Diagnosis of gluten-induced autoimmune diseases
An autoimmune, gluten-based technology, applied in disease diagnosis, anti-enzyme immunoglobulin, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problem of not considering genes, deletions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0301] Example 1: Materials and methods
[0302] 1.1 Molecular Modeling
[0303] In human TG2 (PDB code: 1KV3)[ Liu S et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(5):2743-7.]Residues 1-14, 44-45 and 123-132 are missing from the crystal structure, however, in the TG3 structure (PDB code: 1VJJ) [Ahvazi B et al., EMBO J. 2002; 21(9) :2055-67.], the corresponding region is visible and, therefore, used for modeling of full-length TG2. Homology models were constructed using the multiple template option of the Modeller [Sali A, Blundell TL, J Mol Biol. 1993;234(3):779-815.] program. Graphical analysis was performed on a Silicon Graphics Fuel workstation using the Sybyl program package (Tripos, St. Louis, MO), a study was performed to find amino acids that were located close enough to each other but belonged to different domains. In particular the interface of the core domain and the N-terminal (I) domain, and the interface of the core domain and the C-terminal (IV) domain were s...
Embodiment 2
[0359] Example 2: Pre-experiment for positioning celiac disease antigen epitope
[0360] Binding of celiac antibodies is associated with the calcium-binding site of TG2
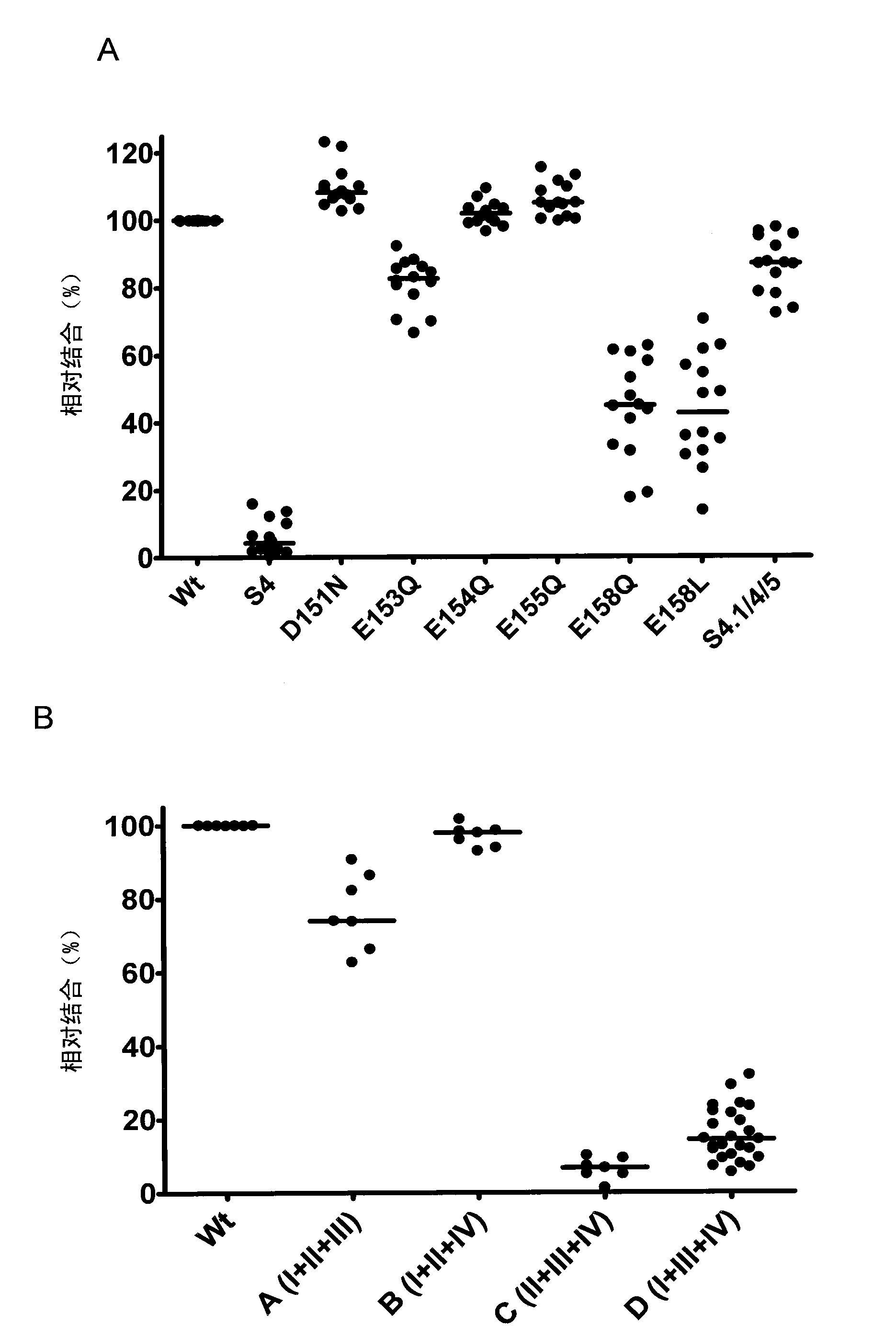
[0361] In the detection of Ca2 + In the process of binding to human TG2, we found two negatively charged surface sheets on the core domain, which are adjacent to each other and can serve as Ca2 + binding site. Multiple mutations of acidic glutamic acid and aspartic acid residues to neutral glutamine and asparagine at position 4 (151DSEEERQE158 → 151NSQQQRQQ158) or position 5 (434DERED438 → 434NQRQN438), resulting in each TG Molecularly bound Ca 2+ The number of ions was reduced from 6 to 3, and was either largely (11.6±-8.5% bound by residues at site 4 compared to wild-type TG2) or moderately (11.6 ± -8.5% at site 5) in an enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA). , 51.3±16.0%) weakened the binding of celiac disease patient serum samples. These ELISA assays used serum samples taken from 62 celiac disease pa...
Embodiment 3
[0371] Example 3: Effect of mutations in putative celiac epitopes and associated surface regions
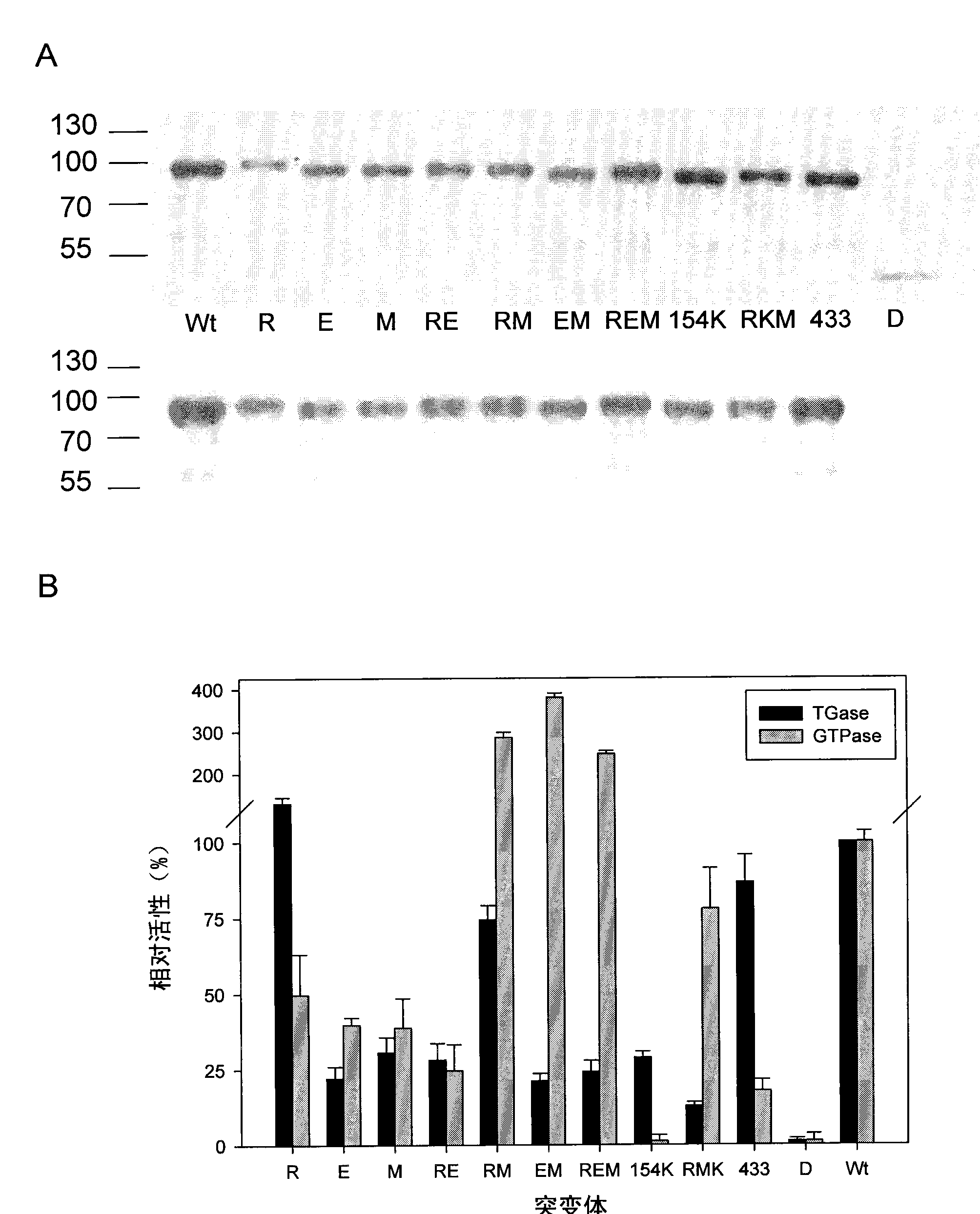
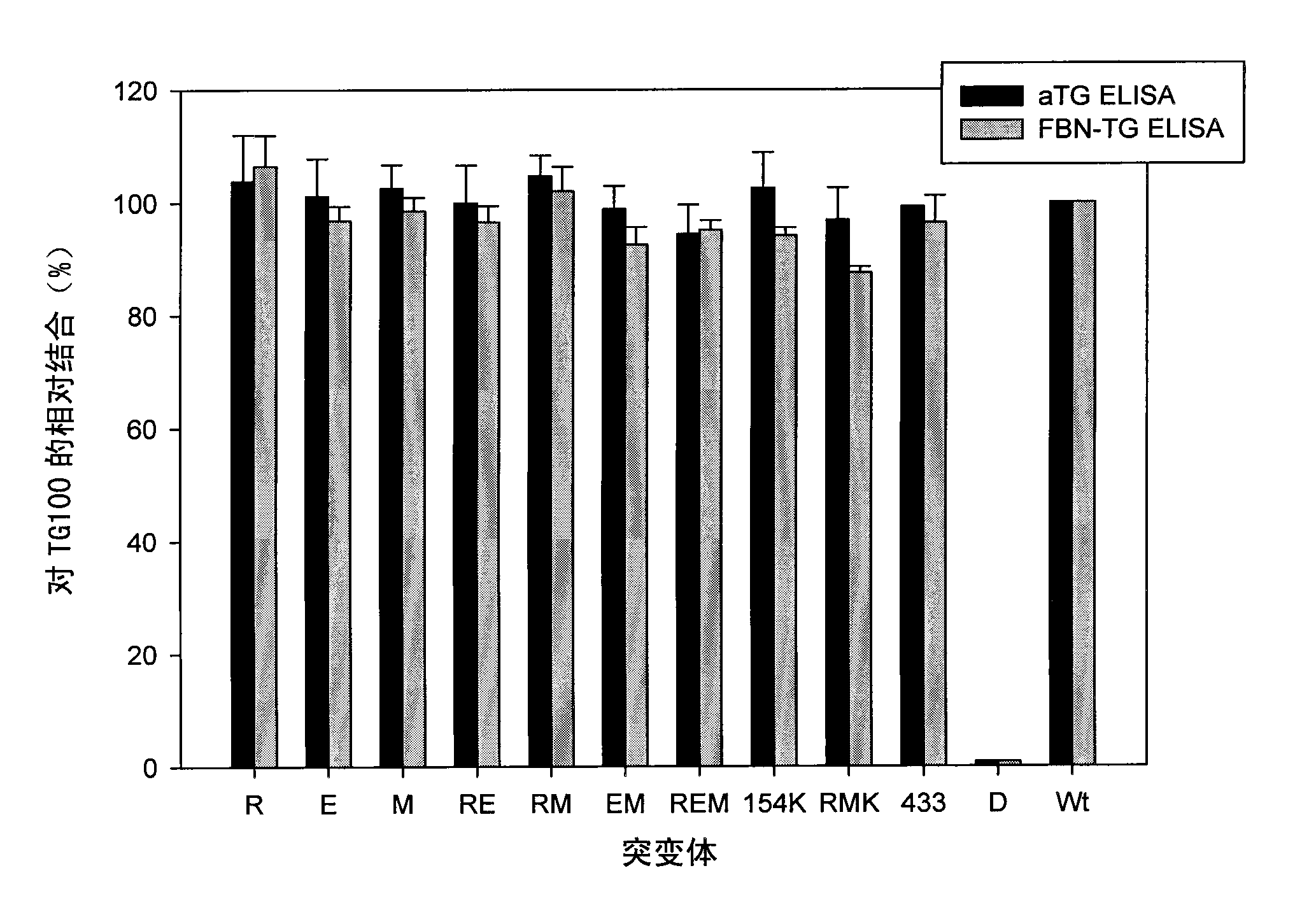
[0372] Based on preliminary results and computational analysis, within a large group of amino acids, six amino acids (R19, D151, E153, E154, E155, M659) were identified that are on or adjacent to the surface of TG2 associated with position 4, and are sufficiently close to each other that it is possible to form complex epitopes. These residues were changed either individually (single mutants) or together (double and triple mutants) by site-directed mutagenesis to serine, or in the case of acidic residues, to its neutral homologue.
[0373] We made the following point mutant TG2 molecules: E153S(E), R19S(R), M659S(M) or combinations of the respective mutations (D151N / E154Q / E155Q, RE, EM, RM, REM, E154K / R19S / M659S[RKM ]), and a large set of serial patient serum samples (n=76) were used to detect the protein. The relative amount of bound antibody can be calculated by comparison w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com