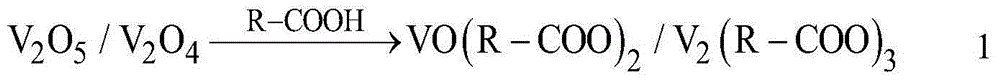Method for extracting vanadium from vanadium-containing waste catalyst reductive organic acid
A waste catalyst and organic acid technology, applied in the field of non-ferrous metallurgy and resource recycling, to achieve low leaching temperature, low energy consumption, and easy purification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
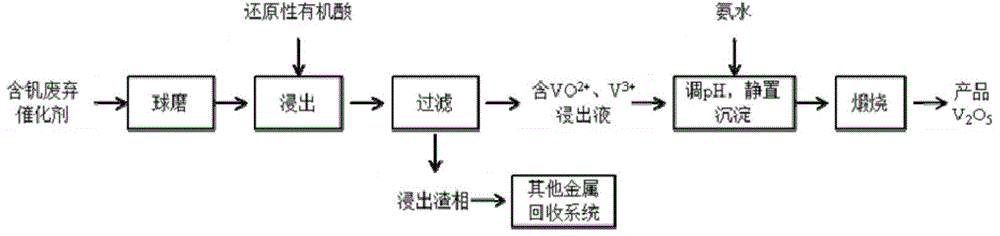
[0032] In this example, V 2 o 5 The sulfuric acid industrial waste catalyst with a content of 3.21% is leached with formic acid to extract vanadium, and the specific process is as follows:
[0033] (1) the sulfuric acid industry waste catalyst is ball milled to a particle size less than 100 mesh;
[0034] (2) The powder obtained in (1) is added to formic acid solution for leaching, the leaching temperature is 80°C during the process, the leaching time is 5h, and the liquid-solid ratio is 6:1m 3 / t, formic acid concentration is 2mol / L, obtains leach solution and leach residue;
[0035] (3) the vanadium content is detected in the leach solution that step (2) obtains, and the extraction rate of vanadium reaches 90.2%, and the leach solution is blue, with VO 2+ Ion-based, adjust the pH to 10 with ammonia water, stand and separate to obtain ammonium vanadate precipitation, and cool and crystallize ammonium vanadate at 400°C to obtain vanadium pentoxide product;
[0036] (4) Apply...
Embodiment 2
[0038] In this example, V 2 o 5 Content is 0.78% synthetic maleic anhydride waste catalyst leaching vanadium with citric acid, concrete process is as follows:
[0039] (1) The waste catalyst of synthetic maleic anhydride is ball-milled to a particle size less than 300 mesh;
[0040] (2) Add the powder obtained in (1) to leaching with citric acid, the leaching temperature in the process is 120°C, the leaching time is 3h, and the liquid-solid ratio is 8:1m 3 / t, the citric acid concentration is 7mol / L, obtains leach solution and leach residue;
[0041] (3) the leach solution that step (2) obtains is detected vanadium content, and the leaching rate of vanadium reaches 97.0%, and the leach solution is yellow-green, with VO 2 + Ion-based, adjust the pH to 8.5 with ammonia water, stand and separate to obtain ammonium vanadate precipitation, and cool and crystallize ammonium vanadate at 500°C to obtain vanadium pentoxide product;
[0042] (4) apply the leaching residue that step...
Embodiment 3
[0044] In this example, V 2 o 5 Vanadium is leached with mixed acid of oxalic acid and ascorbic acid from the waste catalyst of petroleum industry with a content of 14.70%. The specific process is as follows:
[0045] (1) ball-milling waste catalysts from the petroleum industry to a particle size of less than 150 mesh;
[0046] (2) Add oxalic acid and ascorbic acid mixed acid to extract the powder obtained in (1). 3 / t, the concentration of oxalic acid is 1mol / L, and the concentration of ascorbic acid is 0.5mol / L to obtain leachate and leach residue;
[0047] (3) the vanadium content is detected in the leach solution that step (2) obtains, and the extraction rate of vanadium reaches 93.45%, and the leach solution is blue, with VO 2+ Ion-based, the pH is adjusted to 10 with ammonia water, and the ammonium vanadate precipitate is obtained by static separation, and the vanadium pentoxide product is obtained by cooling and crystallizing the ammonium vanadate at 600°C for calcin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com