Conical nanostructures on substrate surfaces, in particular optical elements, methods for the production thereof and use thereof
A substrate surface and nanostructure technology, applied in the process for producing decorative surface effects, microstructure technology, microstructure devices, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to manufacture columnar and conical structures, and achieve the possibility of wide application Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
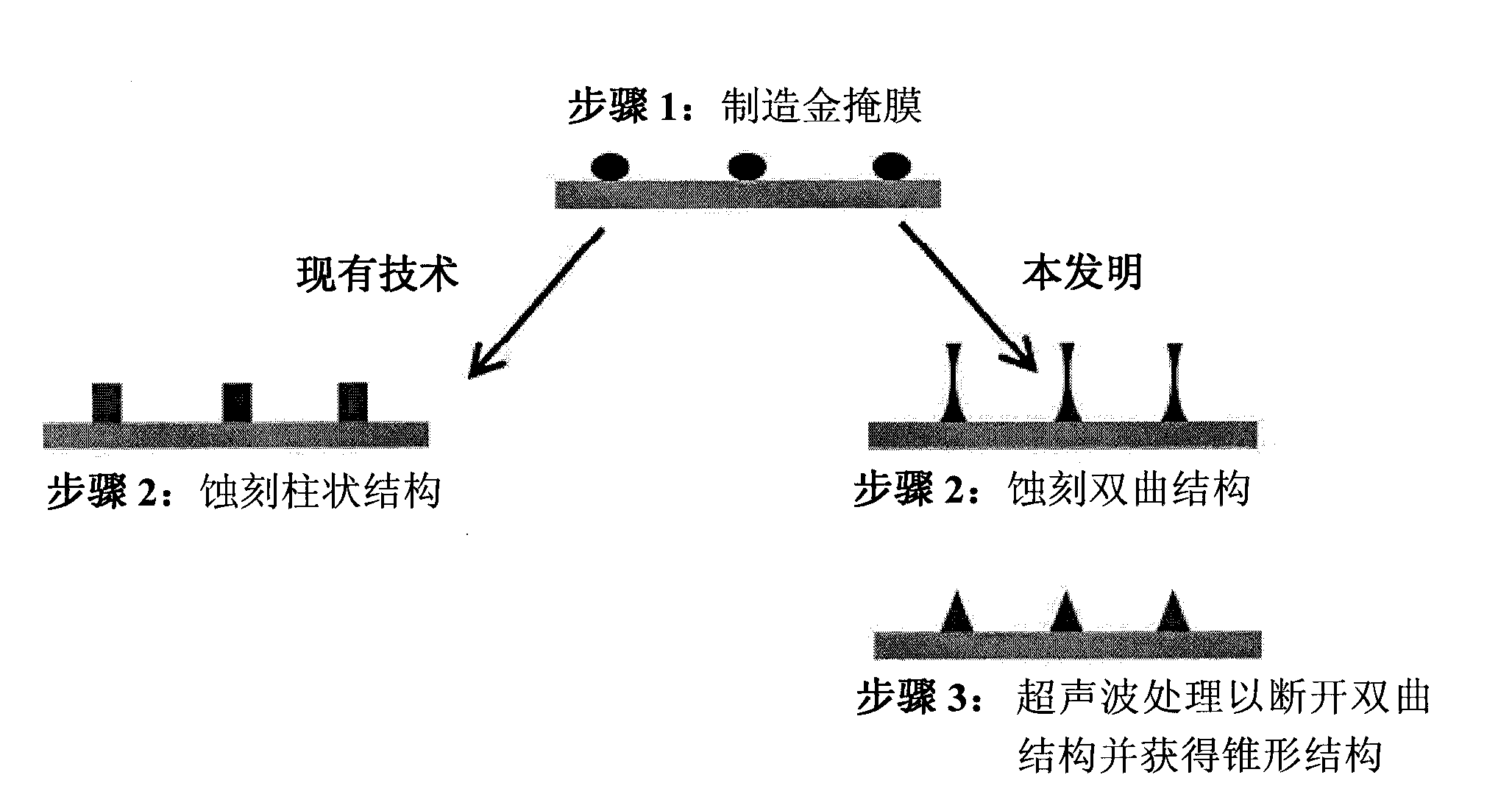
[0034] Creation of tapered nanostructures on substrates with gold nanoparticle alignment
[0035] 1. Provide the substrate surface
[0036] First, the surface of a substrate, such as quartz glass, is covered with gold nanoparticles in a defined arrangement by means of micellar nanolithography. In this step, the reports described in EP 1 027 157 B1, DE 197 47 815 A1 or DE 10 2007 017 032 A1 can be followed. The method involves depositing a micellar solution of a block copolymer such as Polystyrol(n)-b-Poly(2-vinyl-pyridin(m) in toluene) on a substrate, for example by dip coating, whereby the surface Forms an ordered membrane structure of polymer blocks. The micelles in solution contain gold salts, preferably HAuCl 4 , which were reduced to gold nanoparticles with the polymer film after deposition. The reduction can be carried out chemically with hydrazine, or with the aid of high-energy radiation such as electron radiation or light. The polymer film is preferably removed af...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Characterization of Nanostructures
[0053] From the nanostructures obtained according to the invention and the nanostructures of the prior art, photographs were taken at different tilt angles using a scanning electron microscope.
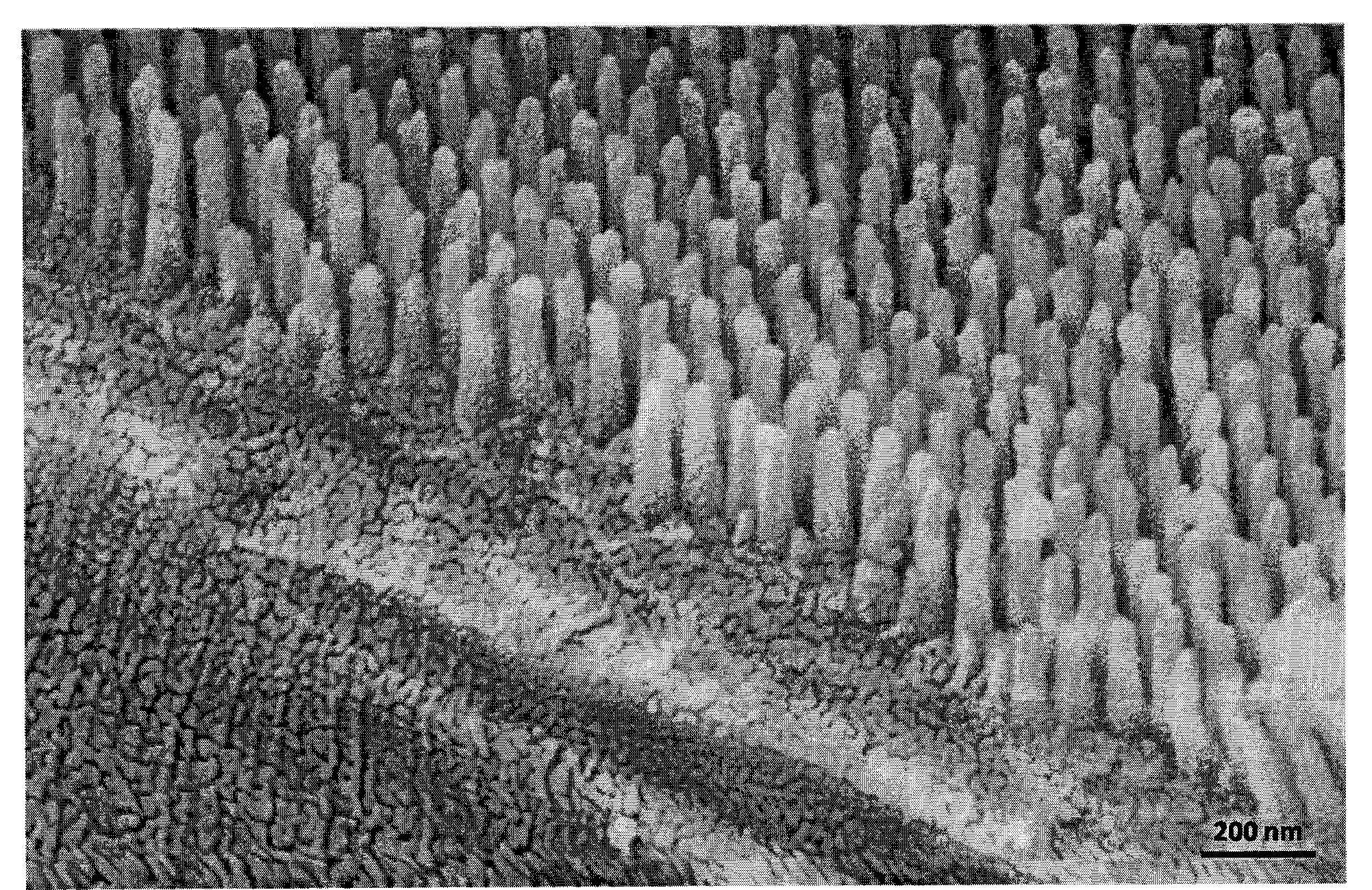
[0054] Figure 2a Shown is a scanning electron micrograph of etched cylindrical nanostructures at a tilt angle of 20°, which was produced using a method similar to that described in DE 2007 014 538. The method was changed slightly (other etch chemistries, multiple etch steps) so that deeper structures could be produced. The etching conditions specifically called by the old method cannot produce structures below 120nm. The height of the pillars is about 250 nm and the diameter is about 50 nm. Its average distance is about 80nm. Figure 2b Shown is a magnified side view of the same structure at a 45° angle. Make scratches on the surface with the aid of a glass knife so that the shape can be seen at a glance.
[0055] image 3 Shown is a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com