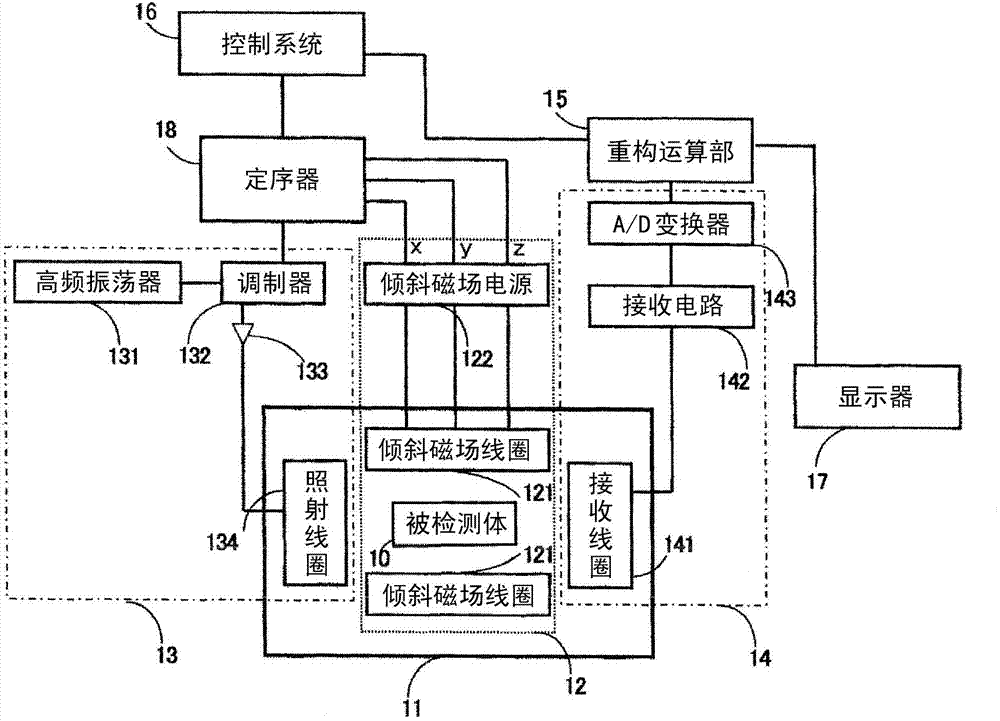
Magnetic resonance imaging device and method for modulating high frequency magnetic field pulses
A technology of magnetic resonance imaging and high-frequency magnetic field, which is applied in magnetic resonance measurement, measurement device, measurement of magnetic variables, etc., can solve problems such as image quality deterioration, and achieve the effect of good image quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
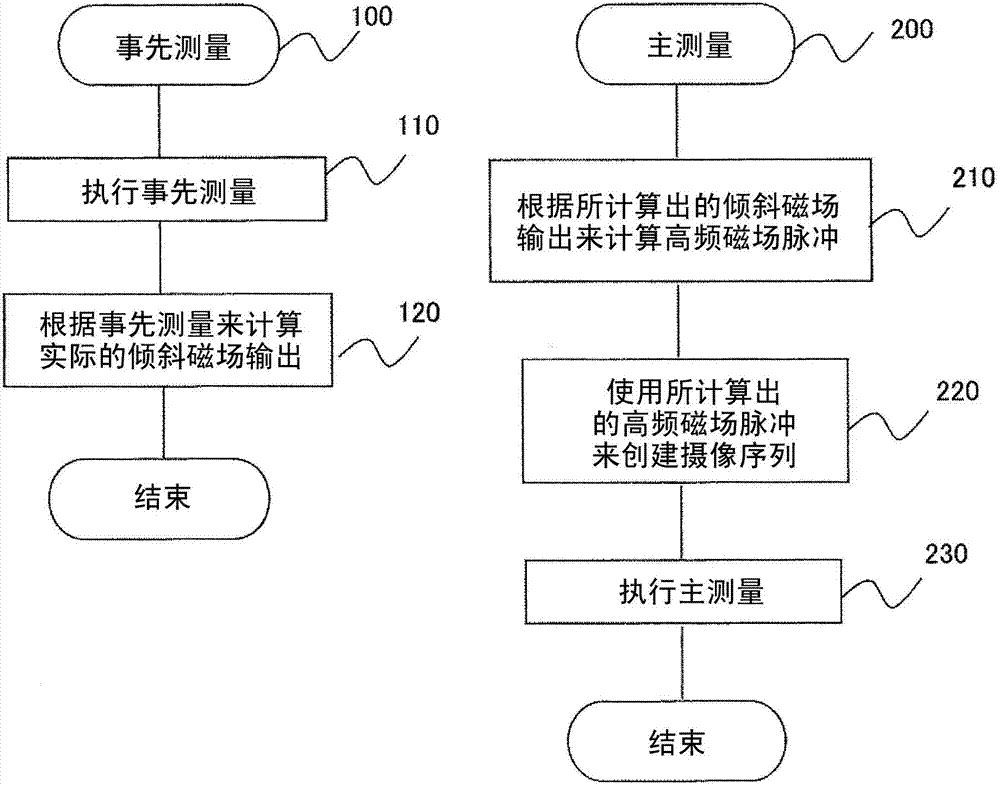
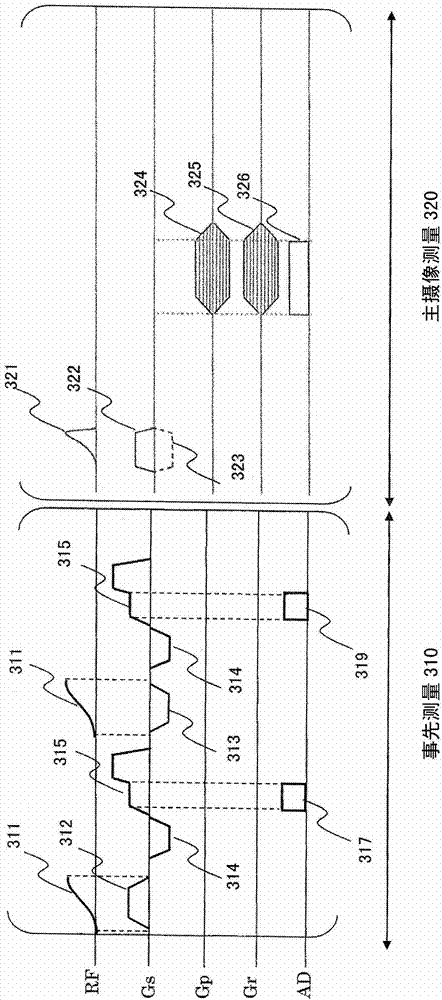
[0045] figure 2 Indicates the operation process of this embodiment, image 3 A pulse sequence diagram of the present embodiment is shown.
[0046] Such as figure 2 As shown, imaging in this embodiment is composed of pre-measurement 100 for measuring a gradient magnetic field pulse, and main measurement 200 using an RF pulse shape determined based on the result of the pre-measurement.
[0047] The previous measurement 100 is a measurement for calculating the output of the slice gradient magnetic field applied under the same conditions as the slice gradient magnetic field used in the main measurement 200, by image 3 The execution step 110 of the shown prior measurement pulse sequence 310 and the subsequent calculation step 120 of the gradient field output (response of the actual gradient field) constitute. The main measurement 200 is the measurement based on the UTE imaging sequence in this embodiment, and is composed of the following steps: the calculation step 210 using ...
no. 2 approach
[0098] Next, an embodiment in which the present invention is applied to an MRI apparatus that continuously performs imaging while changing slice selection conditions will be described. The continuous imaging targeted by this embodiment includes, for example, dynamic imaging in which imaging is performed while interactively changing slice sections and imaging conditions in accordance with subject movements such as joint bending motions, and switching from 3D imaging to 2D imaging. camera etc.
[0099] Figure 9 The imaging process of this embodiment is shown. In the present embodiment, in order to determine the shape of the RF pulse to be used in the main measurement prior to the main measurement, the pre-measurement of the response of the gradient magnetic field pulse is performed as in the first embodiment. That is, also in this embodiment, the same slice gradient magnetic field as that used in the imaging pulse sequence of the main measurement is used to perform image 3 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com