Materials and methods for prevention and treatment of viral infections
A virus infection and compound technology, applied in the direction of antiviral agents, pharmaceutical formulations, plant raw materials, etc., can solve the problems of resistance mutation weakening the efficacy of antiviral drugs, and difficulty in treating compounds.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
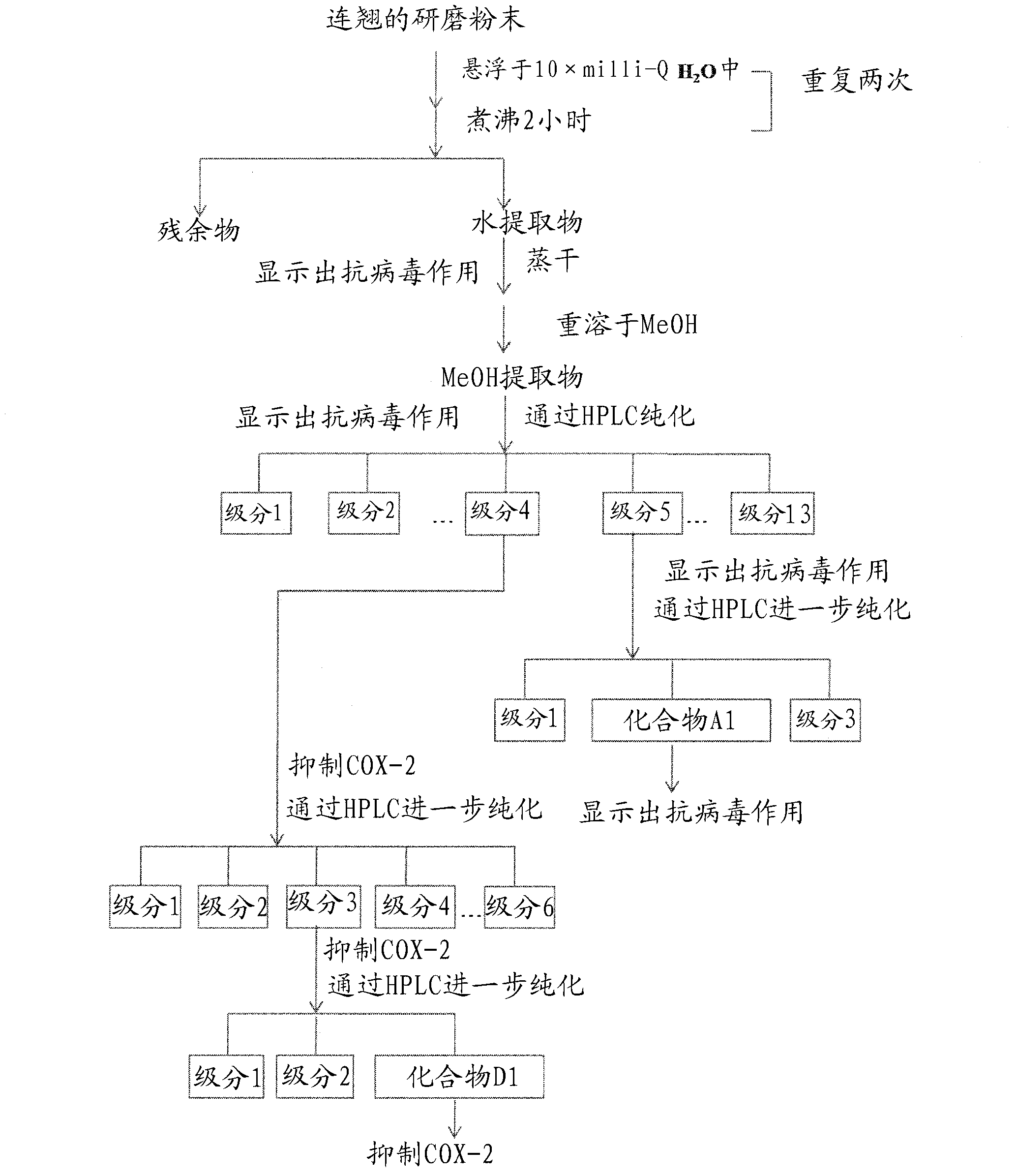
[0198] Preparation of Yinqiaosan (YQS) Extract
[0199] The YQS extract was prepared according to Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2005). Briefly, 3 g of mint and 2 g of nepeta were extracted twice with 20 times milli-Q water at reflux for 1 h. Volatile oil and water extracts were collected. The residue was combined with five other herbs including forsythia (5g), burdock seed (3g), tempeh (2.5g), bamboo leaves (2g) and licorice (2.5g), followed by 10-fold milli-Q The water was refluxed for 2 hours for extraction twice. Collect the supernatant and combine it with the previous aqueous extract. The resulting extract was then lyophilized under reduced pressure. The dried paste was combined with honeysuckle (5 g) and bellflower (3 g), and then extracted three times with 10 times MeOH. About 5 g of MeOH extract were obtained.
[0200] Fractionation of YQS Extracts for Antiviral Bioanalysis
[0201] The MeOH extract of YQS was fractionated by reverse phase HPLC (Lichrospher 100RPC18EC 5...
Embodiment 1
[0226] Example 1-Extraction and Identification of Forsythiaside A and Jacarcarone
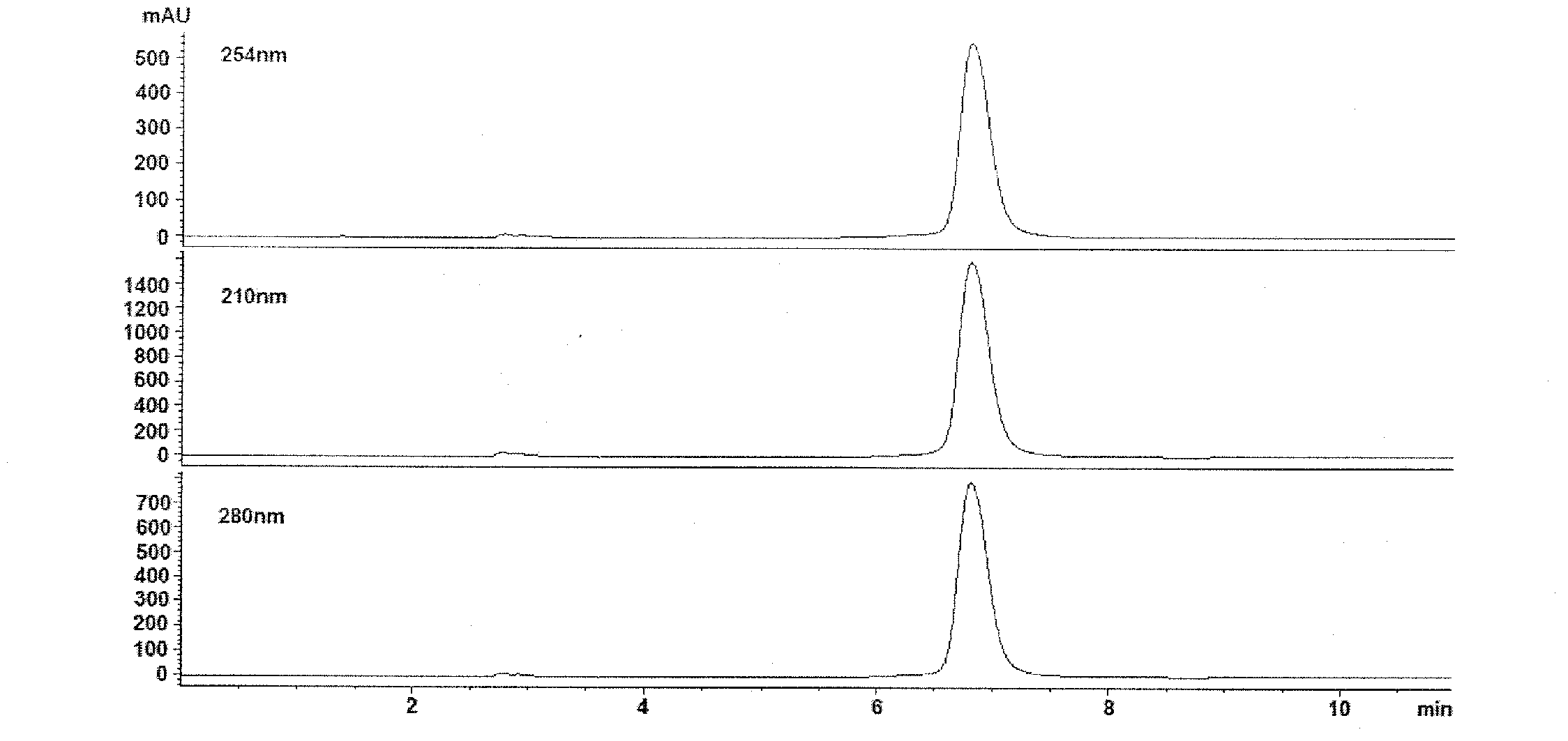
[0227] A light yellow powder was obtained by repeatedly purifying the MeOH extract prepared from Forsythia using reverse-phase HPLC. The detailed process is summarized in Figure 1.
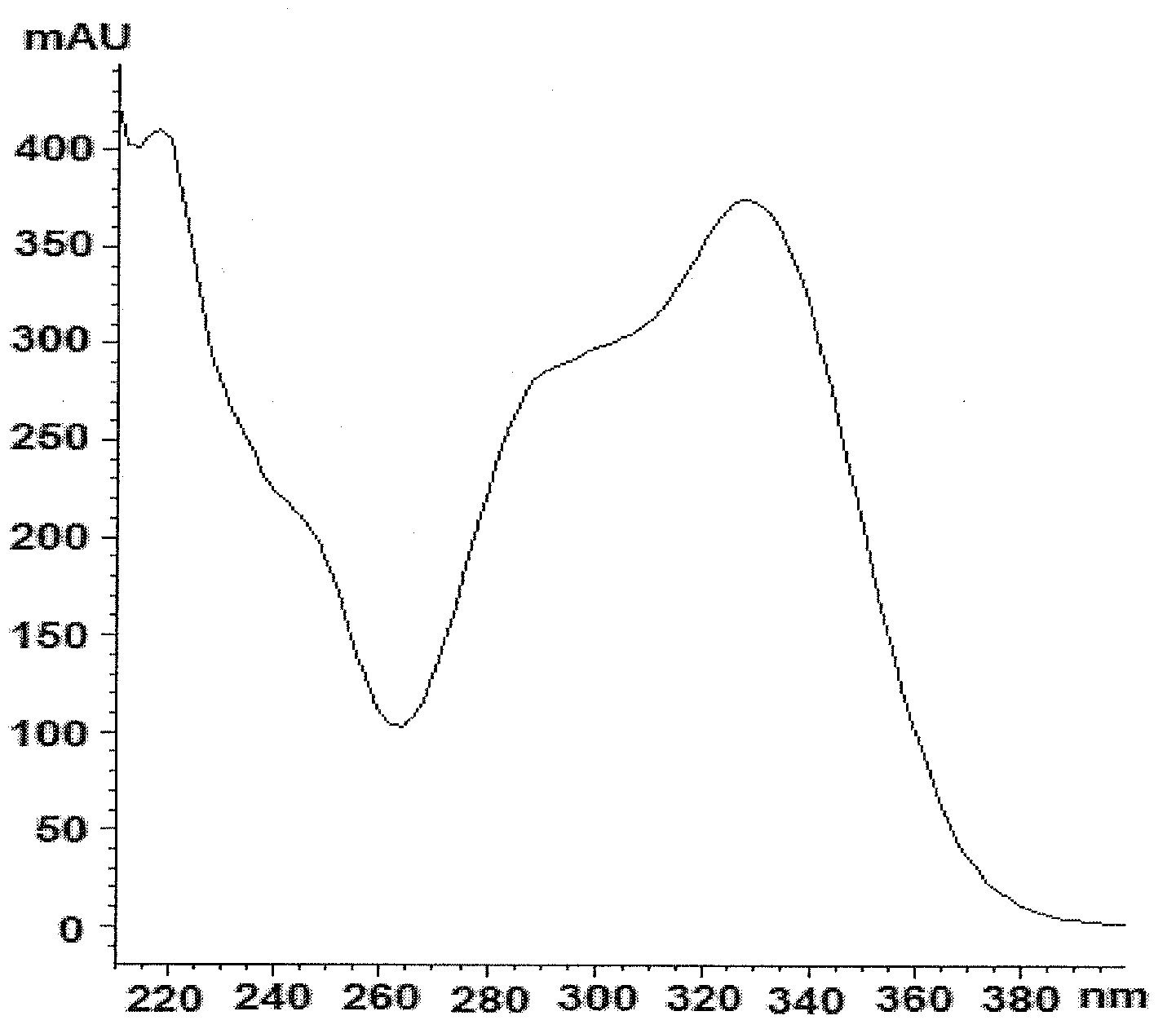
[0228] By bioactivity-guided purification using sequential HPLC, the antiviral molecule known as compound A1 eluted at approximately 6.8 min as a single compound (>95% pure) with UV absorbance maxima at 220, 290 and 330 (Fig. 2). Compound A1 13 The CNMR spectrum is shown in Figure 4, showing the following signals: δ 131.5 (C-1), 116.5 (C-2), 146.2 (C-3), 144.8 (C-4), 117.2 (C-5 ), 121.4(C-6), 72.4(C-α), 36.8(C-β), 104.6(C-1'), 75.3(C-2'), 76.0(C-3'), 72.5(C -4'), 74.9(C-5'), 67.8(C-6'), 102.4(C-1"), 72.1(C-2"), 72.4(C-3"), 74.1(C-3 ”), 70.0 (C-4”), 18.1 (C-5”), 127.8 (C-1”’), 115.2 (C-2”’), 147.0 (C-3”’), 149.9 (C- 4"'), 116.6 (C-5"'), 123.2 (C-6"'), 147.7 (C-7""), 114.8 (C-8"'), 168.4 (C-9"'). Compound A1 s...
Embodiment 2
[0230] Determination of the Cytotoxicity of Example 2-Forsythiaside A
[0231] After determining the inhibitory effect of forsythiaside A (compound A1) on influenza virus replication, the cytotoxicity of forsythiaside A (compound A1) was examined as follows. Briefly, Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells were 5 The density of cells / well was seeded in a 24-well plate and incubated for 18 hours, then forsythiaside A (compound A1) was added at a concentration of 100ug / ml, or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was added in the control.
[0232] At 37°C, 5% CO 2 After 48 hours of incubation under conditioned conditions, cell viability was measured by the thiazolium blue tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. First, MTT was added to the cells at a final concentration of 0.1 mg / ml. After 90 minutes of incubation, the culture supernatant was removed and each well was treated with isopropanol for cell fixation. The MTT metabolite formazan was dissolved in isopropanol with constant shaking for 5 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com