. Including flat-laying refractory bricks for the bottom-covering working lining 7, vertical-laying refractory bricks for the bottom-covering working lining 6, castables for the bottom-covering working lining 11, working lining refractory bricks for the iron flow impact area of the lower part of the wrapping wall, and 5 working lining refractory bricks for the upper part of the wrapping wall and wall covering smear 4; it is characterized in that, on the bottom of the permanent lining 12, from bottom to top, it is the bottom working lining flat laying refractory brick 7, the bottom working lining vertic...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Others are the same as embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0084] The ladle working lining also includes a ladle edge pressing plate 9 located on the upper part of the ladle shell 1; a ladle edge smear layer 10 is applied on the upper part of the ladle edge pressing plate (9).
[0085] The working lining of the molten iron ladle is 30mm thicker than the working lining refractory brick 3 of the upper part of the ladle wall in the iron flow impact zone of the lower part of the ladle wall.
[0086] The thickness d of the flat-laying refractory brick 7 for the bottom-covering working lining is 120 mm, the thickness c of the vertical-laying refractory brick 6 for the bottom-covering working lining is 300 mm, and the thickness m of the bottom-covering working lining castable 11 is 60 mm.
[0087] The thickness a of the working lining refractory brick 3 on the upper part of the cladding wall is 140 mm, and the thickness b of the working lining refractory brick 5 in the impact are...
Embodiment 3
[0107] Others are the same as embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0108] The working lining of the molten iron ladle is 25mm thicker than the working lining refractory brick 3 of the upper part of the ladle wall in the iron flow impact area of the lower part of the ladle wall.
[0109] The thickness d of the flat-laying refractory brick 7 for the bottom-covering working lining is 100mm, the thickness c of the vertical-laying refractory brick 6 for the bottom-covering working lining is 280mm, and the thickness m of the bottom-covering working lining castable 11 is 90mm.
[0110] The thickness a of the working lining refractory brick 3 on the upper part of the cladding wall is 130 mm, and the thickness b of the working lining refractory brick 5 in the iron flow impact area on the lower part of the cladding wall is 155 mm.
[0111] The coating material layer 4 thickness e of the cladding wall is 20mm
[0112] The thickness k of the coating material layer 10 along the package is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bulk density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com