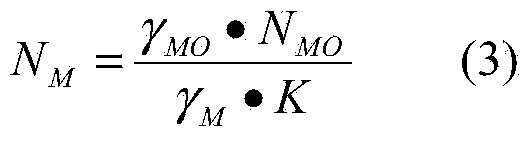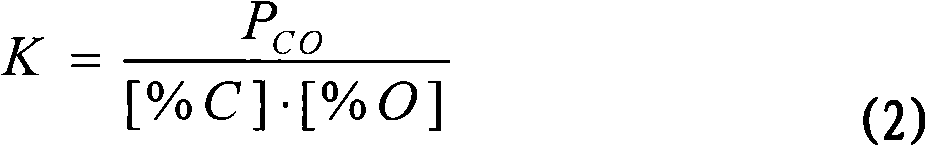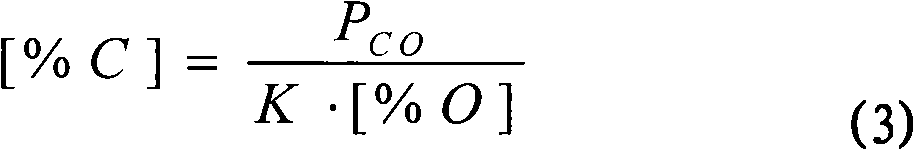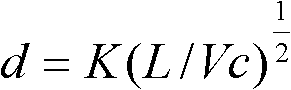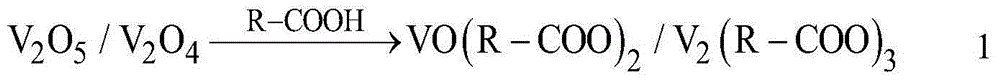Patents
Literature
1287 results about "Ferrous metallurgy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ferrous metallurgy is the metallurgy of iron and its alloys. It began far back in prehistory. The earliest surviving iron artifacts, from the 4th millennium BC in Egypt, were made from meteoritic iron-nickel. It is not known when or where the smelting of iron from ores began, but by the end of the 2nd millennium BC iron was being produced from iron ores from Sub-Saharan Africa to China. The use of wrought iron (worked iron) was known by the 1st millennium BC, and its spread marked the Iron Age. During the medieval period, means were found in Europe of producing wrought iron from cast iron (in this context known as pig iron) using finery forges. For all these processes, charcoal was required as fuel.
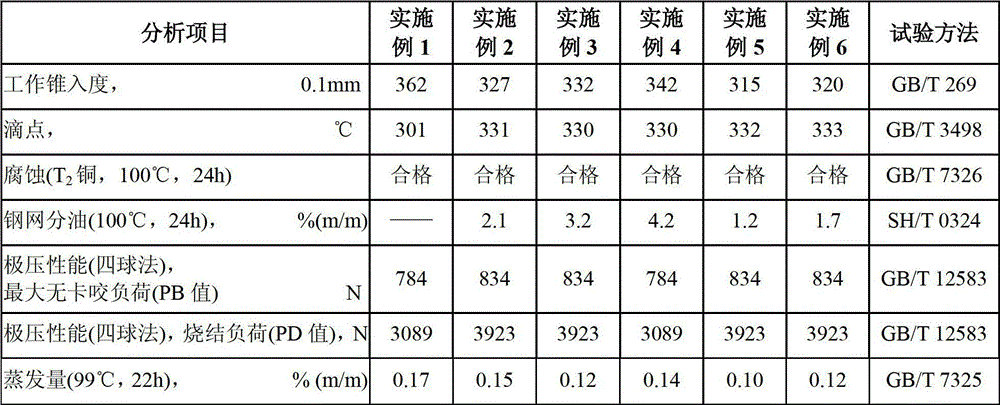
High-temperature-resistant extreme pressure type lubricating grease composition and preparation method
The invention relates to a high-temperature-resistant extreme pressure type lubricating grease composition and a preparation method of the high-temperature-resistant extreme pressure type lubricating grease composition. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: mixing high-base-value calcium naphthenate, high-base-value sulfoacid calcium, and 35 to 65% of base oil; agitating; then adding a transforming agent; heating to reach 75 to 105 DEG C; maintaining the temperature for 40 to 120 minutes until the materials are thick; continuously heating the material until the temperature reaches more than 200 DEG C; removing the water completely, wherein the rest base oil is added during heating; continuously heating the materials until the temperature reaches 220 to 240 DEG C; agitating for 5 to 30 minutes at constant temperature until the materials are thick; and cooling and homogenizing to obtain the product as requirements. The lubricating grease prepared by the preparation method is high in comprehensive performance, excellent in high-temperature resistance, and high in extreme-pressure wear resistance, and can be used for lubricating high-temperature equipment with high load; and the requirements on use in high-temperature and high-load lubricating situations in the ferrous metallurgy industry can be met.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
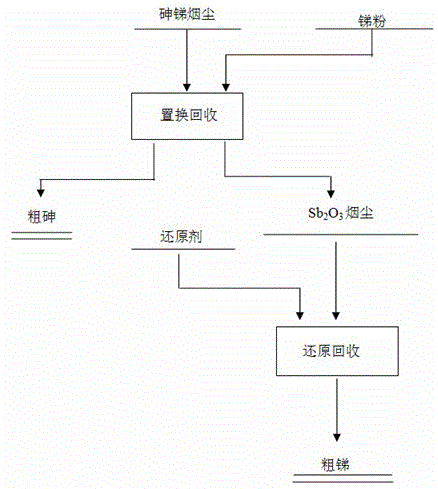
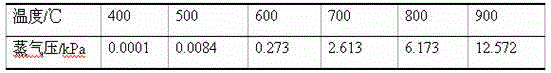
Method for processing arsenic-antimony fume by using replacement-reduction method so as to recover arsenic and antimony
ActiveCN103602835AReduce economic costsLow temperature and easy economic costProcess efficiency improvementDisplacement reactionsAntimony trioxide
The invention relates to a method for processing arsenic-antimony fume by using a replacement-reduction method so as to recover arsenic and antimony, belonging to the field of non-ferrous metallurgy technologies. The method comprises the steps of recovering arsenic by using a replacement method firstly: adding antimony powder into arsenic-antimony fume, and then simultaneously carrying out a displacement reaction on the obtained mixture for 30-120 min at the temperature of 500-800 DEG C and collecting antimony trioxide volatile fume, so that after the reaction is completed, crude arsenic is obtained; recovering antimony by using a reduction method: adding a reducing agent into the antimony trioxide volatile fume obtained in the last step, and then carrying out a reduction reaction on the obtained mixture for 30-180 min at the temperature of 800-1000 DEG C, so that crude antimony is obtained finally, wherein the mass ratio of antimony trioxide to the reducing agent is 10:(1-3). According to the invention, by fully using the characteristic that antimony trioxide is easily volatile at low temperature, arsenic in arsenic-antimony fume is replaced with antimony powder, and antimony trioxide is volatilized, so that crude arsenic is obtained, and then antimony trioxide is subjected to reduction smelting so as to obtain crude antimony, therefore, the method disclosed by the invention is simple in process and has better industrial application prospects.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Titanium Base Alloy
The invention refers to the non-ferrous metallurgy, i.e. to the creation of the modern titanium alloys, having the high genericity. Titanium-base alloy contains aluminum, vanadium, molybdenum, chromium, iron, zirconium, oxygen and nitrogen. Herewith the components of the alloy have the following ratio by weight %; aluminun—4.0-6.0; vanadium—4.5-6.0; molybdenum—4.5-6.0; chromium—2.0-3.6; iron—0.2-0.5; zirconium—0.1-less than 0.7; oxygen—0.2 max; nitrogen—0.05 max; titanium—balance. Technical result—creation of the titanium alloy with the required strength and plastic properties. The alloy may be used to produce the wide range of the products including the large-size forgings and die-forgings as well as semiproducts of small section, such as bars and plates up to 75 mm thick.
Owner:VSMPO AVISMA CORP
Filter element for filtering high-temperature dust and purifying gas as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102008857AOvercome strengthOvercome shockDispersed particle filtrationChemical industryProduct gas
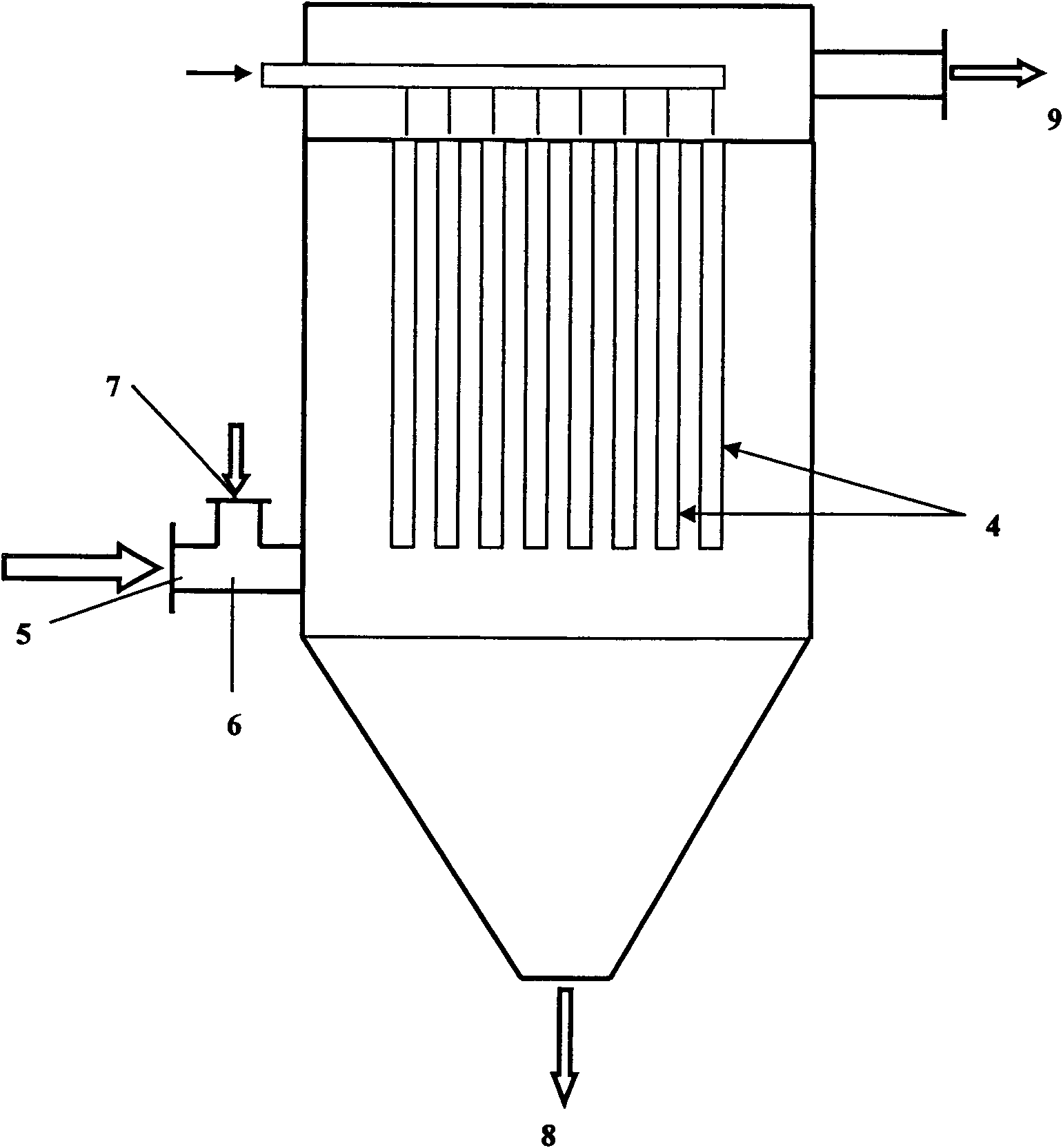
The invention provides a filter element for filtering high-temperature dust and purifying gas as well as a preparation method and application thereof, wherein the filter element comprises a support body and a filtering membrane which covers the surface of the support body; a denitrification catalyst is loaded in a pore space of the support body; and the filter element can be prepared by preparingthe support body first, preparing the filtering membrane on the support body by adopting a spraying method and finally loading the denitrification catalyst in the pore space of the support body by using an impregnating method. The filter element is combined into a filter element assembly and then arranged in a filter container which can be used for filtering the high-temperature dust and purifying the gas in the fields of thermal power, refuse incineration, ferrous metallurgy or petroleum chemical industry. The filter element overcomes the defects that the ceramic filtering membranes have lowbreak strength, poor heat shock resistance and higher assembly difficulty and more difficult high-temperature sealing connection of a membrane pipe and can remarkably improve the filter efficiency and the filter precision and prolong the service life.
Owner:苏州海普过滤分离科技有限公司
Method for controlling center porosity of large section heavy rail steel casting blank
The invention relates to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy, in particular to a method for controlling the center porosity of a large section heavy rail steel casting blank. The method comprises the following steps of controlling the superheat degree of medium-package molten steel; controlling the pulling speed in the normal pouring process; pressing down the final solidification end in the pouring process; setting the stirring strength and stirring frequency of electromagnetic stirring of a crystallizer; setting the stirring strength and stirring frequency of electromagnetic stirring at the final solidification end; controlling the cooling water yield and the secondary cooling specific water yield of the crystallizer. The center porosity of the large section heavy rail steel casting blank produced by adopting the method can be effectively controlled, and the remaining internal quality of the casting blank can be effectively guaranteed.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
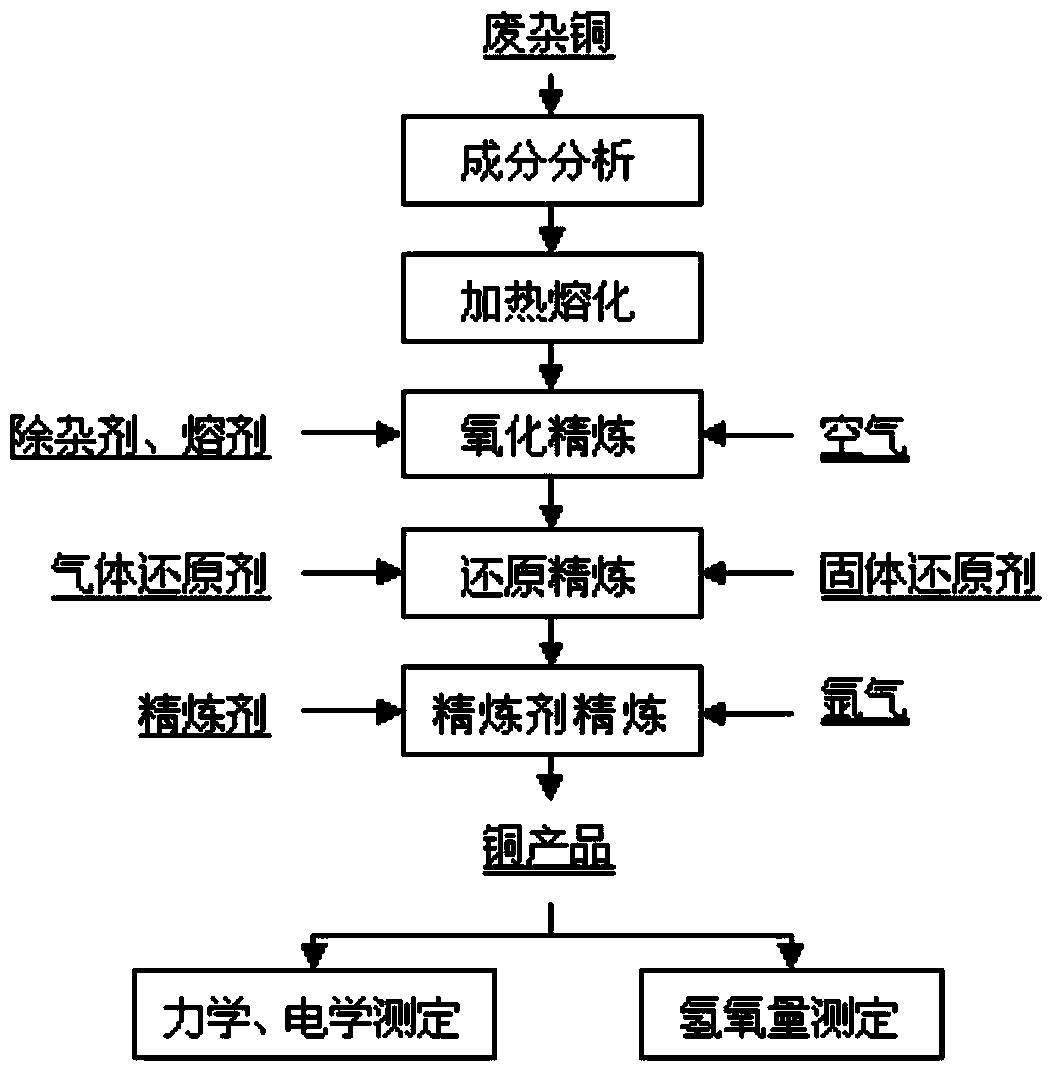
Method for directly producing high-purity oxygen-free copper by pyrogenic process continuous refining of scrap copper
ActiveCN103725897AOptimizing Process ParametersReduce manufacturing costProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisCopper wire
The invention relates to a method for directly producing high-purity oxygen-free copper by pyrogenic process continuous refining of scrap copper, and belongs to the technical field of non-ferrous metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: by taking scrap copper as a raw material; analyzing the component characteristics of each batch of raw material, and then preparing into a mixture, wherein the mass percent of a copper element in the mixture is greater than or equal to 93%; adding metaphosphate or phosphorus pentoxide and flux to the mixture; refining by oxidation; stewing and drossing after oxidation is finished, and then orderly carrying out reduction refining and refining agent refining under an agitation state, so as to obtain the high-purity oxygen-free copper of which the copper content is greater than or equal to 99.95% and the oxygen content is smaller than 0.003%, wherein the electrical resistivity of the obtained copper wire after drawing is below 0.017241omega / (mm), and the relative electrical conductivity is over 100% of International annealed copper standard (IACS). The method is strong in flexibility, significant in refining effect, and applicable to different components of scrap copper materials; the scrap copper can be used for directly making a rod after being refined. Compared with the traditional pyrogenic process smelting-electrolytic refining-copper cathode purification process, the method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the flow is shortened, the cost is reduced, the energy is saved, and continuous operation is achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
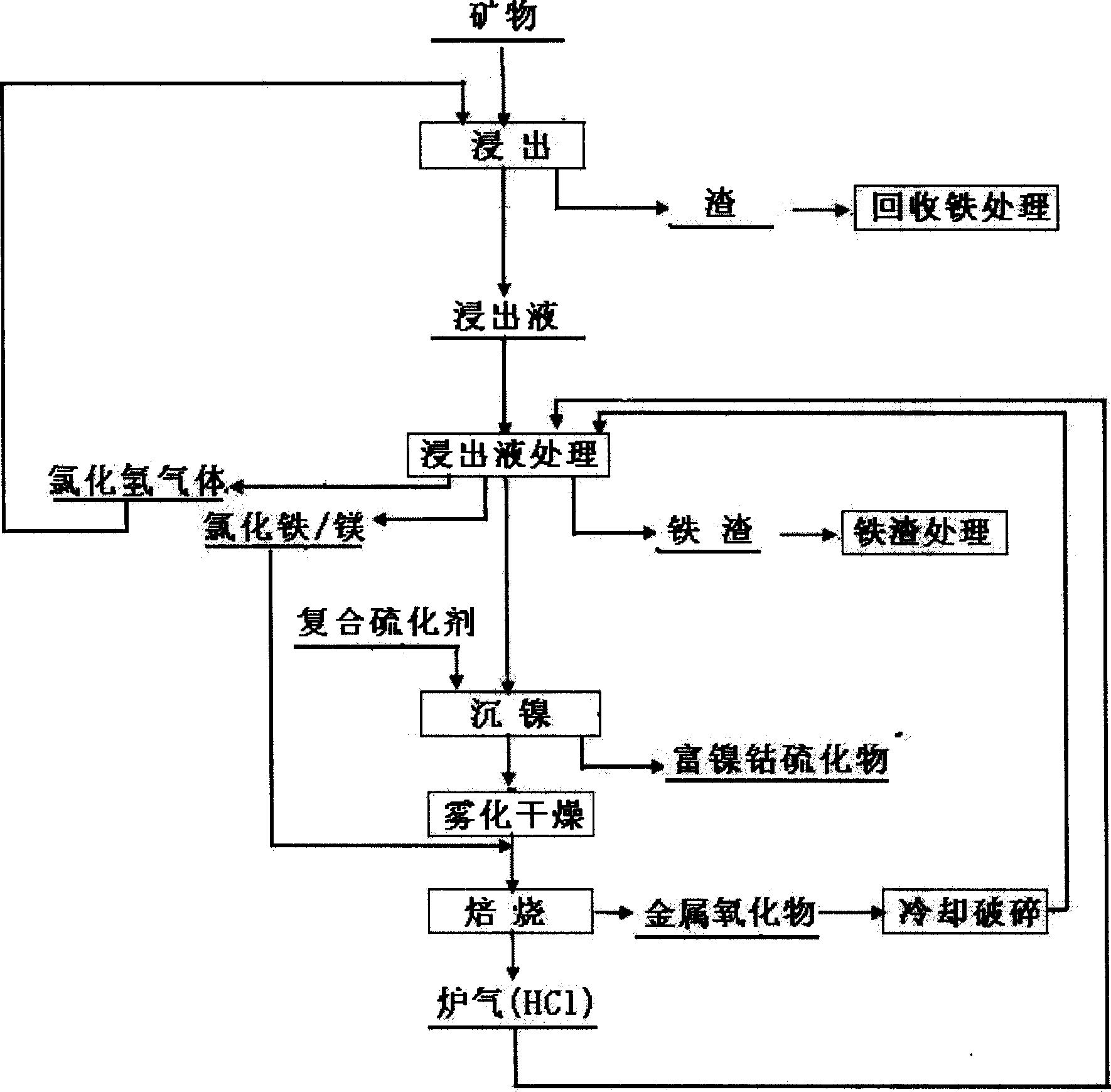
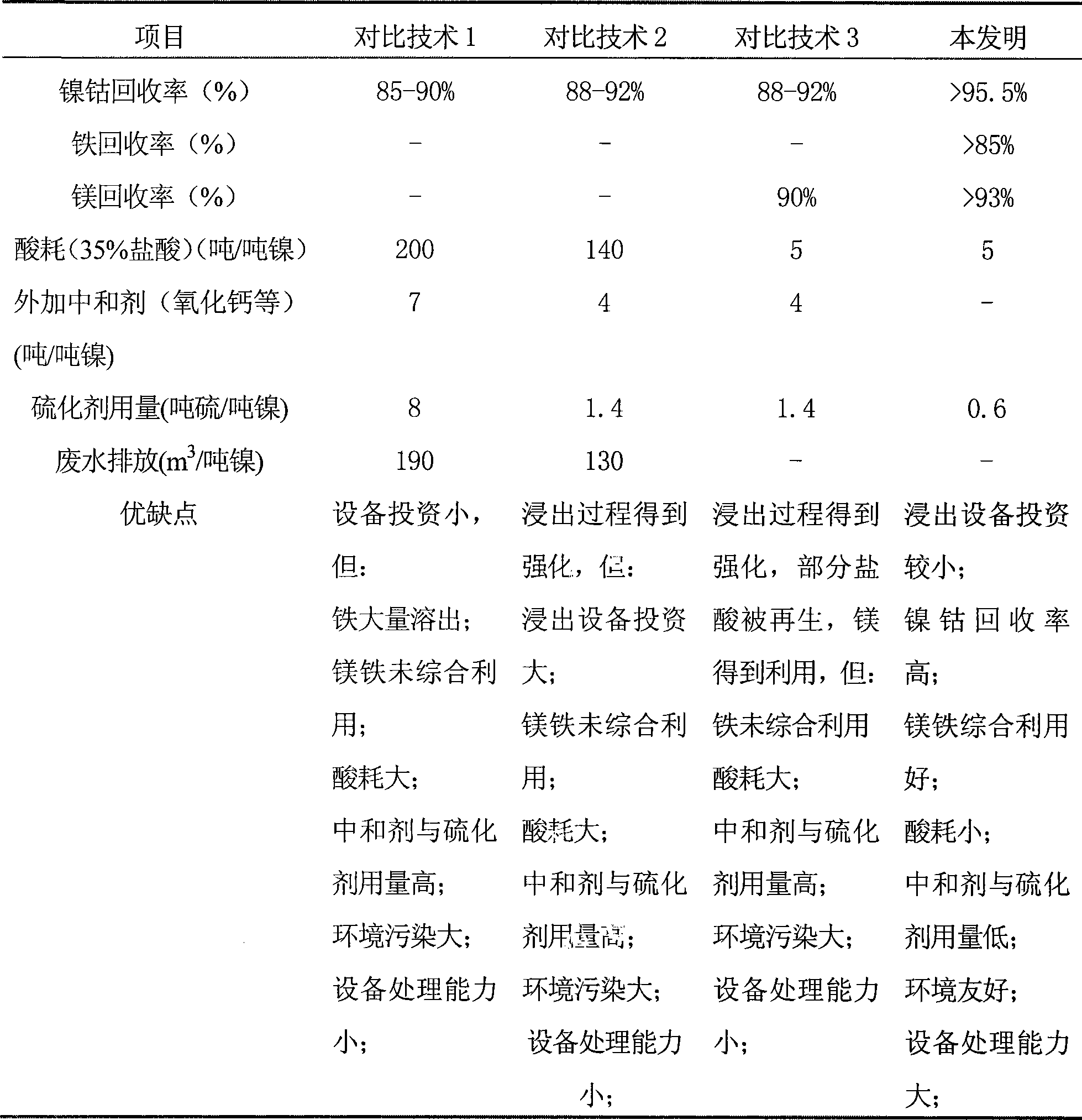
Method for extracting valuable metals from laterite nickel mine with hydrochloric acid full-closed circulation method
ActiveCN101509072AImprove leaching efficiencyIncrease profitMagnetic separationProcess efficiency improvementMetal chlorideWastewater
A method for extracting valuable metals from laterite nickel ore on the basis of the hydrochloric acid fully-closed circulation method belongs to the field of non-ferrous metallurgy. Crushed laterite nickel minerals are taken as raw material and the technique comprises the following technological steps: chlorination-leaching; recovering iron (Fe) from leaching residue; extracting nickel (Ni) and cobalt (Co); spray-drying the mother liquor; and calcining. By leaching the laterite nickel minerals with a mixed solution of hydrochloric acid and metal chlorides as a leaching agent under the proper conditions of heating and pressurizing and further precipitating nickel and cobalt with a compound vulcanizing agent, the overall recovery rate of nickel and cobalt is high; the closed circulation of hydrochloric acid is realized while processing the laterite nickel minerals with water and hydrochloric acid, therefore, the method is environment-friendly by realizing the zero discharge of waste water; comprehensive utilization of the resources, such as Ni, Co, Fe and Mg, in the laterite nickel ore can be realized; and the resources can be efficiently utilized and the clean production can be realized by recovering and reutilizing the waste heat and the residue acid during the production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for producing aluminum anode by using waste cathode carbon block of aluminum cell
InactiveCN102146570AAchieving processing powerRealize comprehensive utilizationAluminum anodeElectrolysis
The invention relates to a method for producing an aluminum anode by using a waste cathode carbon block of an aluminum cell, belonging to the technical field of non-ferrous metallurgy environmental protection. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) crushing the waste cathode carbon block of the aluminum cell and sorting a steel rod, a refractory material, an electrolyte and the like in the waste cathode carbon block; (2) performing coarse crushing on the sorted waste cathode carbon block of the aluminum cell; (3) grinding into powder less than 0.075 millimeters; (4) separating impurities in the waste cathode carbon block of the aluminum cell by adopting methods including a floatation method, an acid method, an alkali method, an acid-alkali combination method and the like; (5) drying the treated waste cathode carbon block powder of the aluminum cell; (6) mixing according to the formula requirement of aluminum anode production; and (7) entering an aluminum anode production system and mixing the powder to produce a pre-baked anode. In the method, the waste cathode carbon block of the aluminum cell is taken as mixing powder for the aluminum anode, so that harmless treatment and comprehensive utilization of the waste cathode carbon block of the aluminum cell are realized, the using amount of petroleum coke is reduced, resources are saved, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:王建军
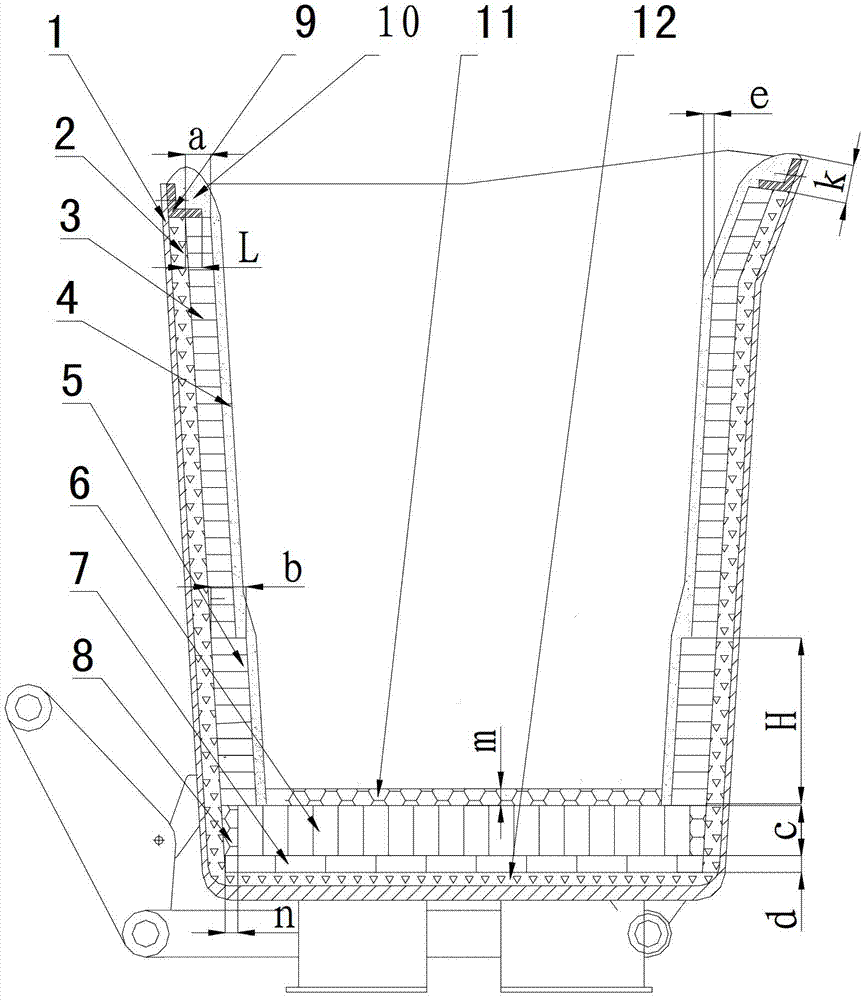
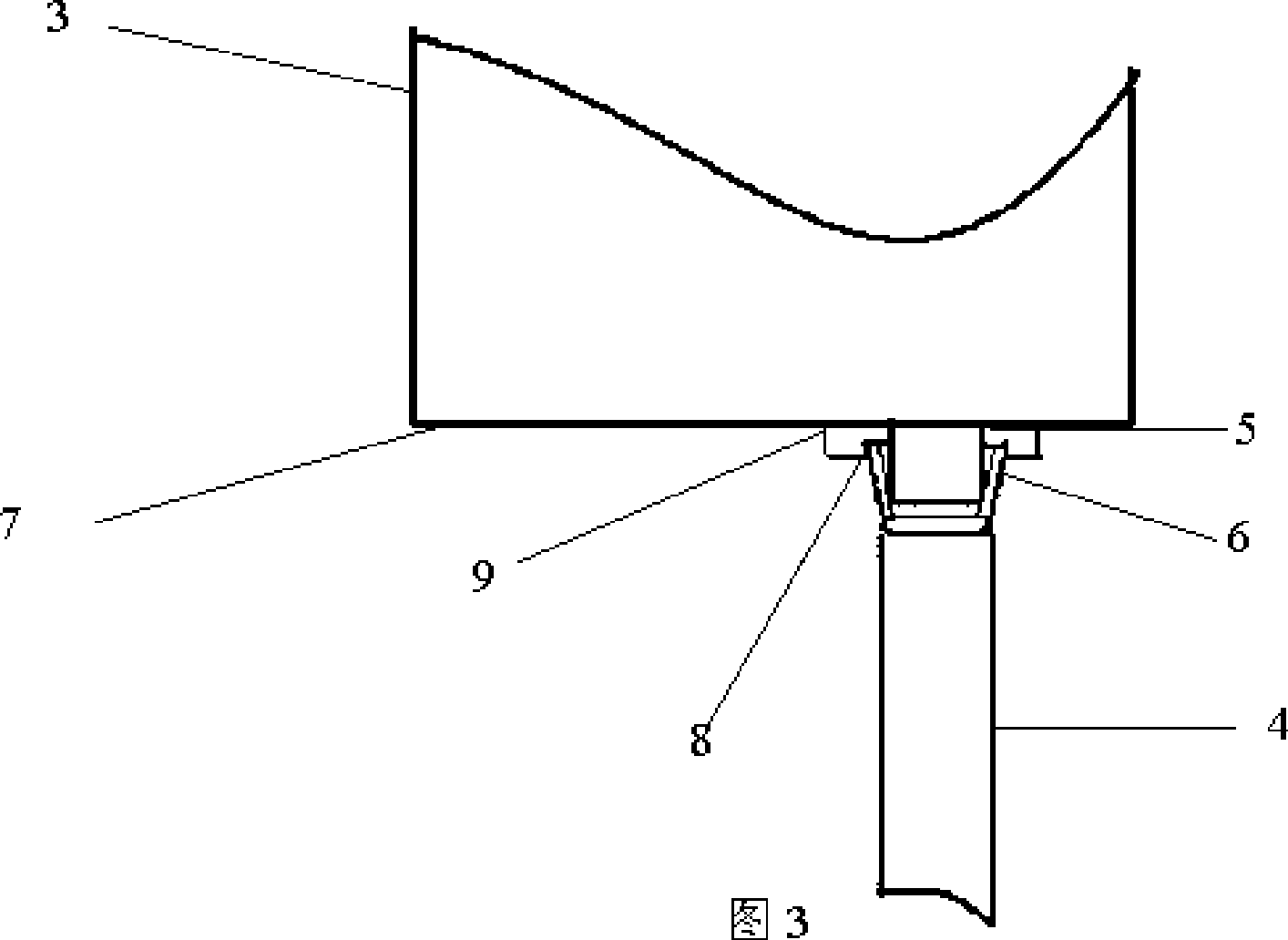
Ladle working liner and preparation method thereof
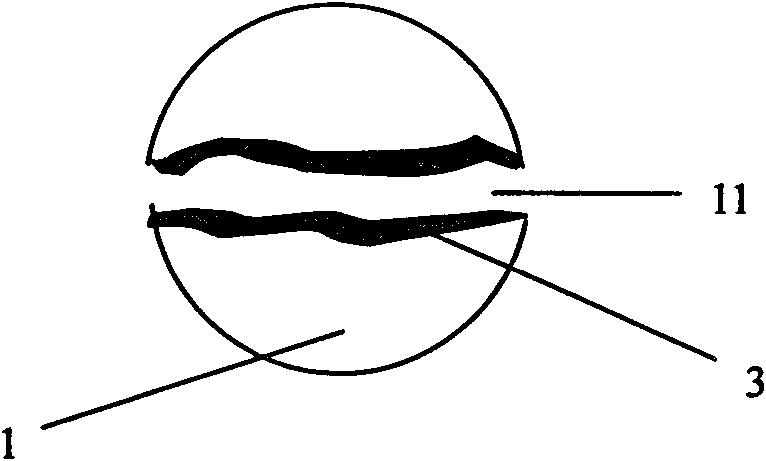
InactiveCN102728828ASolve surface oxidationSolve the iron seepage problemMelt-holding vesselsBrickRefractory
The invention relates to a ladle working liner and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of a ferrous metallurgy ladle process. The ladle working liner is characterized in that a ladle bottom working liner consists of three layers of structures which are ladle bottom working liner flat laid refractory bricks (7), ladle bottom working liner vertical laid refractory bricks (6) and ladle bottom working liner castable (11) from bottom to top in sequence, wherein the iron flow impact region working liner refractory bricks (5) on the lower part of a ladle wall is 20-30 mm thicker than the working liner refractory bricks (3) on the upper part of the ladle wall; a ladle wall coating layer (4) is coated on the outer surfaces of the working liner refractory bricks (3) on the upper part of the ladle wall and the iron flow impact region working liner refractory bricks (5) on the lower part of the ladle wall; and a ladle edge coating layer (10) is coated on the upper part of a ladle edge pressing plate (9). By using the ladle working liner, the service life of the ladle working liner is prolonged by 300-400 heats and the ladle refractory material cost is reduced by over 30 percent on year-on-year basis.
Owner:LAIWU IRON & STEEL GRP
Titanium micro-alloyed 400MPa grade high-strength steel bar and production method thereof
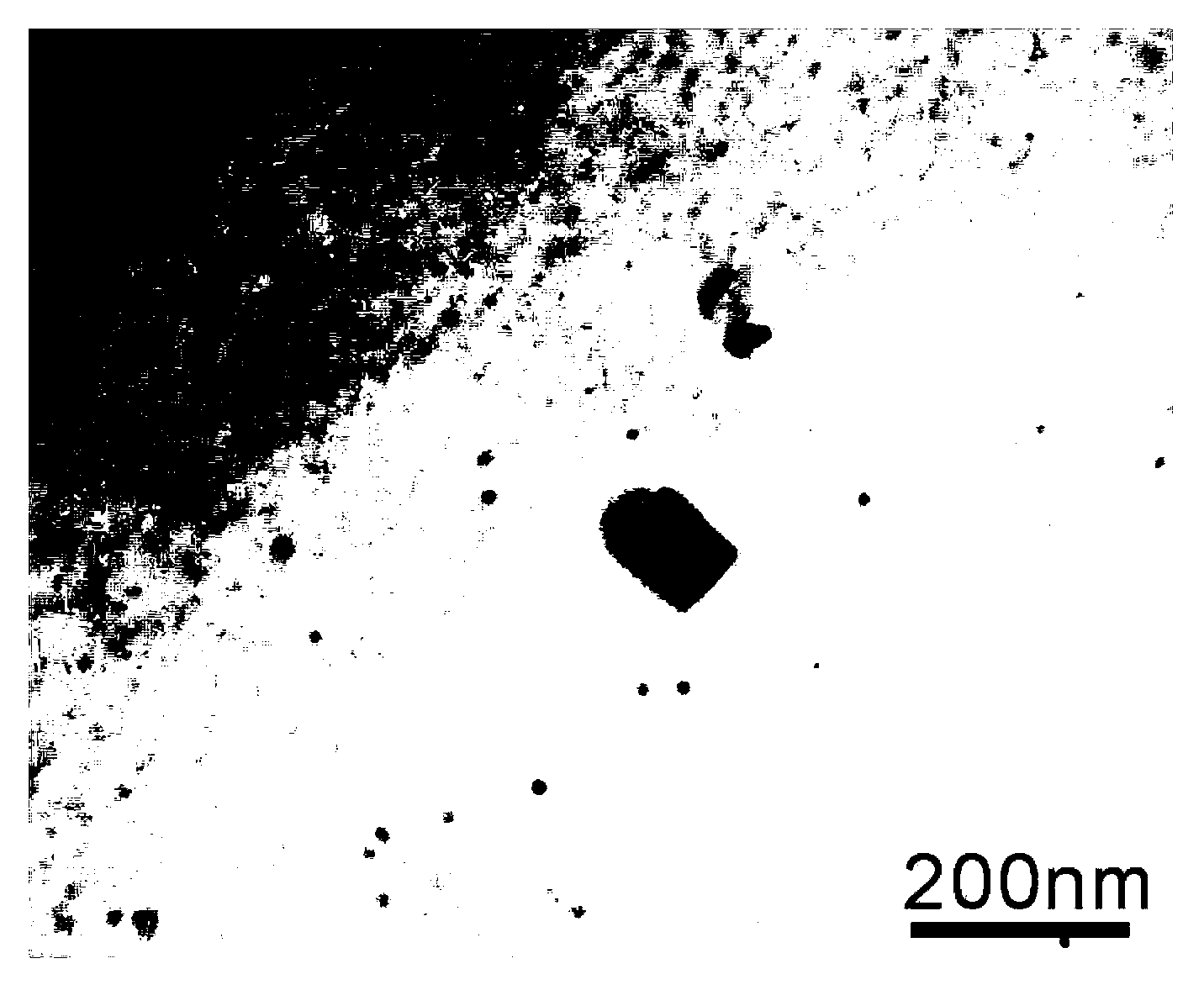
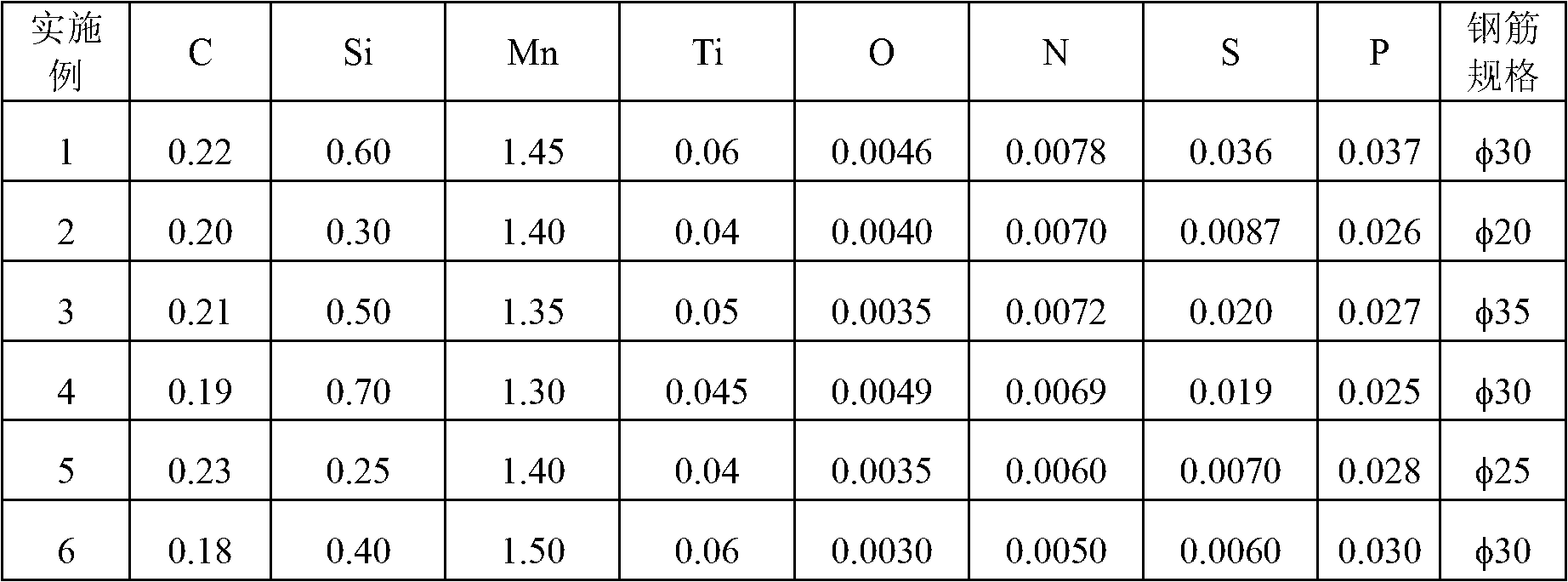
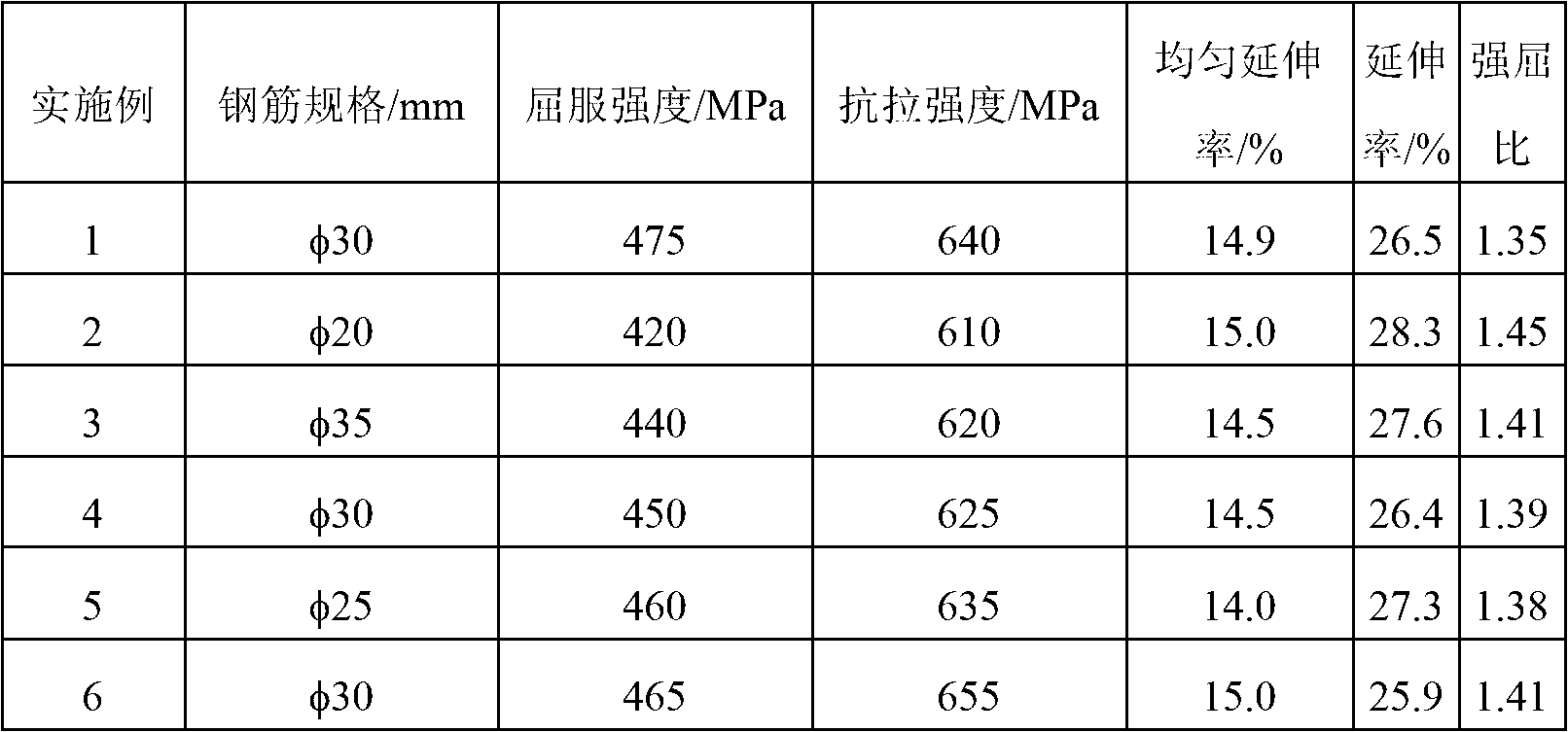
The invention discloses a hot-rolled 400MPa grade high-strength steel bar for reinforced concrete and a production method for the steel bar, and belongs to the technical field of micro-alloying of ferrous metallurgy. The steel in the steel bar comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.16 to 0.25 percent of C, 0.20 to 0.80 percent of Si, 1.20 to 1.50 percent of Mn, 0.02 to 0.06 percent of Ti, less than or equal to 0.01 percent of N, less than or equal to 0.045 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.045 percent of P, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The preparation method for the steel bar comprises the following steps of: a, smelting crude molten steel, tapping, deoxidizing and alloying; b, refining, finely regulating the components, and pouring; and c, hot rolling, wherein titanium is alloyed in the tapping process and after deoxidizing or in the refining process. By using the principle that the titanium plays a role in precipitation and reinforcement in the steel, the mechanical properties of the steel such as yield strength and tensile strength are improved, and the property requirement of the 400MPa grade high-strength steel bar is met..
Owner:PANZHIHUA GANGCHENG GROUP
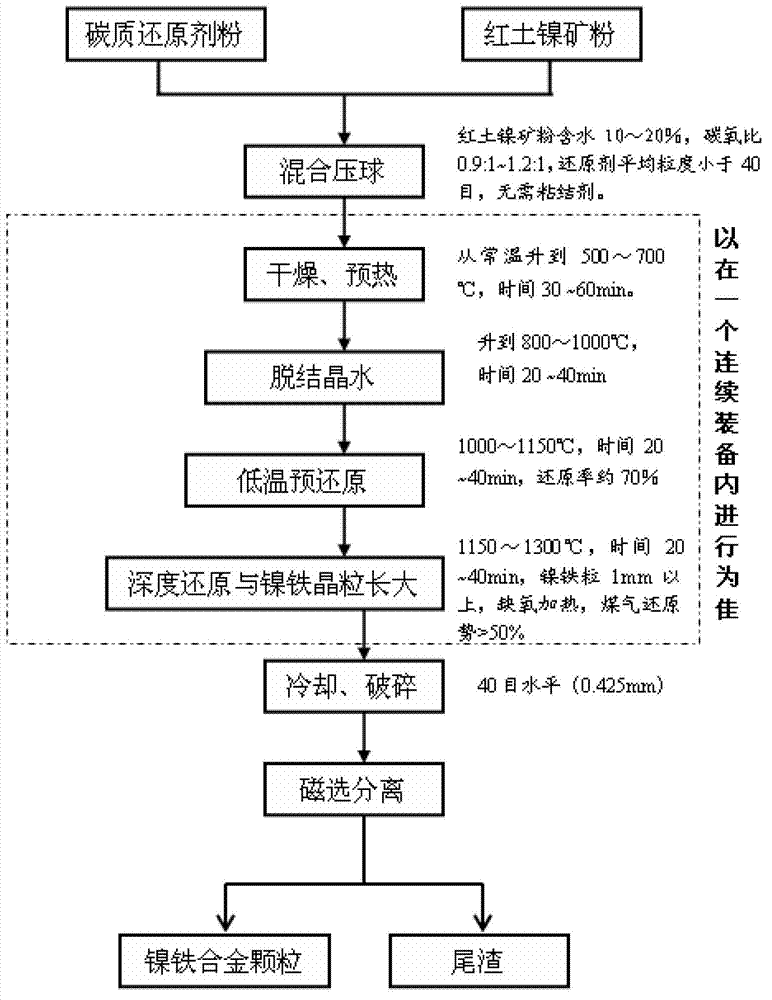
Method for producing nickel-iron alloy by smelting red earth nickel mineral at low temperature
The invention provides a method for producing nickel-iron alloy by smelting a red earth nickel mineral at a low temperature and belongs to the field of preparation of non-ferrous metallurgy. A process flow is as follows: after the red earth nickel mineral and a carbon reducing agent are molded, molding raw materials are subjected to drying, pre-heating and crystallization water removing; pre-reduction, deep reduction and growth of nickel-iron alloy grains are carried out; and after a cooling step, the separation of the nickel-iron alloy and furnace dregs is realized in a magnetic selection manner. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of being low in reaction temperature, low in energy consumption, easy to obtain the high-quality nickel-iron alloy grains, simple in preparation process and low in production cost.
Owner:NEW METALLURGY HI TECH GRP
Method for producing tire cord steel wire by converter billet continuous casting process
ActiveCN102534094AGuaranteed surface qualityLow costManufacturing convertersMetal rolling arrangementsSlagSilicon alloy
The invention relates to a method for producing a tire cord steel wire according to a converter billet continuous casting process and belongs to the technical field of production of tire cord steel wires in the field of ferrous metallurgy. The method comprises the following process steps: desulfurizing by pre-treating molten iron, namely desulfurizing by spraying magnesium on a foundry ladle; smelting by using a converter, namely deoxidizing and alloying, modifying steel ladle slag, re-carburizing the molten iron and adding low-alkalinity pre-melted slag into the steel ladle after tapping; adding ferro-silicon alloy, manganese iron alloy and micronitrogen carburant in the tapping process and re-carburizing; and in the refining process and after the refining is finished, rolling the wire at high speed by adopting a two-stage steel ladle bottom blowing argon system and adopting billet continuous casting of 130mm*130mm or 160mm*160mm. The method has the advantages that: the production isreduced; the production efficiency is improved; and the method is particularly suitable for development and production of tire cord steel products in steel enterprises without big billet or rectangular billet continuous casting and without vacuum treatment equipment.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
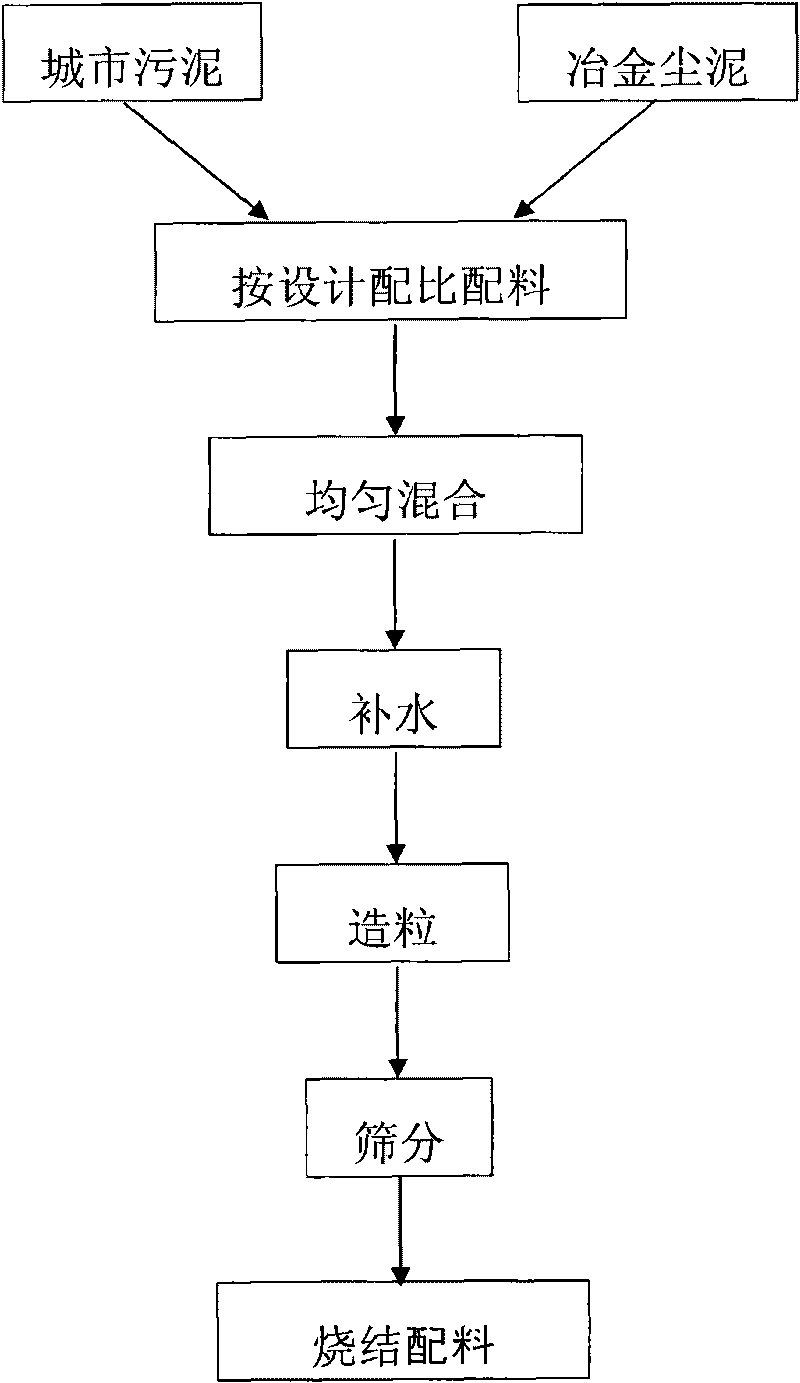
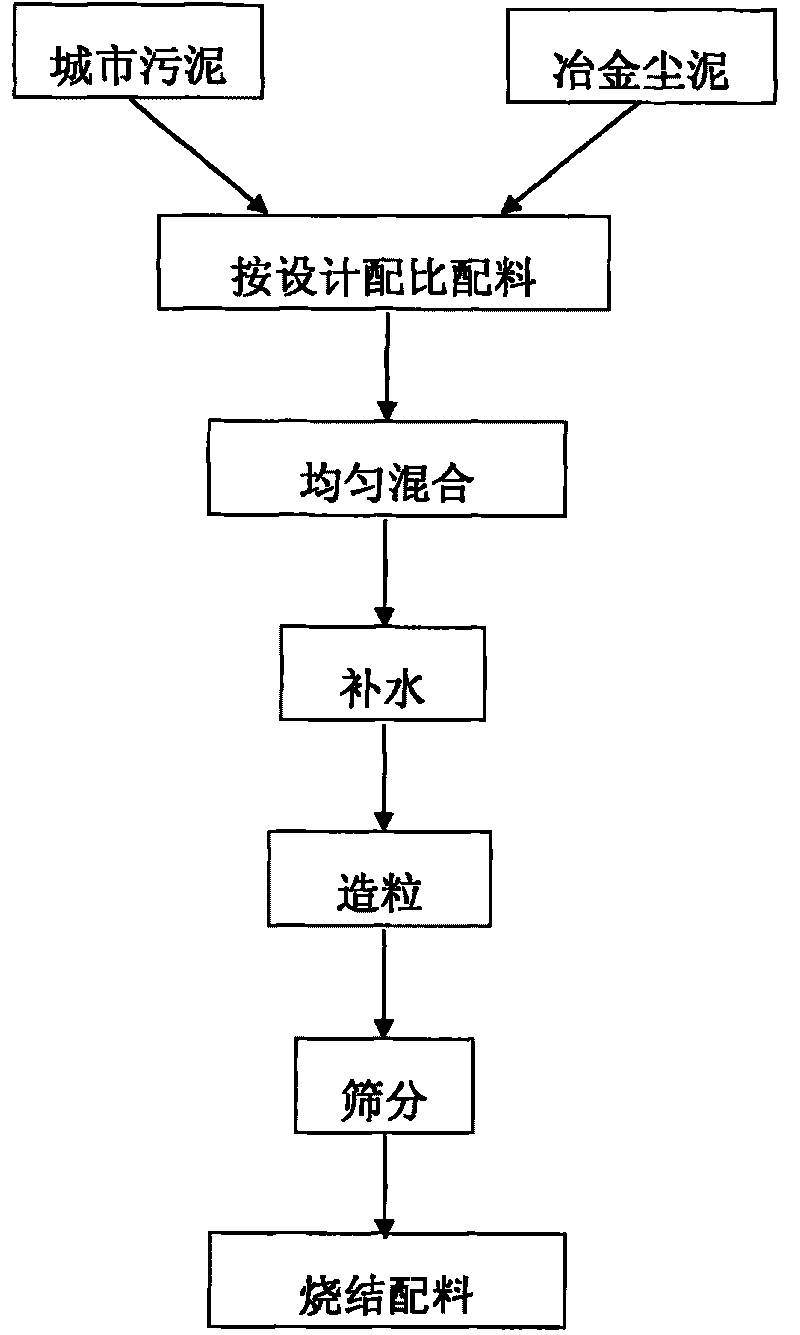
Method for preparing sintered mixture from municipal sludge and ferrous iron containing metallurgical dust
ActiveCN101717853ARealize unified utilizationEfficient recyclingProcess efficiency improvementSludgeNew energy
The invention relates to a method for preparing a sintered mixture from municipal sludge and iron containing metallurgical dust, which belongs to the technical field of resource recycling of the municipal sludge and the iron containing metallurgical dust. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing raw materials from 5-50 percent by weight of municipal sludge and 50-95 percent by weight of iron containing metallurgical dust, adding 0-20 percent by weight of water into the raw materials, then mixing and granulating to produce a sintered granular material, and using the sintered granular material as the mixture to be mixed into a sintering working procedure, wherein the proportion mixed into the sintering working procedure is 0.5-10 percent by weight of the total sintered raw materials quality. The method has the advantages that the processing flow of the municipal sludge is transferred to the mature sintering process flow of ferrous metallurgy, avoiding the problems of new energy consumption, secondary pollution and the like caused in traditional landfill and sintering processes of the municipal sludge, thereby recycling effective elements in the metallurgical dust and the municipal sludge in the steel production flow, improving sintering production process conditions to a certain degree and improving the sintering production efficiency.
Owner:SHOUGANG ENVIRONMENTAL IND +1
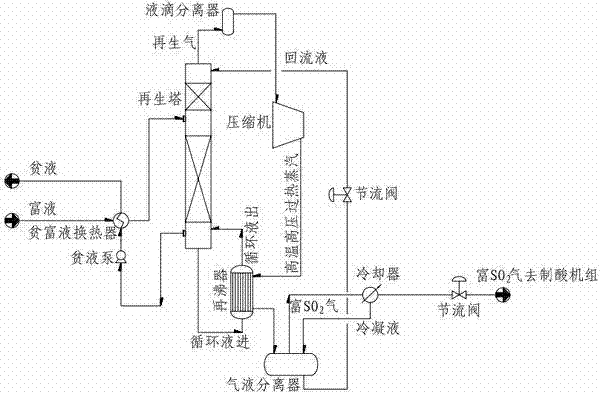
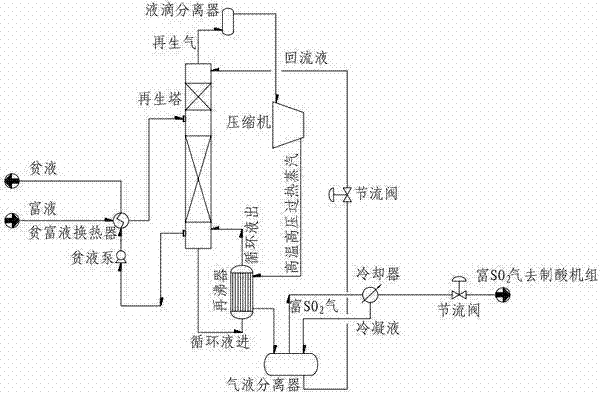
Heat pump regeneration process for desulphurization solvent used in flue gas desulphurization by solvent cyclic absorption method
ActiveCN102225297AAchieve recyclingImprove energy efficiencyHeat recovery systemsDispersed particle separationFlue gasEngineering
The invention relates to a heat pump regeneration process for a desulphurization solvent used in flue gas desulphurization by the solvent cyclic absorption method. According to the invention, regeneration gas produced in the regeneration of a desulphurization solvent is compressed by a compressor so as to obtain high temperature high pressure superheated steam, and the superheated steam is used as a heat source to heat and vaporize regeneration tower bottoms, thereby recycling afterheat of the low temperature regeneration gas at tower top; therefore, the heat pump regeneration process for a desulphurization solvent used in flue gas desulphurization by the solvent cyclic absorption method is formed, and the process has the characteristics of high efficiency, low energy consumption and low operation cost. The invention is applicable to flue gas desulphurization in a plurality of fields like steel, non-ferrous metallurgy, thermoelectricity, chemicals, building materials, etc.
Owner:成都华西工业气体有限公司
Converter vanadium extraction process adopting top blowing oxygen lance to blow cooling agents
The invention relates to a converter vanadium extraction process adopting a top blowing oxygen lance to blow cooling agents, belongs to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy, and is used for solving the problems that the temperature of a molten pool is difficult to control in the vanadium extraction course, the dynamic condition is poor and the like and increasing the oxidation conversion rate of vanadium and the quality of vanadium slag. The converter vanadium extraction process comprises a powder supply system and an oxygen supply system; and the cooling agents are blown through using a supersonic oxygen jet of the top blowing oxygen lance, and the aims of controlling the temperature of the molten pool in the vanadium extraction course and improving the stirring ability of the molten pool are achieved by utilizing a principle that powder rapidly reacts with hot iron to absorb heat, thereby achieving the technical effect of efficient vanadium extraction. The cooling agents enters the oxygen lance via a powder supply pipe in the powder blowing process; an outlet of the powder supply pipe can be positioned between the upper part of a lance body and an Raoult outlet of a blowing head; and the inner diameter of the powder supply pipeline is in the range of 15 to 180mm, the powder blowing flow rate is in the range of 20 to 800kg / min, the carrier gas flow rate is in the range of 100 to 4000Nm3 / h, and the carrier gas pressure is in the range of 0.5 to 1.6Mpa. The converter vanadium extraction process is suitable for vanadium extraction converters of 200 to 300t; and by adopting the converter vanadium extraction process, the semi-steel vanadium content can be reduced to below 0.03 percent, and the quality of vanadium slag (V2O5) is increased by more than 1 percent, so that the recovery rate of vanadium resources is increased.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Continuous casting method of sulfur-containing easy-cutting pinion steel
The invention discloses a continuous casting method of a sulfur-containing easy-cutting pinion steel, belonging to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy and solving the problems of low pulling rate and output influence when qualified sulfur-containing easy-cutting pinion steel is produced in the prior art. The continuous casting method of the sulfur-containing easy-cutting pinion steel comprises the following steps of: a, injecting molten steel with the superheat degree of 15-30 DEG C into a crystallizer of a continuous casting machine charged with covering slag for cooling so as to obtain a continuous casting billet, and controlling the using amount of cooling water and the intensity of electromagnetic stirring; and b, pulling the continuous casting billet out of the crystallizer obtained from the step a, sequentially cooling through a secondary cooling zone and an air cooling zone, wherein the pulling rate is 1.3-1.8 m / minute, and the surface temperature of the continuous casting billet is controlled at 1000-1150 DEG C in the secondary cooling zone and controlled at 900-1050 DEG C when entering the air cooling zone. The continuous casting method disclosed by the invention ismainly used for the continuous casting of pinion steel with the section of 200*200 mm.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON AND STEEL +2
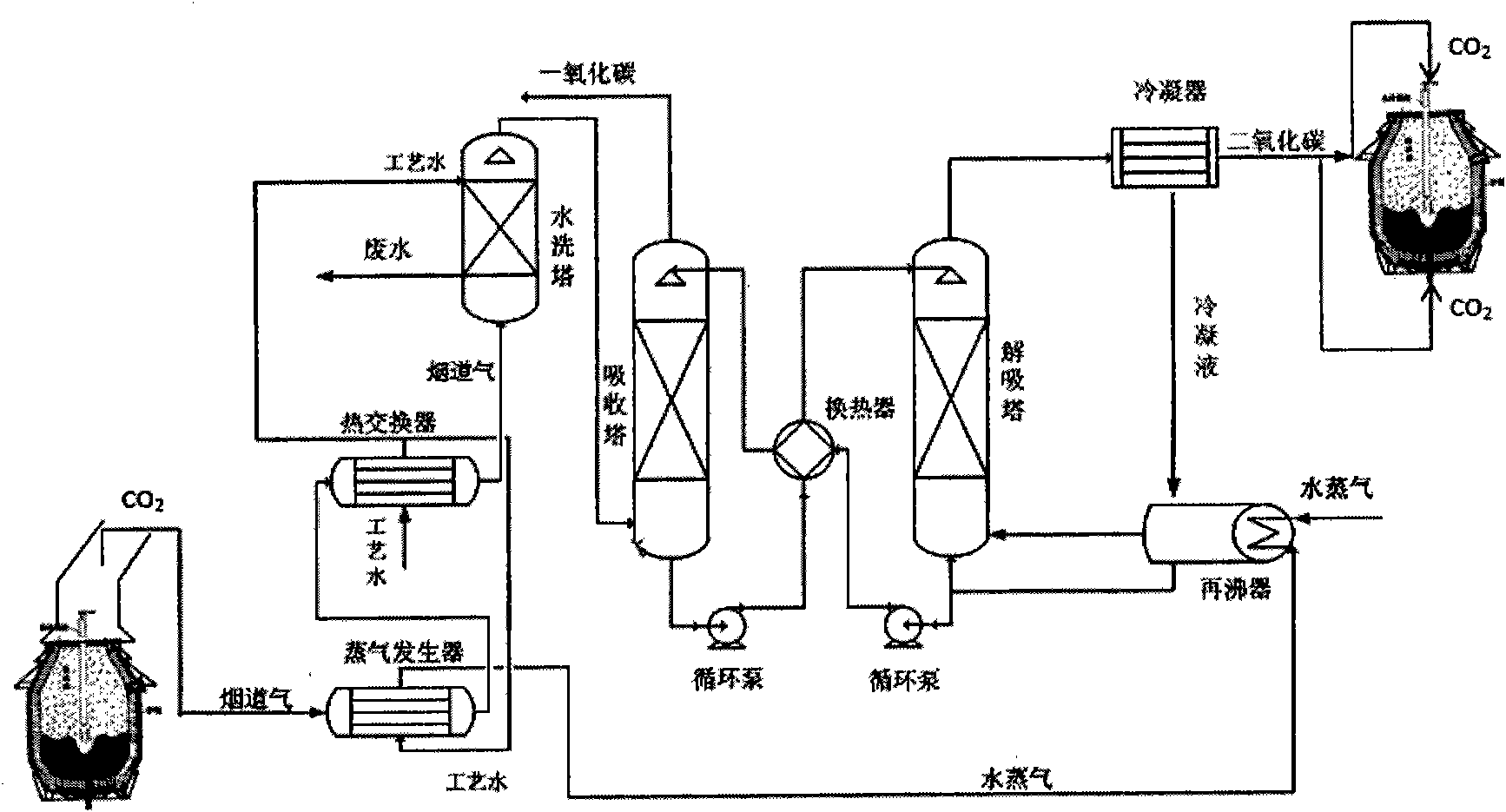
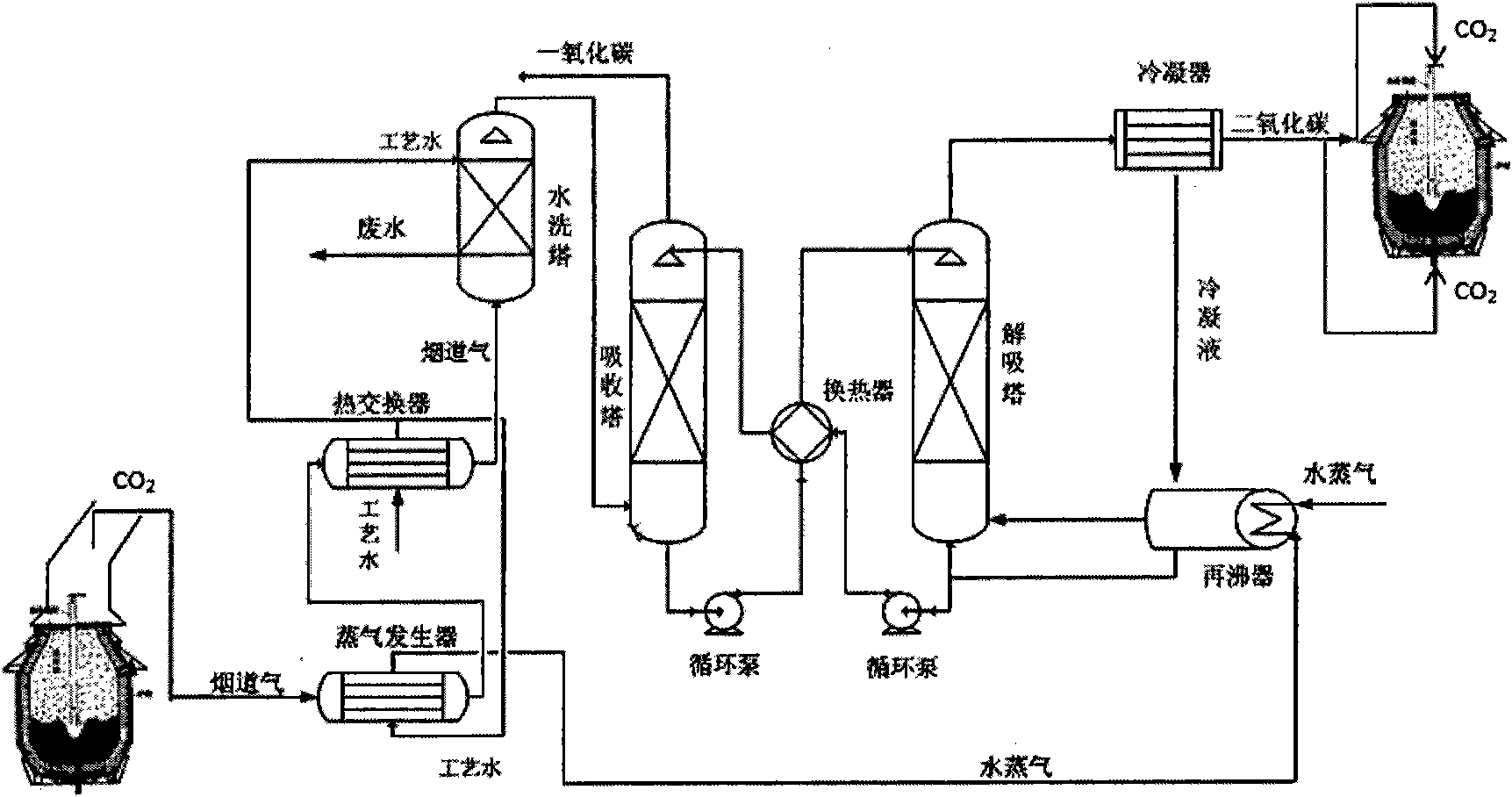
Method for recycling CO2 separated from converter steel-making gas for top blowing and bottom blowing
InactiveCN101818227AHigh carbon contentControl heating rateManufacturing convertersGas emission reductionProduct gasProcess engineering
The invention discloses a method for recycling CO2 separated from converter steel-making gas for top blowing and bottom blowing and belongs to the fields of ferrous metallurgy, energy conservation and environment protection. In the invention, the CO2 in the converter steel-making gas is separated and recycled after being cooled and dedusted; the recovery is 100 to 15,000Nm<3> / h; and the concentration of CO in the converter gas is improved by 5 to 20 percent at the same time. The CO2 serves as a gas source for the top blowing and the bottom blowing of a top and bottom combined blown converter. A chemical absorption separation method is adopted to separate the CO2; steam added with rich liquid is generated by using the residual heat of the converter gas; and almost no additional energy is consumed in the process for separating the carbon dioxide. 1 to 30 percent of the CO2 and 99 to 70 percent of O2 are blown from the top part; pure CO2 or a mixture of the CO2 and N2 or Ar or O2 or gas and the like is adopted in the whole process of the bottom blowing; and the amount of the CO2 is 100 to 3,000Nm<3> / h. The method is applicable to a steel-making process for a 30 to 350 ton converter. By adopting the method, for each ton of steel, 1 to 20 m3 of CO2 emission is reduced synthetically; the soot amount is reduced by 1 to 30 percent; and the content of the CO in the gas is improved to more than 2 to 15 percent.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
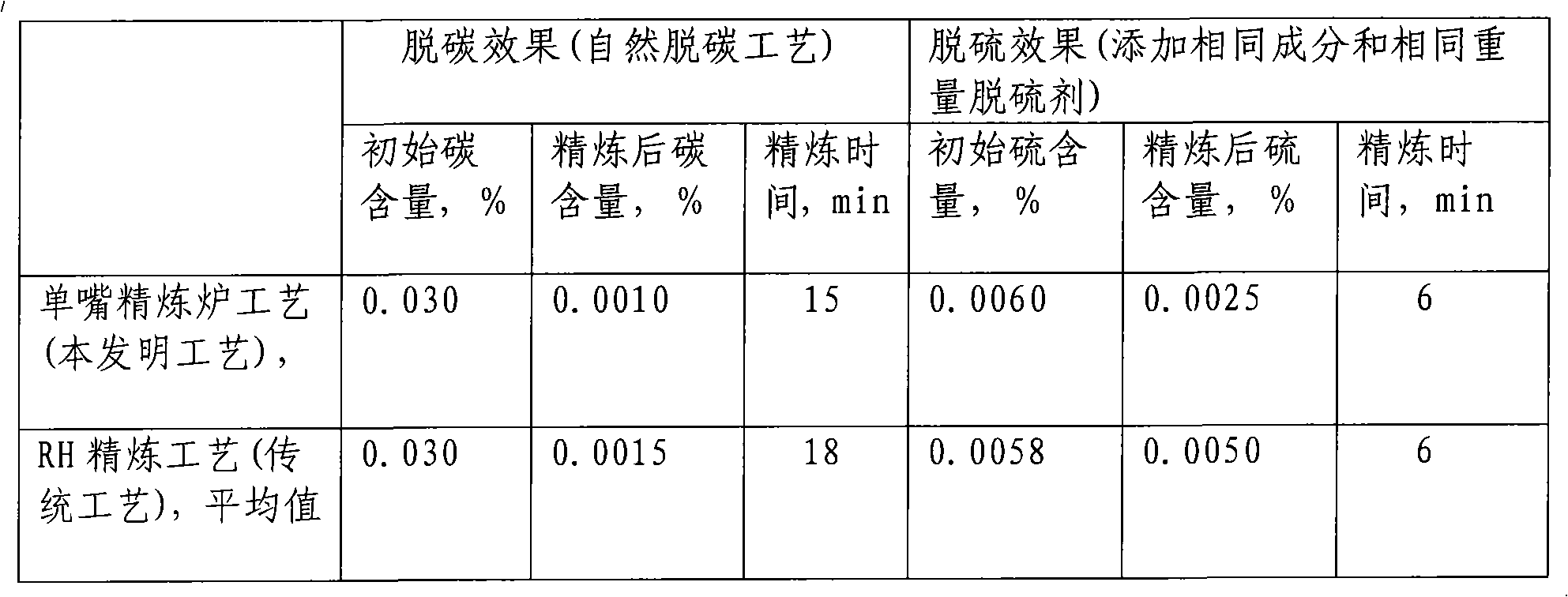
Process for smelting ultra clean steel by single-nozzle refining furnace
The invention discloses a process for smelting ultra clean steel by a single-nozzle refining furnace, belonging to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy. The process comprises the followings steps of: blowing in argon gas from the bottom of steel ladle with the blowing gas flow quantity of 1-10 NL / min per ton of steel, and inserting a suction nozzle into the steel ladle; carrying out a vacuum natural decarburization technology when the initial carbon content in liquid steel is smaller than 0.035%, and carrying out a vacuum forced decarburization technology when the initial carbon content in the liquid steel is greater than 0.035%, wherein the time for decarburization is 12-22 min; after decarburization, maintaining the pressure of a vacuum chamber to be les than 100-200 Pa, adding 1-6 kg of deoxidizer per ton of steel, and adding 0.5-8 kg of desulfurizer per ton of steel in 1-2 min after the deoxidizer is added, wherein the flow quantity of argon gas is 1-10 NL / min per ton of steel, and the time for desulfurization is 5-15 min; and deoxidizing and removing impurities after desulfurization. The process can simultaneously reduce the content of impurity elements comprising carbon, sulfur, nitrogen, hydrogen and oxygen and impurities in the liquid steel to an extremely low level within limited refining time, and the refining efficiency is obviously superior to that of an RH refining furnace.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Continuous casting method of high chrome steel
The invention discloses a continuous casting method of high chrome steel, belonging to the technical filed of ferrous metallurgy, and solving the internal and external quality problems easily generated during continuous casting of high chrome steel in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: a, pouring L80-3Cr high chrome molten steel with the superheat degree of 15-30 DEG C into a crystallizer of a continuous casting machine with added casting powder, cooling to obtain a continuously cast bloom, and carrying out water cooling and electromagnetic stirring during cooling; and b, pulling out the continuously cast bloom obtained in the step a from the crystallizer at a speed of 0.5-0.6m / min, cooling the continuously cast bloom in a secondary cooling area and an air cooling area in sequence, and treating the continuously cast bloom at a solidified tail end by using a dynamic light-pressing technology, wherein the total pressing amount is controlled to be 6-10mm. The methoddisclosed by the invention is mainly applied to continuous casting of L80-3Cr high chrome steel.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON AND STEEL +2
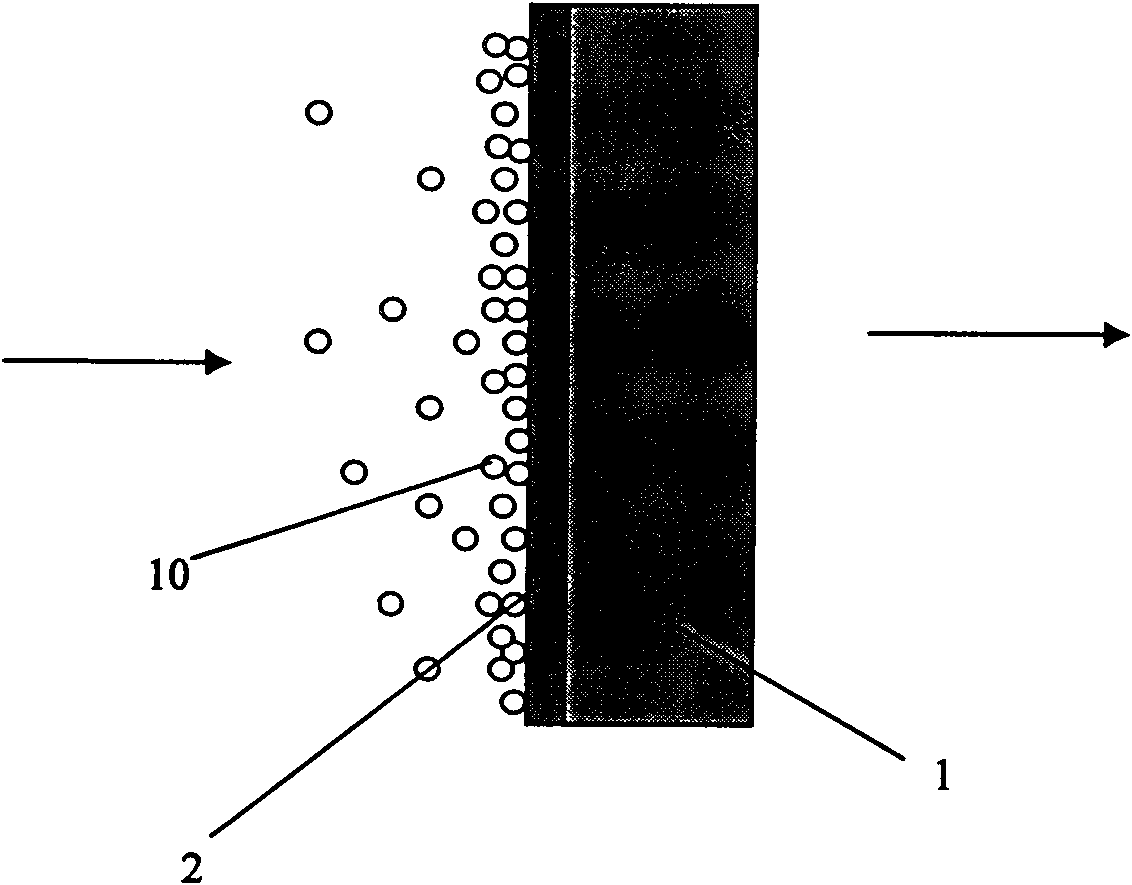
Tundish flow control device for slab casting machine, preparation method thereof and slagging method using tundish flow control device
ActiveCN102744393AReduce the balanceImprove erosion resistanceMelt-holding vesselsCasting cleaning apparatusSlab casterSlag
The invention relates to a tundish flow control device for a slab casting machine, a preparation method of the tundish flow control device and a slagging method using the tundish flow control device, and belongs to the technical field of the ferrous metallurgy slab casting tundish technology. The tundish flow control device for the slab casting machine comprises a turbulence controller, a slag blockage weir and a slag blockage dam, and is characterized in that the upper edge of the slag blockage weir (5) is higher than the highest liquid level (10) of molten steel normally poured by the tundish, but is lower than the working face of tundish overflow port coating (1); the slag blockage weir (5) and the slag blockage dam (6) are vertically staggered; two ends of the slag blockage dam (6) are respectively provided with a through hole; a center distance a between the slag blockage weir (5) and the turbulence controller (4) is 400-600mm; and a center distance b between the slag blockage weir (5) and the slag blockage dam (6) is 300-400mm. After the tundish flow control device for the slab casting machine is adopted, slab tundish injection residue can be reduced by more than 25%, the service life of the flow control device is improved by one time and is above 14 hours, and the production cost of continuous casting refractory material is lowered by more than 30%.
Owner:LAIWU IRON & STEEL GRP
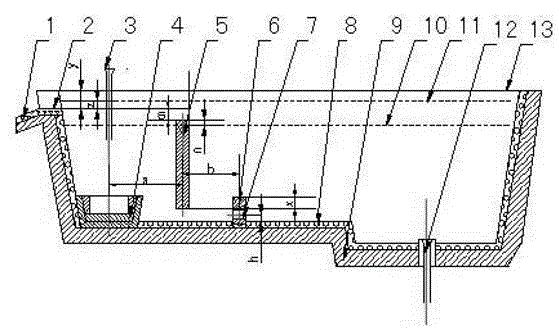
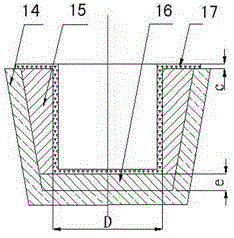
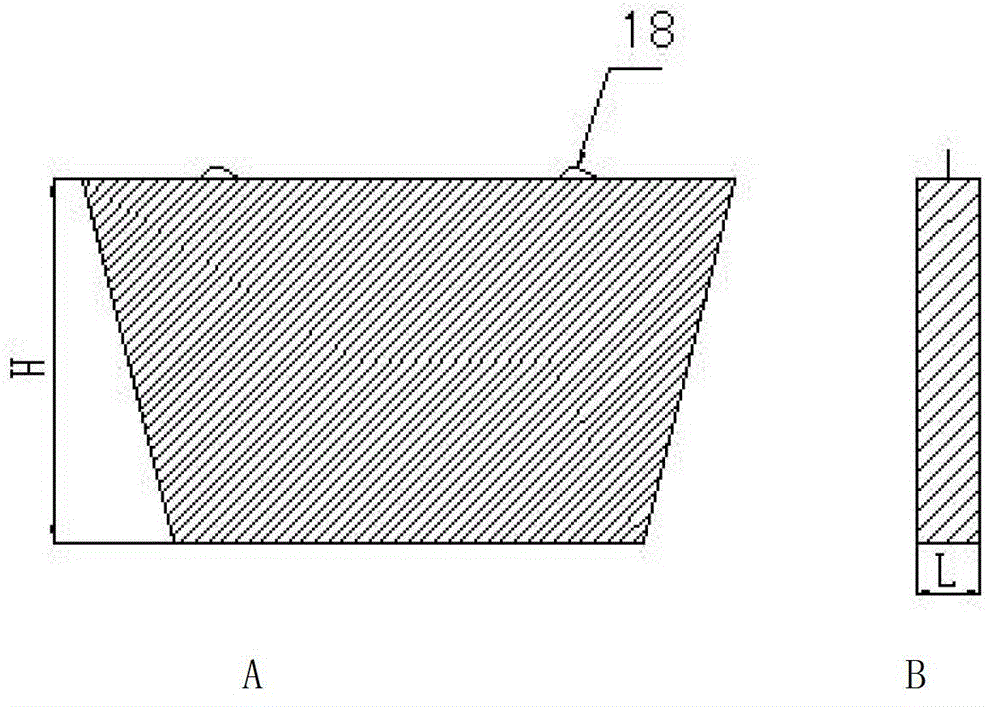
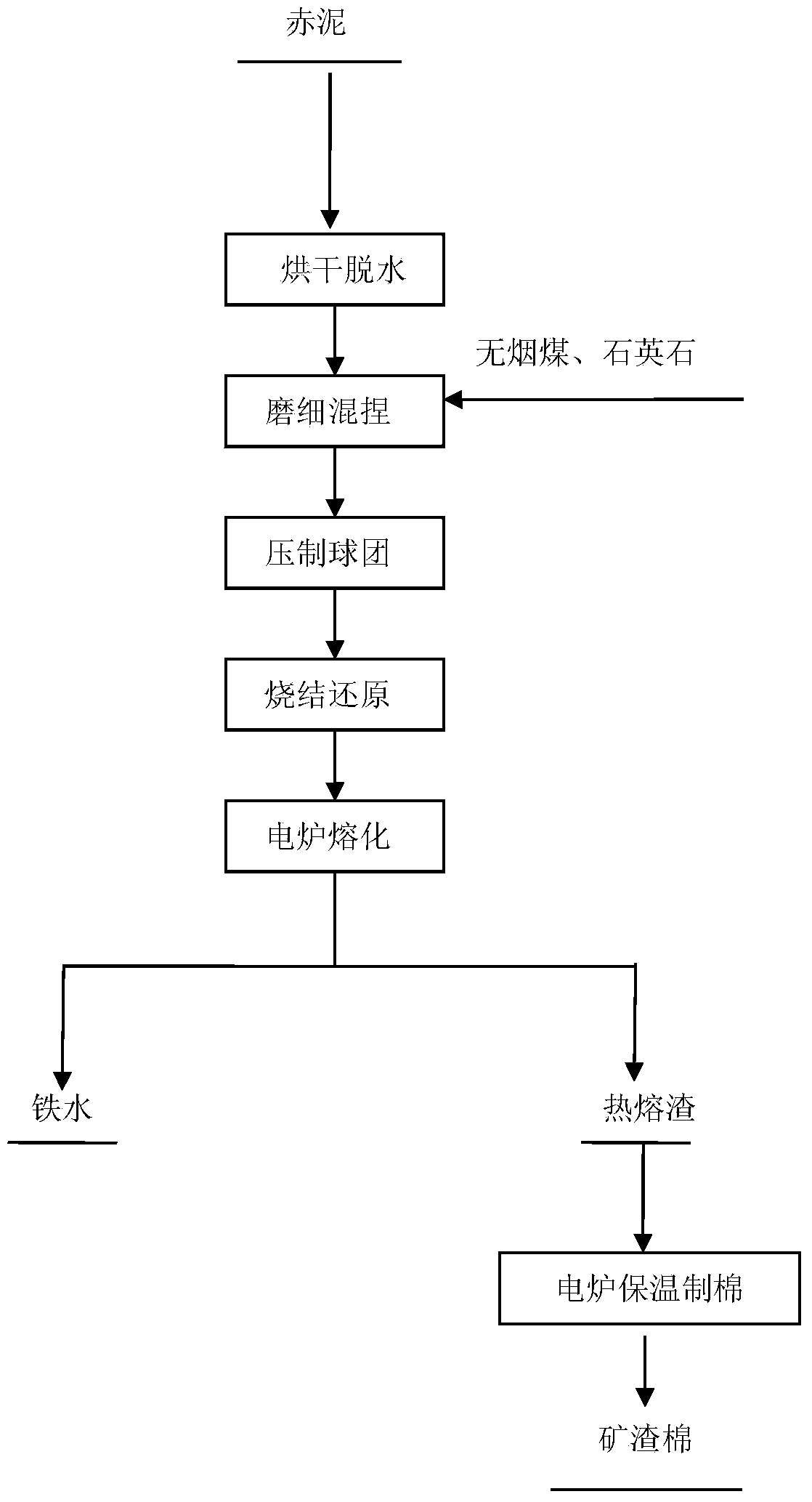
Method for producing high-strength and high-flexibility heatproof mineral wool and iron by using red mud
ActiveCN104046771ARealize comprehensive utilizationReduce pollutionGlass making apparatusProcess efficiency improvementRed mudSlag
The invention discloses a method for producing high-strength and high-flexibility heatproof mineral wool and iron by using red mud, and belongs to the field of comprehensive resource recycling in the non-ferrous metal metallurgy industry. The method comprises the following steps: 1, dehydrating and drying red mud, adding a reducing agent and a conditioning agent, and uniformly mixing; 2, adding pellets into a rotary kiln, and carrying out sintering pre-reduction; 3, adding hot pellets into an electric furnace, fusing, separating iron and slag, discharging molten iron through an iron outlet, and discharging the slag through a slag outlet; 4, collecting the slag discharged from the slag outlet, carrying out heat insulation by using the electric furnace, discharging, and processing to prepare the mineral wool; and 5, collecting the discharged molten iron. The method realizes the comprehensive utilization of a secondary non-ferrous metallurgy resource by using the red mud as a raw material to produce the mineral wool and iron, reduces environment pollution, maintains the ecologic balance and realizes the sustainable development. The high-strength and high-flexibility heatproof mineral wool can be produced, the recovery rates of the mineral wool and iron are high, and the economic benefit is substantial. The method also has the advantages of simple technology and easy popularization.
Owner:JILIN JIEN NICKEL IND +2
Superlarge thickness hydrogen chromium molybdenum steel plate for hydrogenation equipment and manufacture method thereof
The invention relates to a superlarge thickness hydrogen chromium molybdenum steel plate for hydrogenation equipment and a manufacture method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy. A technical scheme is as below: the steel plate comprises the following components by weight: no more than 0.15% of C, no more than 0.10% of Si, 0.300.60% of Mn, no more than 0.007% of P, no more than 0.005% of S, 2.00-2.50% Cr, 0.90-1.10% of Mo, no more than 0.02% of Nb, no more than 0.20% of Cu, no more than 0.20% of Ni, no more than 0.003% of Sb, no more than 0.005% of Sn, no more than 0.016% of As, no more than 0.003% of O, N no more than 0.008%, no more than 0.0002% of H, no more than 0.03 of Ti and the balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities; a round steel ingot with piece weight of 80 tons is produced by electric arc furnace smelting and casting; and the steel ingot is subjected to forging cogging, rolling and a heat treatment process including normalizing, accelerated cooling and tempering to prepare the superlarge thickness chromium molybdenum steel plate with a maximum thickness of 256mm for hydrogenation equipment. A finished steel plate has maximum single weight reaching 60 tons, good cold bending property, no cracking during material manufacture and good resilience. The method provided by the invention reduces labor intensity, saves time and improves the utilization rate of materials.
Owner:WUYANG IRON & STEEL +1
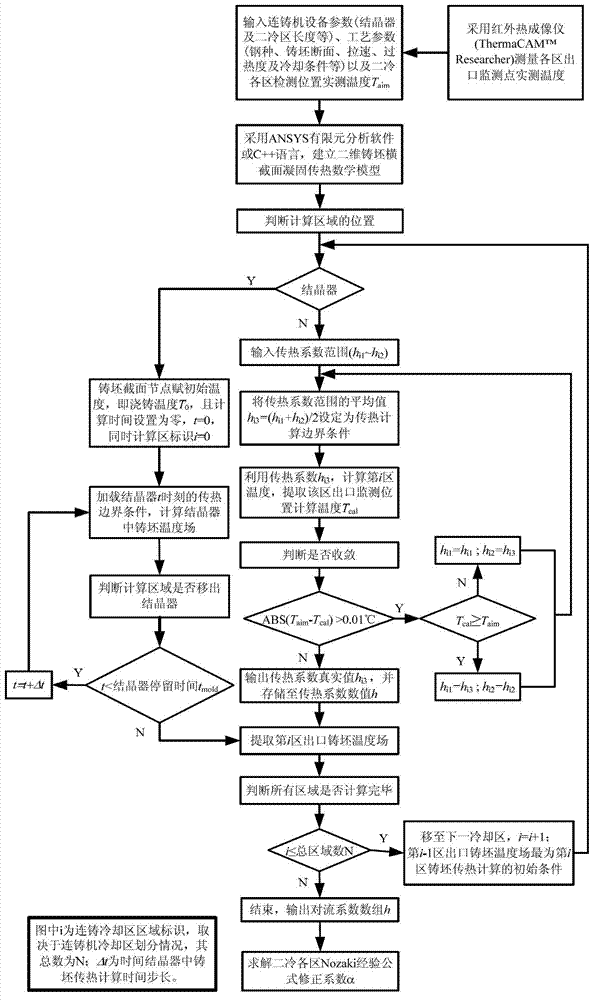
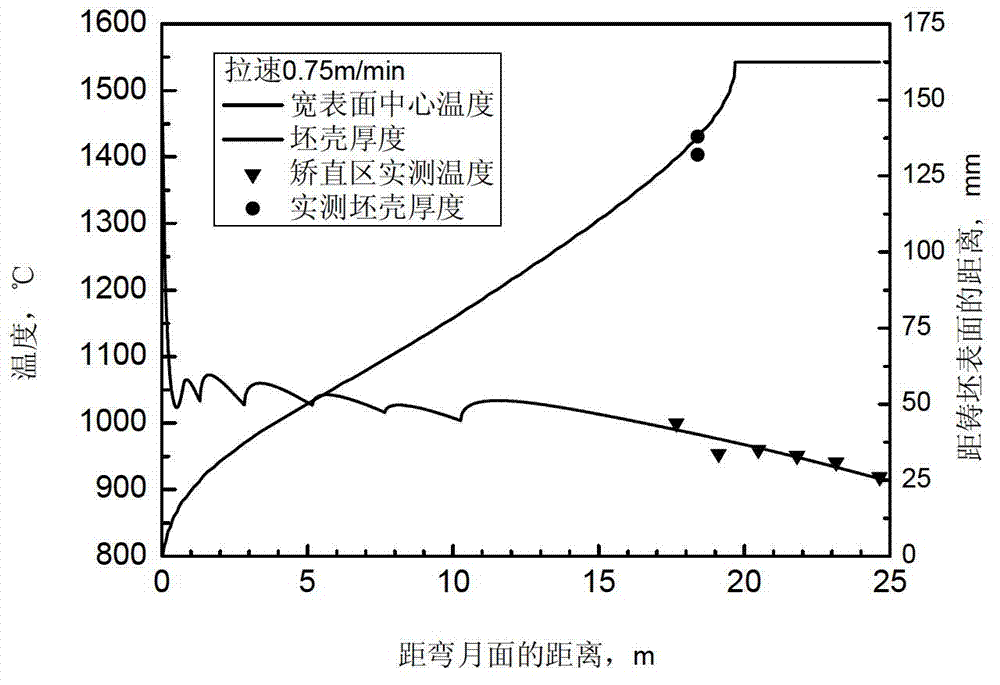
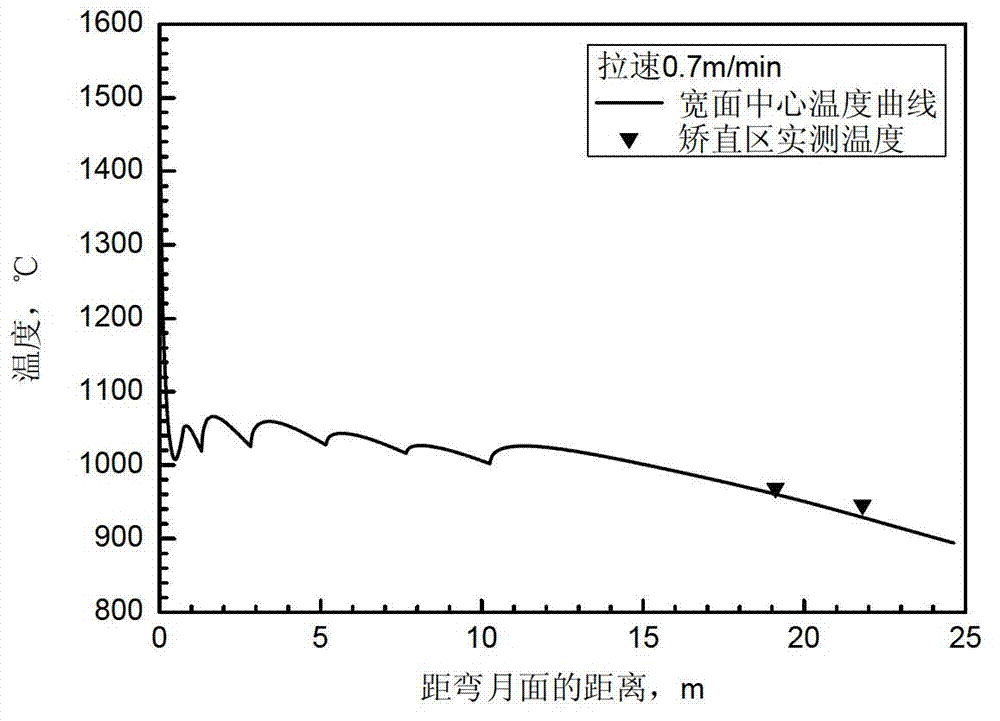
Method for determining heat transfer coefficient of secondary cooling zones in steel continuous casting process
The invention relates to the field of ferrous metallurgy, in particular to a method for determining heat transfer coefficient of secondary cooling zones in a steel continuous casting process. The method is based on actually measured temperatures of outlets of all secondary cooling zones of casting steel grades and is simultaneously applicable to continuous casting of slabs and square billets. A computer is used as a continuous casting process server connected with an infrared thermal imaging instrument, the actually measured temperatures of the outlets of all the secondary cooling zones serve as the target temperatures, the heat transfer coefficient between casting blanks and cooling water is solved in iteration mode by aid of numerical simulation means so as to amend a heat transfer coefficient empirical formula and determine the heat transfer coefficient in different casting speed conditions. Blank casing thickness and the calculated value of temperature in an air cooling zone which are obtained in the method can be well matched with the actually measured values, namely the method can be effectively applied to the continuous casting process of casting machines of different types.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
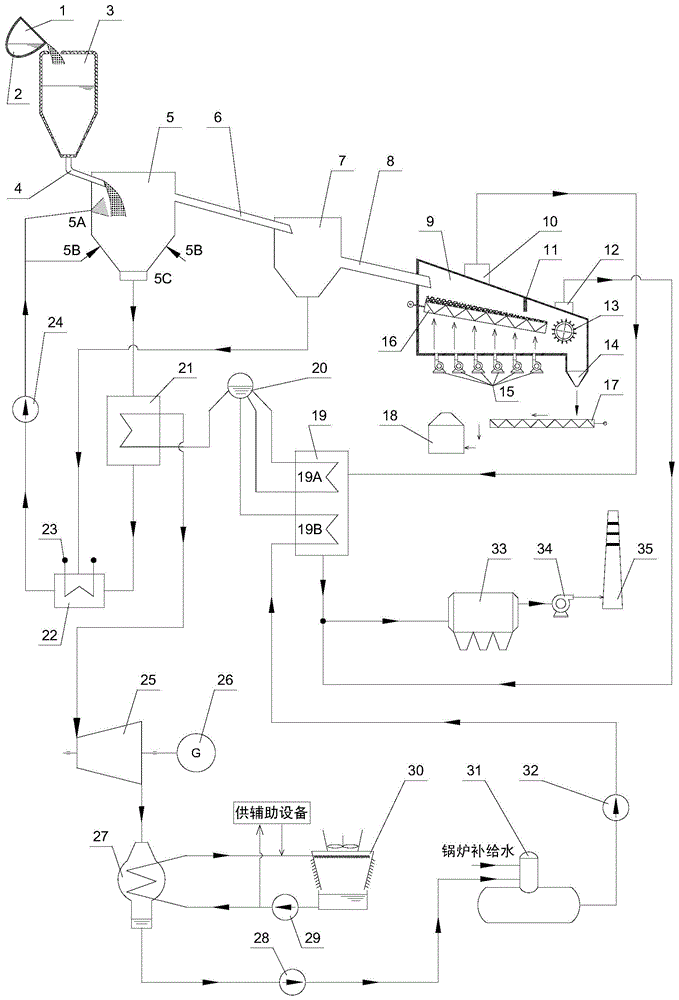
Molten slag rapid cooling, granulation and waste heat recovery power generation system and method
ActiveCN103557711AIncrease temperatureImprove efficiencyIncreasing energy efficiencyMachines/enginesHeat carrierWater activity
The invention provides a molten slag rapid cooling, granulation and waste heat recovery power generation system and method, and belongs to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy molten slag processing and waste energy recovery. The molten slag rapid cooling, granulation and waste heat recovery power generation system comprises a slag receiving device, a heat carrier slag rapid cooling and granulation device, a slag slow-cooling device, a waste heat recovery power generation device and a waste gas purification treatment device. The molten slag is rapidly cooled and granulated by the heat carrier slag rapid cooling and granulation device, and is rapidly cooled to a glass body state; the molten slag is further cooled slowly by heat exchange to facilitate the follow-up sensitive heat recovery. According to the system and the method, the rapid cooling and granulation of molten slag are effectively realized, and the high-temperature waste heat resource is fully recycled on the basis of unaffecting the water activity of the slag.
Owner:NANJING KESEN KENEN ENVIRONMENT & ENERGY
Method for plating nickel on iron powder surface
InactiveCN101429652APlating volume controllableUniformity controllableLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingReduction treatmentFiltration
The invention discloses a method for plating a layer of metallic nickel or nanometer nickel powder onto the surface of iron powder through a hydrothermal reduction technology, which belongs to the technical field of non-ferrous metallurgy and powder metallurgical material. The method comprises the following steps: adding nickel sulfate or nickel sulfate aqueous solution, ammonia water and ammonia sulphate into water according to the certain proportion to prepare mixed solution; adding a small amount of anthraquinone and additive into the mixed solution; then adding the iron powder to be plated by nickel into the mixed solution, shifting the mixed solution containing the iron powder into an autoclave, and sealing the autoclave; carrying out the hydrogen reduction treatment through applying high temperature and pressure to the aqueous solution; forming the compact metallic nickel layer or nanometer nickel powder plating layer through the nickel ions reduced and precipitated onto the surface of the iron power in the solution; and when the plating reaction is completed, cooling down the materials in the autoclave, discharging the iron powder with the surface plated by metallic nickel and the aqueous solution, and obtaining the iron powder product with the surfaced plated by metallic nickel after filtration and drying. The method has a simple production method, easy operation and the controllable plated nickel layer.
Owner:张建玲
Method for recovering germanium from zinc dross
ActiveCN101760653ANo pollution in the processSolve the technical problems of recyclingProcess efficiency improvementIndiumEvaporation
Then invention relates to a method for recovering germanium from zinc dross, belonging to the technical field of non-ferrous metallurgy. After the secondary extracted zinc is leached by adopting the wet method, and the leached dross can be pre-treated, the germanium can be converted into the germanic from the low-valence in metal or germanium monoxide. Namely, hydrogen peroxide is used for oxidizing germanium, lead, indium, arsenic and other elements in the hydrochloric acid medium, so that the elements can be oxidized from low valence to high valence; the lead, indium, arsenic, gallium and the like react into solution, the low-valence germanium wrapped by the elements can be exposed and oxidized to be the germanic by the hydrogen peroxide under the acid condition into hydrochloric acid solution, and the germanic can escape in a form of germanium tetrachloride by evaporation, so as to realize the separation with other purities; and then, the separated germanium tetrachloride is purified and hydrolyzed, so as to prepare germanium dioxide. In the zinc dross with the germanic being more than 2.0%, the recovery rate of the germanic can reach more than 98%; in the zinc dross with the germanic being more than 1.0-2.0%, the recovery rate of the germanic can reach more than 95%; and in the zinc dross with the germanic being 0.1-1.0%, the recovery rate of the germanic can reach more than 90%.
Owner:YUNNAN WUXIN IND
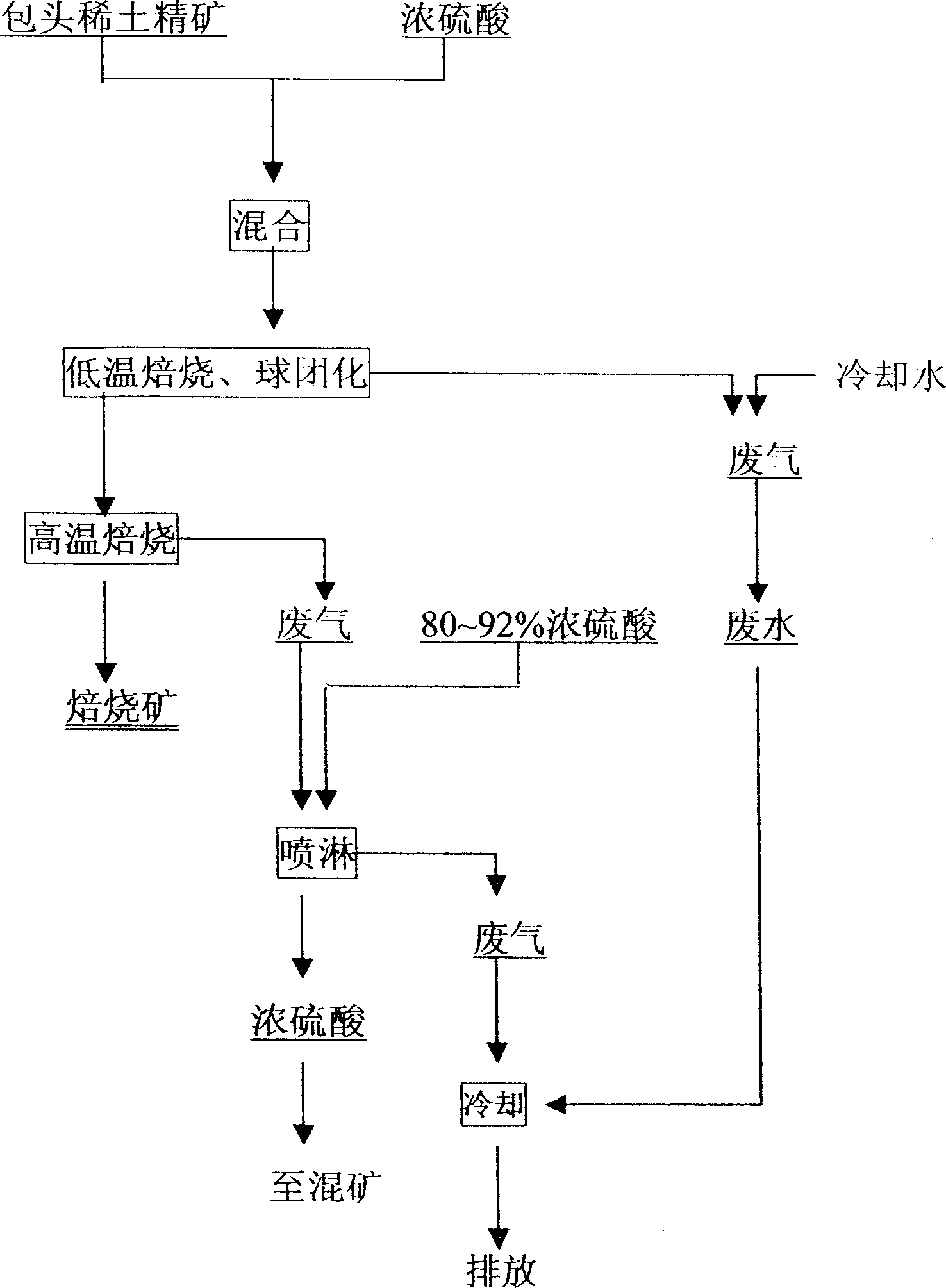
Stepped sulfuric acid treatment and roasting process for decomposing Baotou RE ore concentrate
The present invention belongs to the field of non-ferrous metallurgy technology, and is stepped roasting process for decomposing Baotou RE ore concentrate. The technological process includes the following steps: 1. mixing Baotou RE ore concentrate with concentrated sulfuric acid; 2. roasting at 100-320 deg.c for 1-7 hr and spraying water to cool produced gas; and 3. roasting at 600-850 deg.c for 1-4hr, absorbing partial harmful gas with 80-92% concentration sulfuric acid, returning the absorbed concentrated sulfuric acid, cooling gas with water from the second step, and transferring the roasted material to the next step. The present invention combines the low temperature roasting and the high temperature roasting, and has less water consumption, raised resource utilization rate and other advantages.
Owner:CHINA NORTHERN RARE EARTH (GROUP) HIGH TECH CO LTD
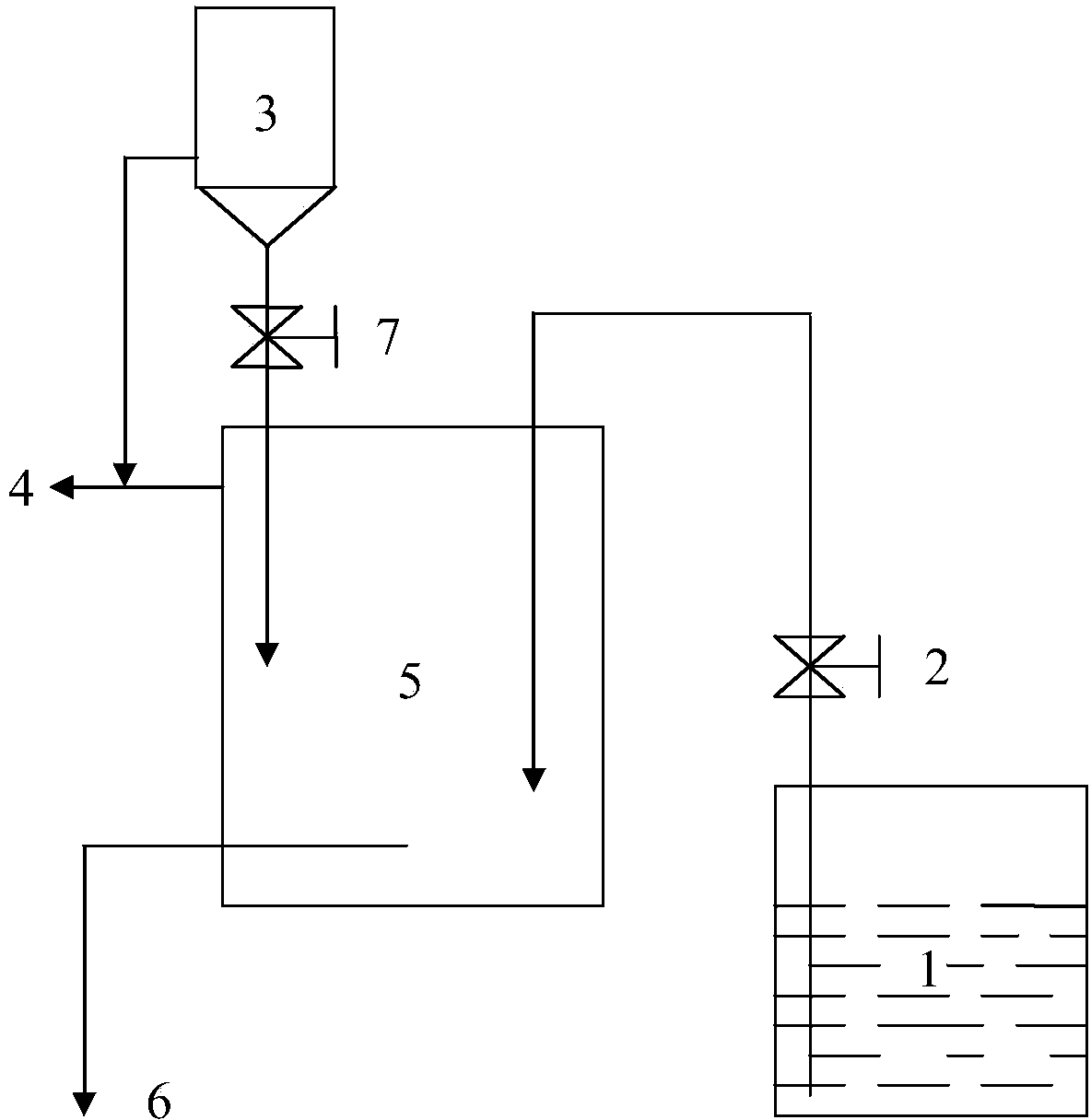
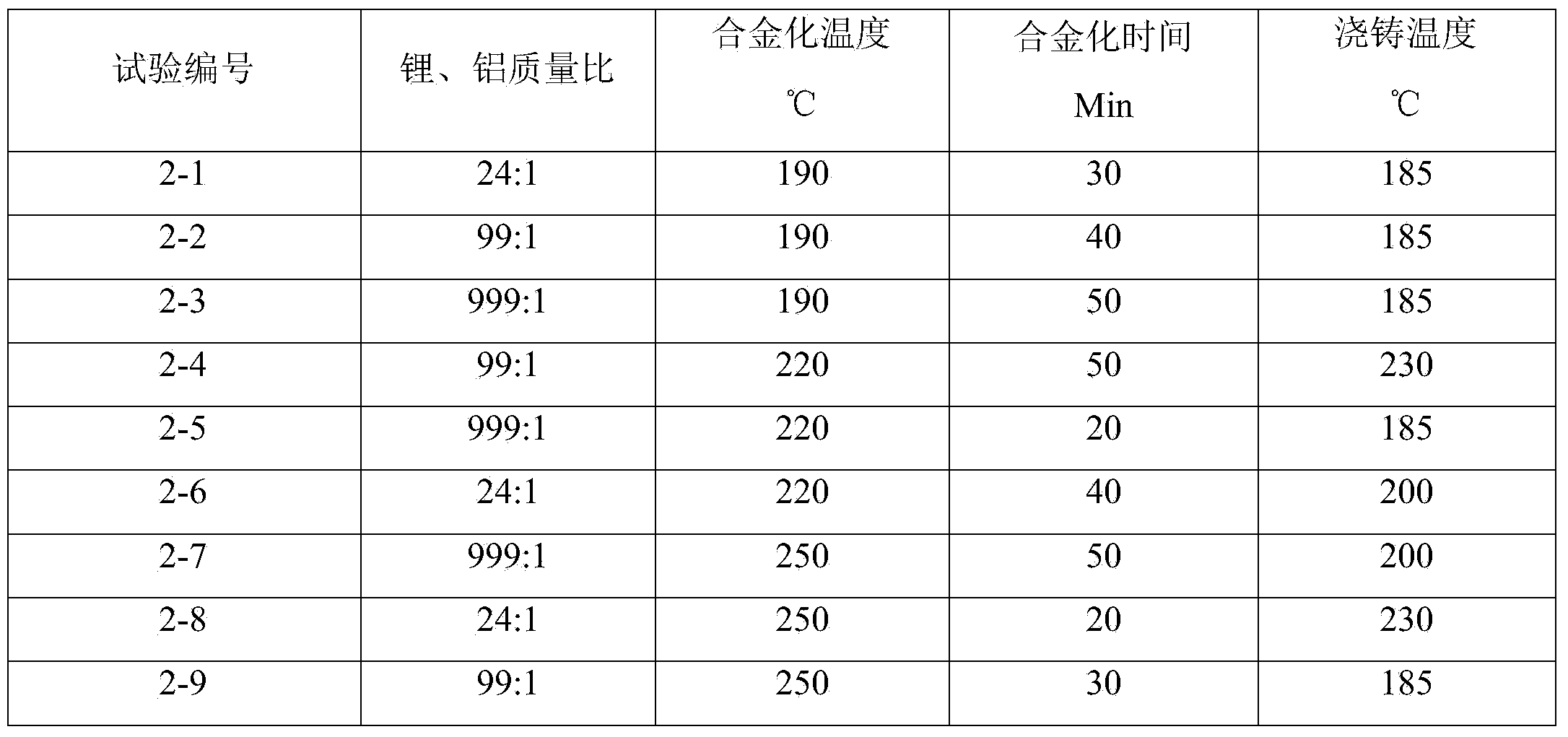
Vacuum synthesis method of lithium-aluminum alloy
ActiveCN104060141AShorten alloying timeIncrease productivityCell electrodesThin metalSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a vacuum synthesis method of lithium-aluminum alloy, belongs to the fields of non-ferrous metallurgy and batteries, and aims at solving the technical problem of providing a vacuum synthesis method of a lithium-aluminum alloy. The vacuum synthesis method of the lithium-aluminum alloy disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: evenly mixing aluminum with molten metal lithium in a vacuum environment at a weight ratio of 1:(24-999), then smelting at 190-250 DEG C, and cooling, so as to obtain the lithium-aluminum alloy. Furthermore, the invention also discloses the lithium-aluminum alloy prepared by the method disclosed by the invention and use thereof in preparation of a battery cathode material. By adopting the vacuum synthesis method of the lithium-aluminum alloy disclosed by the invention, the alloying time is greatly reduced, the production efficiency is obviously improved, meanwhile, the impurity nitrogen content is obviously reduced, the product quality of the lithium-aluminum alloy is improved, and preparation of a high-end ultra-thin metal belt is facilitated.
Owner:TIANQI LITHIUM CORP
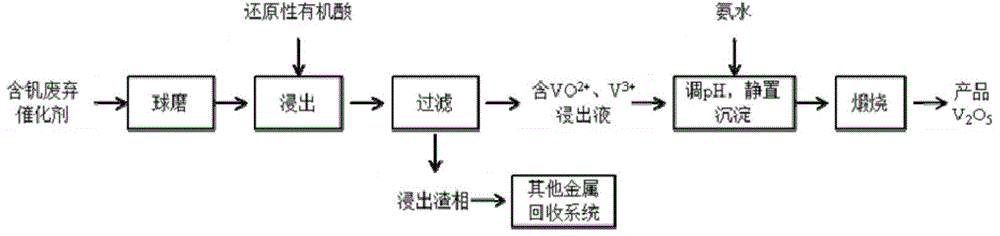
Method for extracting vanadium from vanadium-containing waste catalyst reductive organic acid
ActiveCN105986123AImprove leaching rateLow leaching temperatureProcess efficiency improvementSlagOxygen
The invention relates to the field of non-ferrous metallurgy and resource recycling, in particular to a novel process for extracting vanadium from vanadium-containing waste catalyst reductive organic acid. The novel process comprise the steps that a vanadium-containing waste catalyst is directly extracted in a reductive organic acid system, and other reductive agents are not added, so that pentavalent or tetravalent vanadium is directly reduced into vanadium-oxygen-based ions or trivalent vanadium ions, the vanadium-oxygen-based ions or the trivalent vanadium ions are combined with organic acid radical anions and enter a solution, and vanadium-containing leaching liquid and vanadium-containing leaching slag are obtained; and ammonia water is added into the vanadium-containing leaching liquid to adjust pH so that ammonium vanadate can be formed and precipitated, and after separating is conducted, a vanadium pentoxide product is obtained by calcining precipitation slag. According to the novel process for extracting the vanadium from the vanadium-containing waste catalyst reductive organic acid, the vanadium is extracted by adopting the reductive organic acid system; the extracting condition is mild; the vanadium extracting rate is 95% or above and higher than the direct inorganic acid fluid extracting rate; and other impurity ions are not introduced in the extracting process, so that recycling of other metal elements in the waste catalyst is not affected.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for controlling nitrogen content in Al deoxidization steel by converter process
ActiveCN101457275AAvoid Nitrogen ProblemsReduce the nitrogen content of the slabManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementAlkalinitySmelting process
The invention belongs to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy, in particular relates to a method for controlling nitrogen content of aluminum killed steel produced in a converter process, and is used for preventing the problem that the nitrogen content increases in the aluminum killed steel produced in the converter process. The technical problem is solved by controlling the nitrogen content of the aluminum killed steel produced in the converter process according to the technical proposal as follows: the alkalinity of converter slag CaO / SiO2 is adjusted to 5-7 when a converter starts to produce the slag, the denitrification rate can be increased in the converter smelting process by controlling the alkalinity of the converter slag, the denitrification rate is increased from 50%-70% to 65%-85%, and the terminal nitrogen content of the molten steel in the converter can be controlled within 15PPm. The alkalinity is controlled, special slag is added, and a seal washer with brim is employed to seal between a steel ladle lower opening and a protection tube before starting continuous casting, thus realizing the stable control that the casting blank nitrogen content is not more than 35PPm by an LD-LF-SCC process and the casting blank nitrogen content is not more than 30PPm by an LD-LF-RH-BCC process.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com