Light receiving subassembly
A sub-component, optical receiving technology, applied in electromagnetic receivers, coupling of optical waveguides, etc., can solve the problems affecting the signal quality of optical communication systems, and achieve the effect of improving optical communication quality and reducing optical energy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
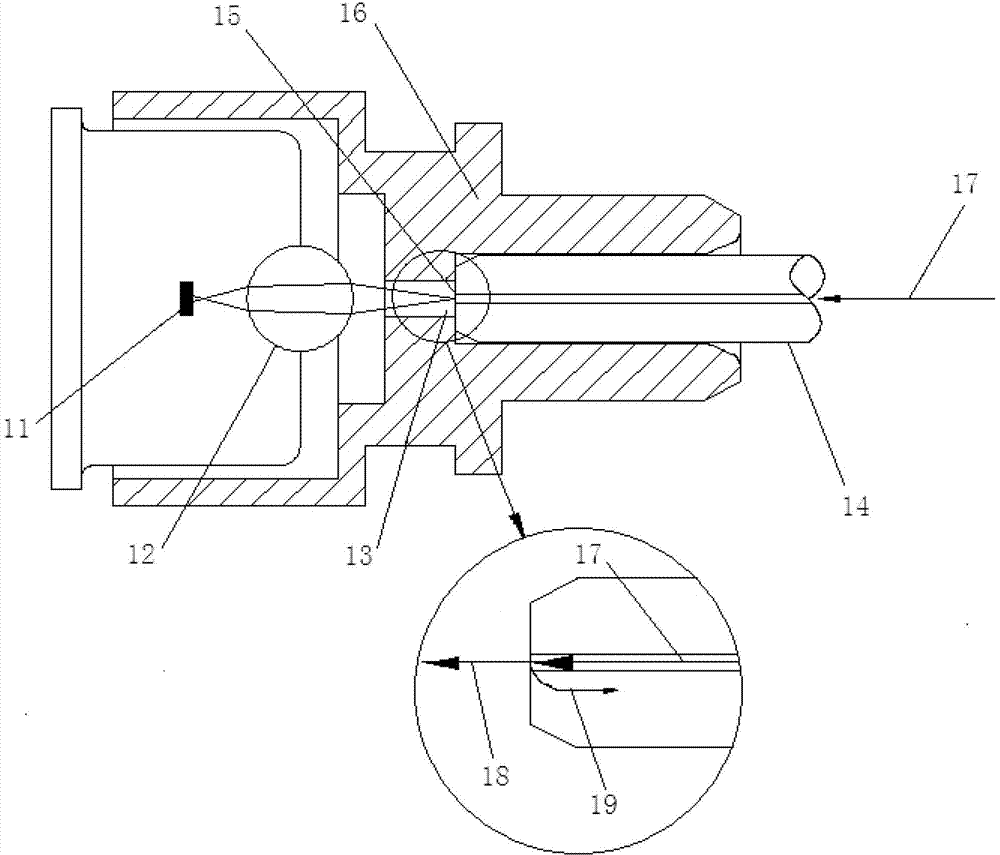
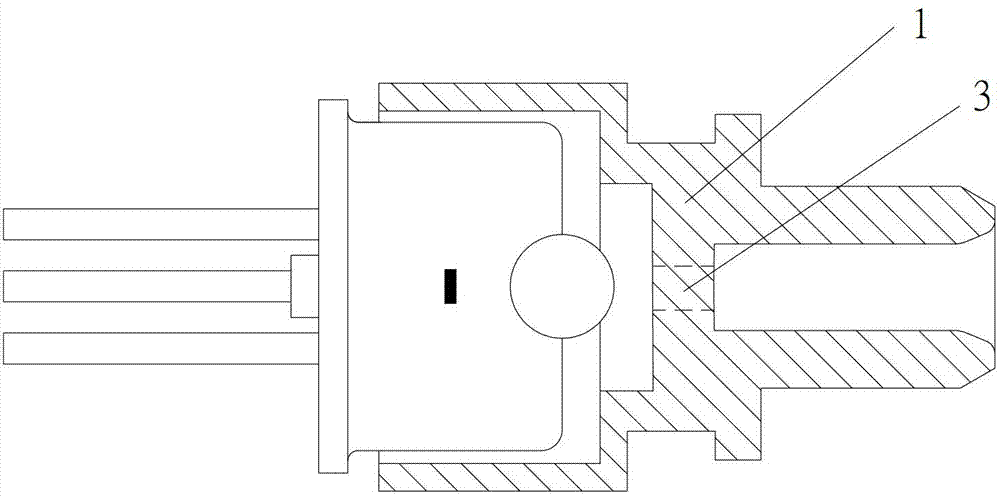
[0020] refer to figure 2 , the light-receiving subassembly listed in this embodiment includes a photodiode, a coupling lens, and an optical fiber connection sleeve 1. A through hole is provided on the optical fiber connection sleeve 1, and a filling block 3 is provided at the through hole. The filling block 3 is made of optically transparent material, and the filling block 3 is adapted to the through hole, that is, the filling block 3 and the optical fiber connection sleeve 1 realize seamless filling. Preferably, the filling block 3 and the optical fiber connection sleeve 1 are integrally formed by injection molding, which saves the process of assembling the filling block 3 and the optical fiber connection sleeve 1, and avoids the displacement caused by the filling block 3 and the optical fiber connection sleeve 1. The effect of reducing light energy returning to the optical fiber is not good. In addition, the filling block 3 and the optical fiber connection sleeve 1 are int...
Embodiment 2
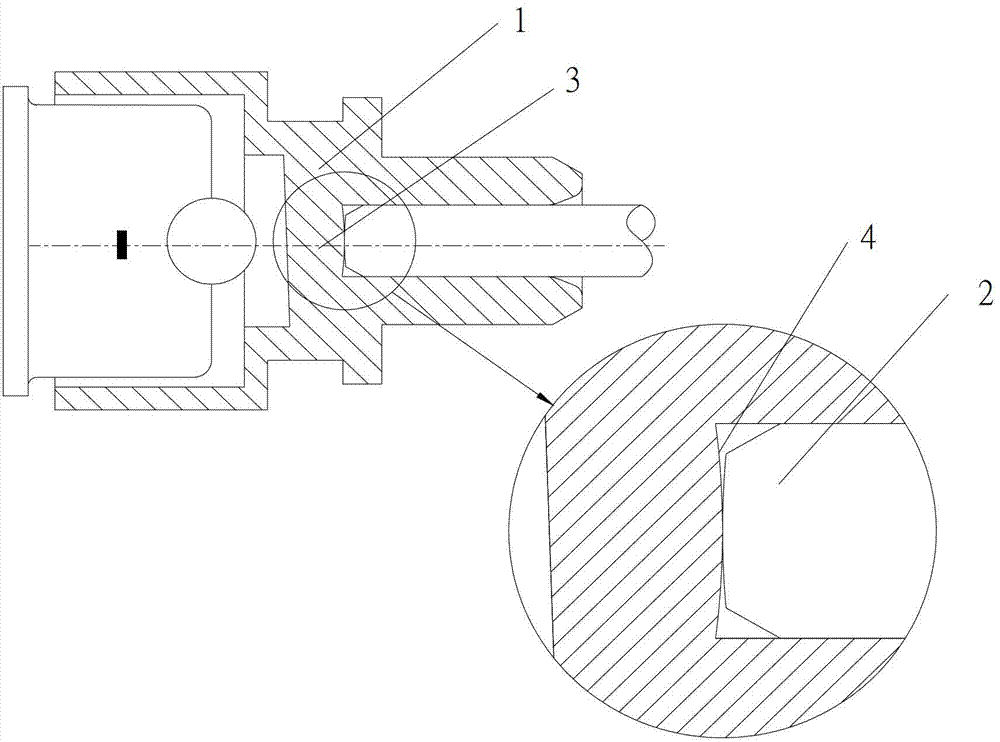
[0023] refer to image 3 , the light-receiving subassembly listed in this embodiment includes a photodiode, a coupling lens, and an optical fiber connection sleeve 1. A through hole is provided on the optical fiber connection sleeve 1, and a filling block 3 is provided at the through hole. The filling block 3 is made of optically transparent material, and the filling block 3 is integrally formed by injection molding with the optical fiber connection sleeve 1. The optical interface between the filling block 3 and the optical fiber 2 is the first optical interface 4, and the first optical interface 4 is a convex spherical surface, so that The contact between the optical fiber 2 and the first optical interface 4 is bump-to-bump contact, so that there is no gap between the optical fiber 2 and the filler block 3 (a gap means that there is air in the middle, which will reduce the transmission efficiency and increase the reflectivity), and reach the optical fiber. 2 is in the best co...
Embodiment 3
[0025] refer to Figure 4 The structure of the light-receiving subassembly listed in this embodiment is the same as that described in Embodiment 2, the difference is that the optical interface of the filling block away from the optical fiber is the second optical interface 5, and the second optical interface 5 is inclined plane. The light signal is reflected through the second optical interface 5 which is an inclined plane, which can further reduce the light energy reflected back to the optical fiber.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com