Synchronous processing method based on CMMB signals
A synchronization processing and signal technology, applied in synchronization devices, baseband system components, digital transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as reduced effect and poor estimation effect, and achieve the effect of improving synchronization accuracy and improving synchronization performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
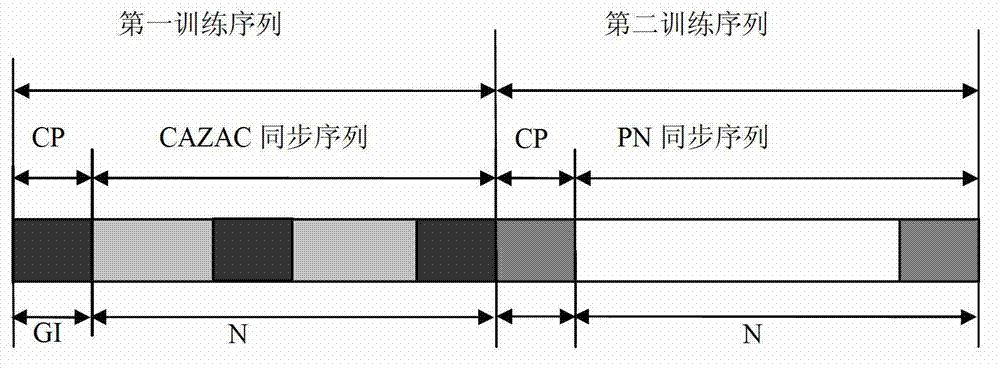
[0047] The structure of the CMMB synchronization signal of the present invention is as follows figure 2 As shown, it is composed of a first training sequence and a second training sequence. The first training sequence includes a constant envelope zero autocorrelation CAZAC sequence of length N and a cyclic prefix CP of length GI, and the second training sequence includes A PN sequence of length N and a cyclic prefix CP of length GI. The parts with the same gray scale represent the same value.
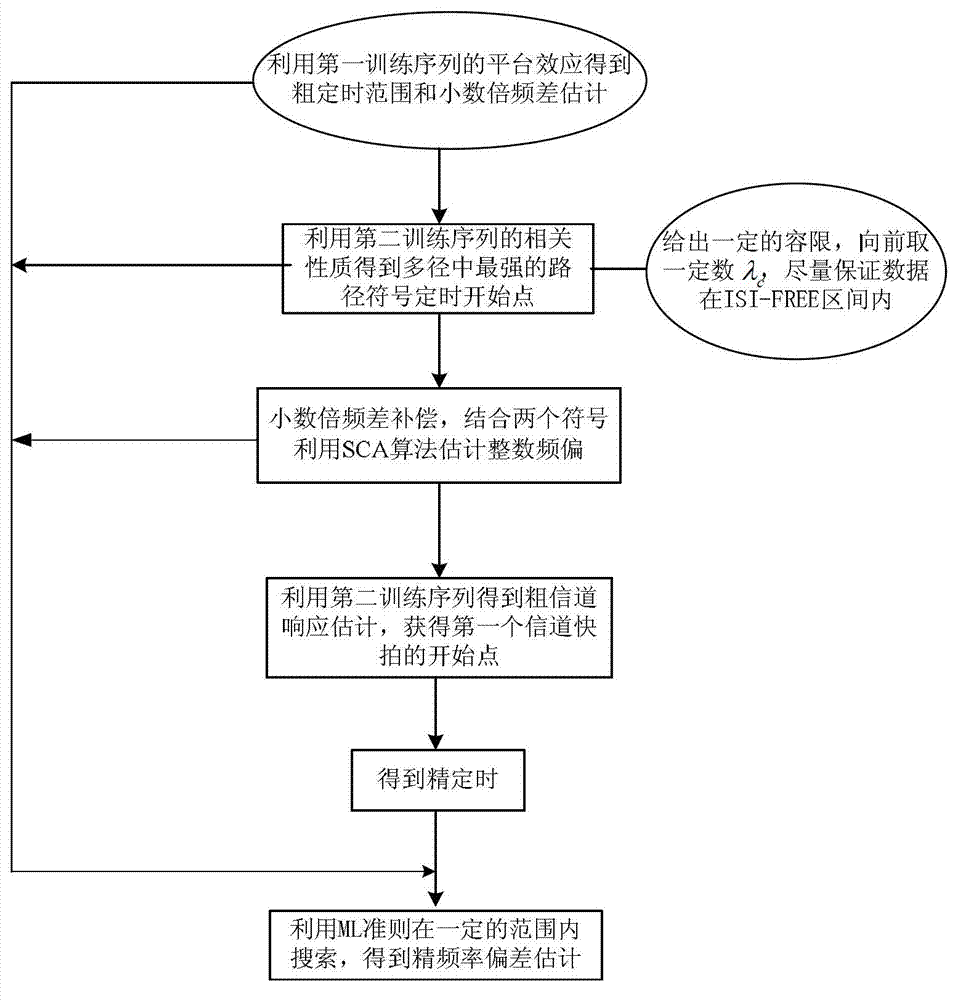
[0048] The embodiment process is attached image 3 As shown, the method of the specific embodiment includes the following steps:
[0049] 1. Use the properties of the CAZAC sequence part in the first training sequence to complete rough timing estimation and rough estimation of fractional frequency difference:
[0050] Suppose the received signal sequence of a frame is discretely expressed as r(n), n=1,2...,N.
[0051] Use the autocorrelation of the same repeated part of the CAZAC sequence to ...
specific Embodiment
[0113] The method of the specific embodiment includes the following steps:
[0114] a) From the received signal, use the properties of the CAZAC sequence part in the first training sequence to complete rough timing estimation and rough estimation of fractional frequency difference. The symbol rough timing offset estimation expression is:
[0115] θ opt =mean(U)
[0116] Among them: mean(U) represents the average of all values in U, and U is the peak plateau range.
[0117] U=(d |abs(M(d))≥0.95C 1 ,d∈{1,2…,P}}
[0118] M(d)=|P(d)| 2 / (R(d)) 2 C 1 = arg max d ( M ( d ) )
[0119] P ( d ) = X k = 0 511 r ( d + k ) r * ( d + k + 512 ) R ( d ) = 1 2 X k = 0 1023 | r ( d + k ) | 2
[0120] Rough estimation of fractional frequency deviation Use symbol timing position θ opt P(θ opt ) Is obtained as shown in the following formula. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com