Current detection circuit
A current detection circuit and circuit technology, applied in the direction of measuring current/voltage, measuring device, measuring electrical variables, etc., can solve difficult integrated circuit applications, prominent cost problems of rectifier bridges and diodes, loss of AC signal amplitude and interference conditions, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of easy low-cost integration, easy and accurate phase identification, and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
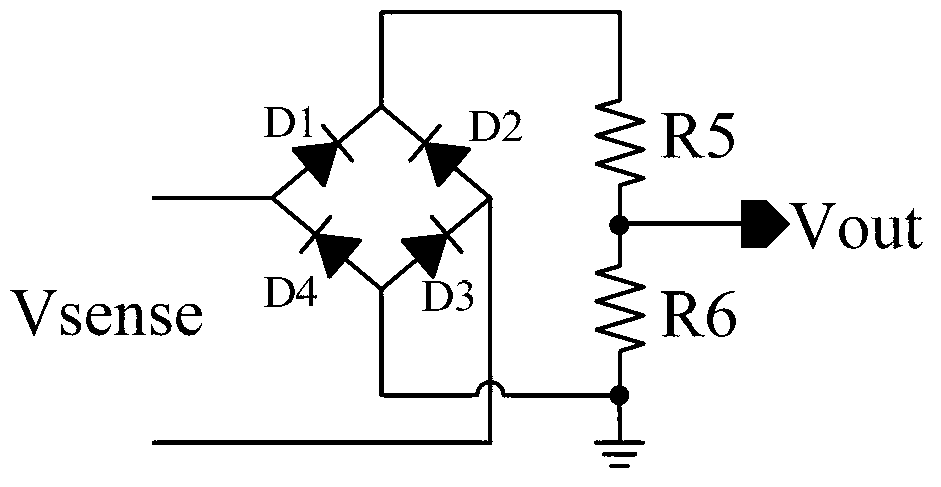
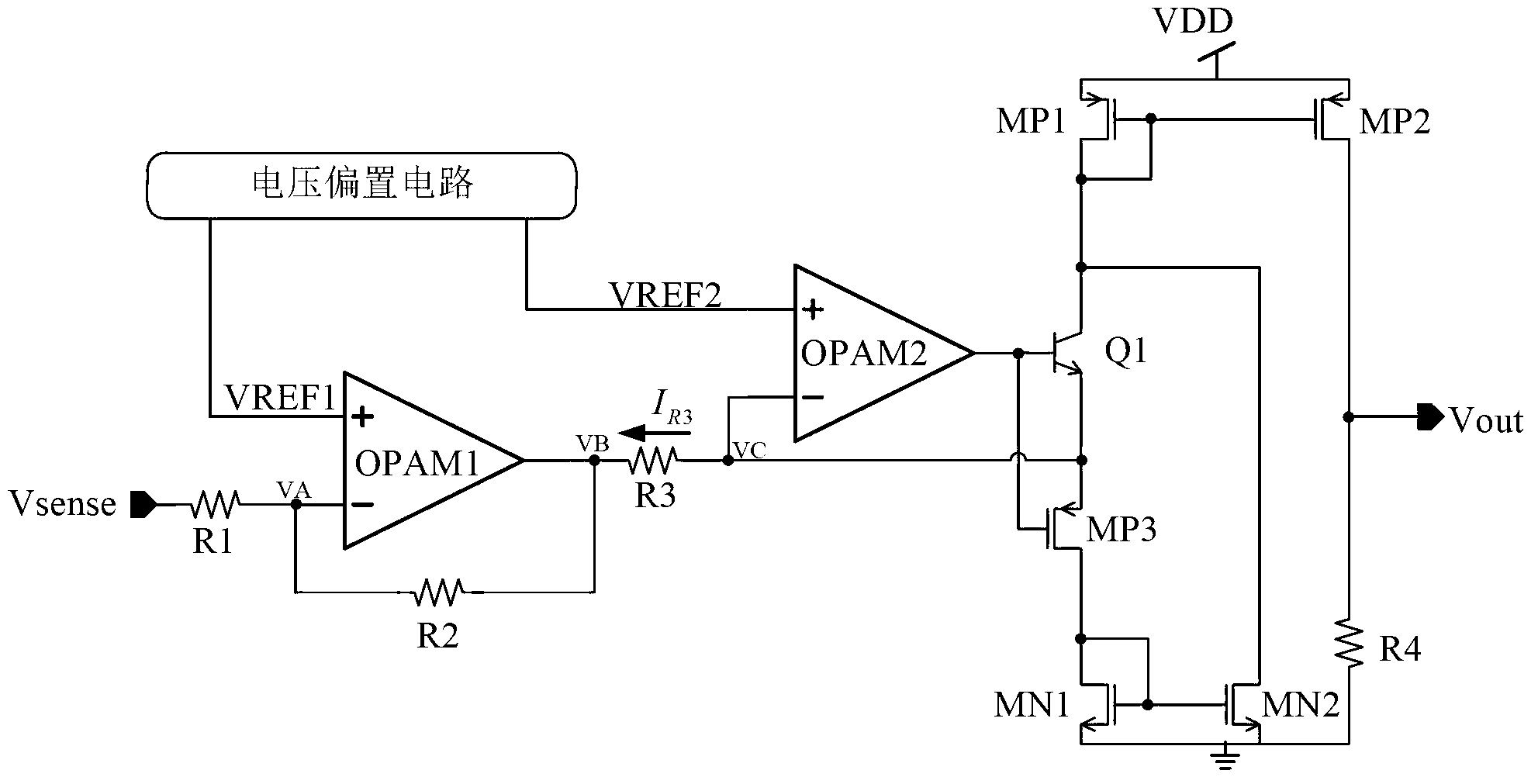
[0016] Embodiment one: if figure 2 As shown, the current detection circuit specifically includes: a voltage bias circuit, a first amplifier OPAM1, a second amplifier OPAM2, a first resistor R1, a second resistor R2, a third resistor R3, a fourth resistor R4, a first NMOS transistor MN1, The second NMOS transistor MN2, the first PMOS transistor MP1, the second PMOS transistor MP2, the third PMOS transistor MP3 and a switch element, wherein the voltage bias circuit provides the amplifier OPAM1 and the amplifier OPAM2 with the first reference voltage VREF1 and The second reference voltage VREF2 is respectively input to the positive input terminals of the amplifiers OPAM1 and OPAM2, the first terminal of the first resistor R1 is used as the input terminal of the current detection circuit for inputting the signal Vsense to be detected, and the second terminal of the resistor R1 Connect the negative input terminal of the amplifier OPAM1 and the first terminal of the resistor R2, th...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment two, such as Figure 4 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the second amplifier OPAM2 at this time uses MOS transistors as the differential pair of transistors, and the switching element uses NMOS transistor MN0, wherein the gate of MN0 is used as the first end of the switching element, and the source is used as the first end of the switching element. The second end and the drain of the switch element are used as the third end of the switch element. Here, using the switching element of the MOS tube will reduce the distortion of the detection signal and improve the accuracy of the current detection. The principle and working process of the second embodiment are the same as those of the first embodiment, and will not be described in detail.
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment three, such as Figure 5 As shown, an NMOS transistor MN3 is connected in series between the output terminal of the second mirror circuit and the input terminal of the first mirror circuit, and its gate can be connected to the third reference voltage VREF3. This structure will reduce the mirror deviation of the second mirror circuit and further improve the accuracy of current detection, which can also be applied to the second embodiment. The principle and working process of the third embodiment are the same as those of the first embodiment, and will not be described in detail.
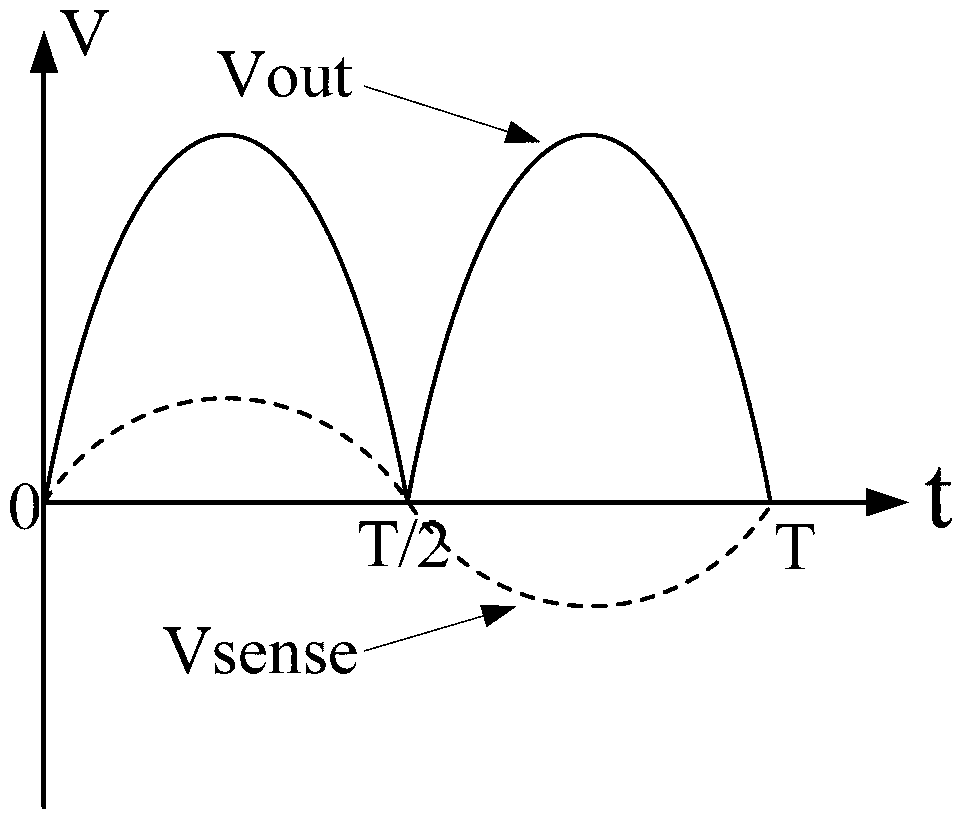
[0053] The current detection circuit with full-phase current detection function proposed by the present invention uses the amplifier to judge the phase, and the mirror image process of the current mirror realizes the direction change processing of the current, and completes the following steps: image 3 The rectified linearized amplification function is shown. The current detection ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com