WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) indoor positioning method based on subregion information entropy gain
An indoor positioning and information entropy technology, applied in the field of WLAN indoor positioning, can solve the problems of removal, poor positioning ability in other areas, and unfavorable partial area positioning.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
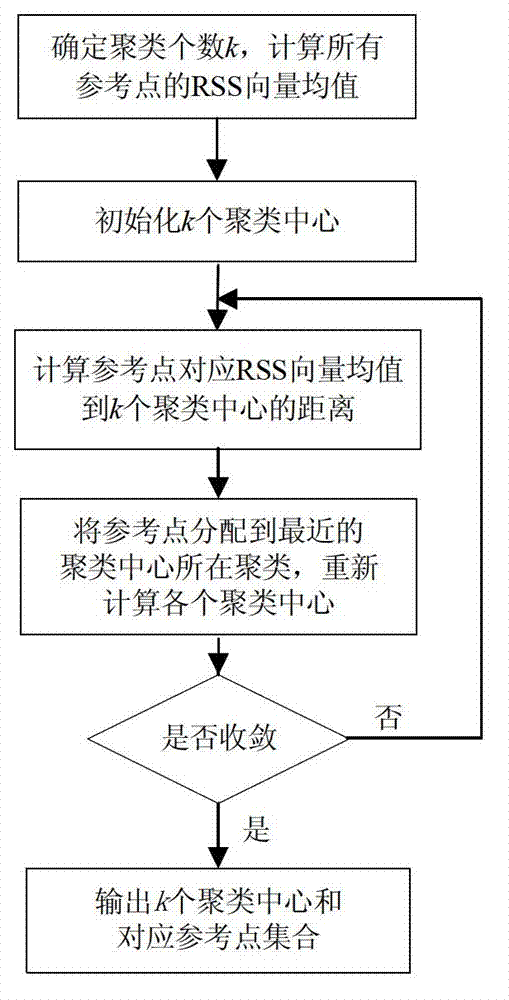
[0049] The specific embodiment one, based on the WLAN indoor positioning method of partition information entropy gain, it is realized by the following steps:
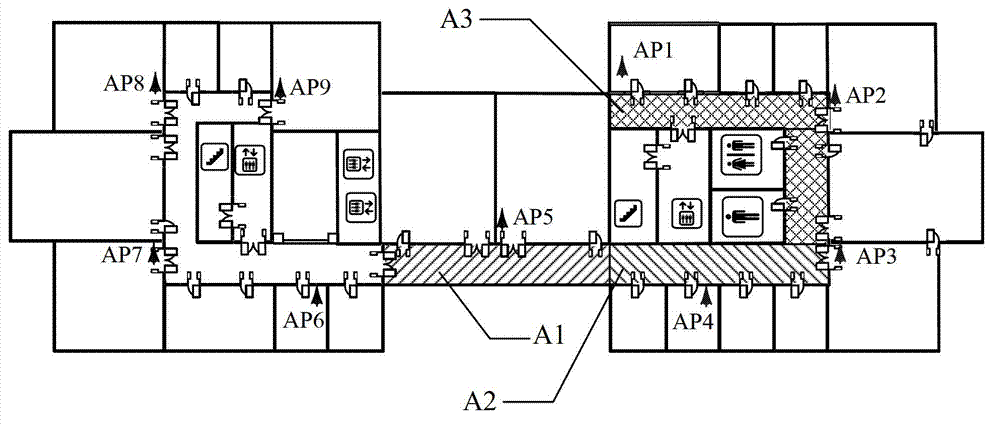
[0050] Step 1. Arrange m access points (APs) (APs) for the indoor environment j ,1≤j≤m), ensuring that any point in the environment is covered by signals from two or more APs;
[0051] Step 2. Set reference points evenly in the indoor environment, choose a reference point as the origin to establish a rectangular coordinate system, obtain the coordinate positions of each reference point in the rectangular coordinate system, and use the signal receiver to collect and collect the coordinates of each reference point on each reference point. Record the received signal strength RSS value k times from each AP and perform corresponding data processing;
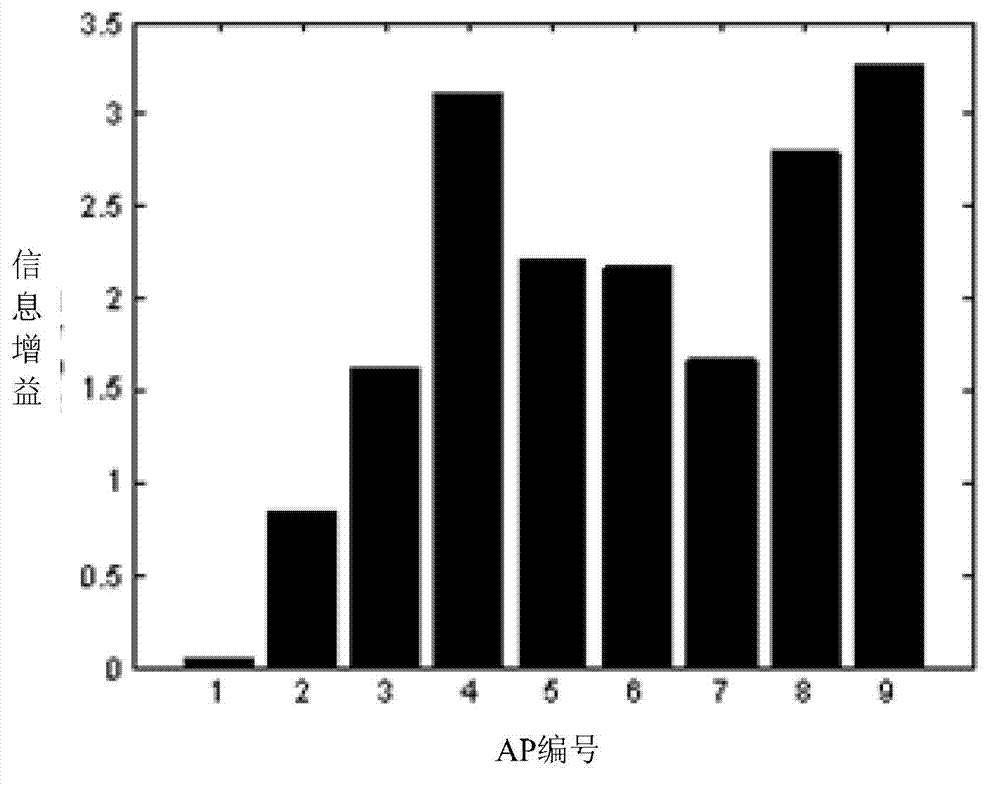
[0052] Step 3, according to the K-means clustering algorithm, the indoor positioning environment is divided into K sub-areas, and the received signal strength RSS values of ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0056] Specific embodiment 2. This specific embodiment is a further limitation of the WLAN indoor positioning method based on partition information entropy gain described in specific embodiment 1. In step 2 of specific embodiment 1, using signal reception at each reference point The computer collects and records the received signal strength RSS value k times from each AP and performs corresponding data processing. The specific steps are as follows:
[0057] Step A1: Obtain a k×m order matrix for each reference point, and the i'th row and j'th column of the matrix represent the RSS value received from the jth AP in the i'th collection;
[0058] Step A2. Add all the elements in the k×m order matrix column vector obtained by each reference point to obtain a value, and then divide this value by k, so that each reference point obtains a 1×m vector, For each reference point, this vector is called the feature vector of the reference point, and the jth element in the vector (that is, ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0060] Specific embodiment three. This specific embodiment is a further limitation of the WLAN indoor positioning method based on partition information entropy gain described in specific embodiment two, and the indoor positioning according to the K-means clustering algorithm described in step three in specific embodiment one The specific steps for dividing the environment into K sub-regions are:
[0061] Step B1, each location fingerprint in the Radio Map, that is, the feature vector should be represented by the RSS mean value vector on the corresponding reference point. Input the eigenvectors of all reference points measured in step A2 and the number of subregions K; in order to avoid the negative impact of the randomness of the initial cluster center selection on the clustering algorithm, the data obtained from step A2 are uniformly selected according to the physical space position The RSS values of K reference points (that is, the eigenvectors of each reference point) are...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com