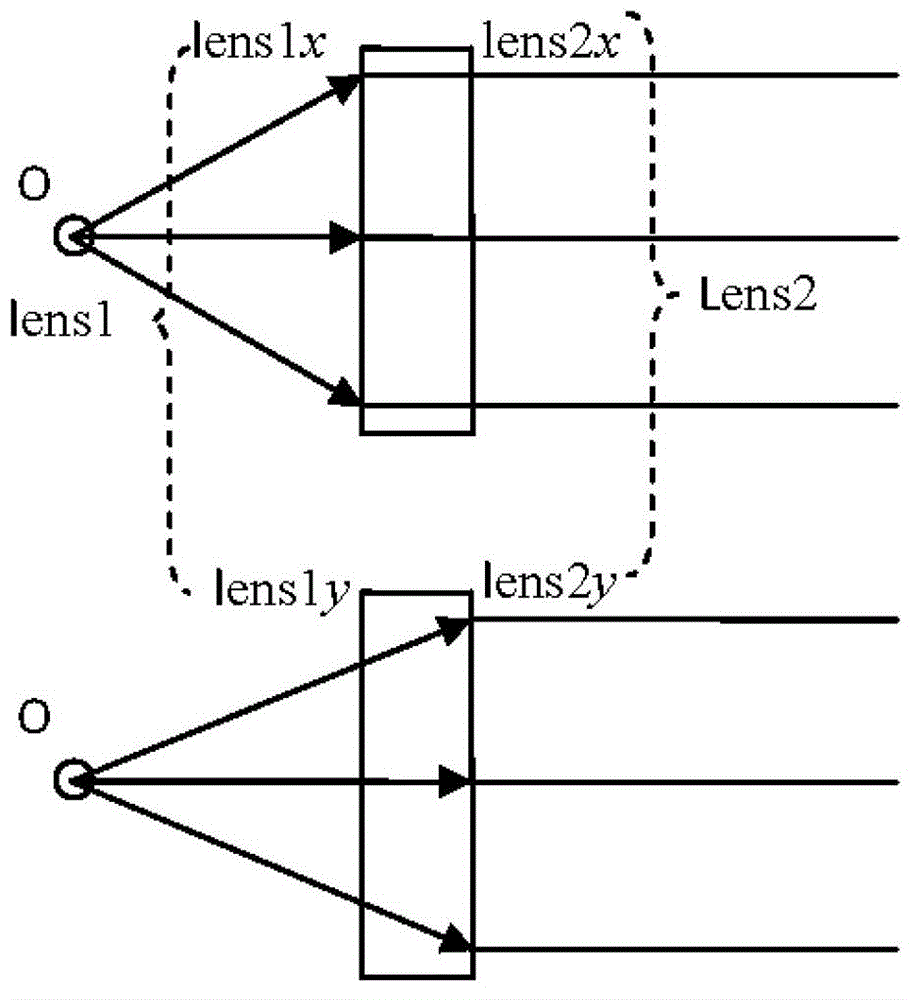
Device for shaping and collimating elliptic laser spots of semiconductor lasers
An elliptical spot and laser technology, applied in the field of optics, can solve the problems of large divergence angle, unrealized shaping, and many optical elements, and achieve the effect of less optical elements, small size, and meeting application requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
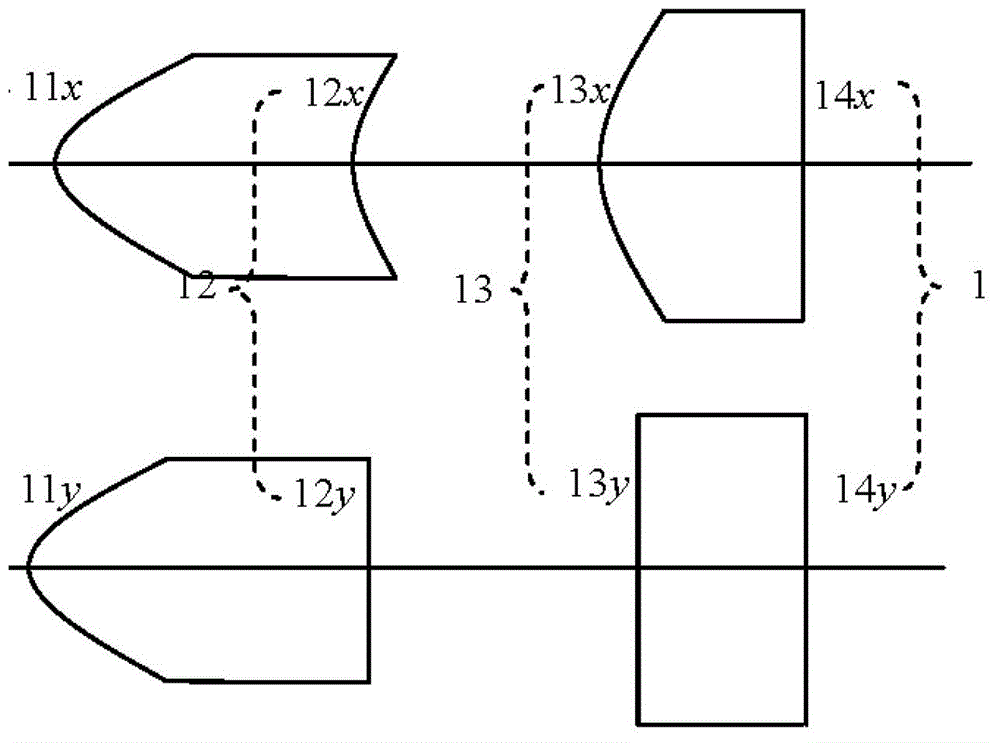
[0054] Embodiment 1 This embodiment adopts the above first kind of implementation scheme and figure 2 The lens shown is realized.
[0055] Since the diameter of the MEMS galvanometer is 1 mm, the beam section radius after the fast axis direction is collimated by the surface 11y ω 11y 0.5mm. In order to use Zemax to simulate the aspheric surface shape of surface 11, according to the law of paraxial optical propagation, firstly determine the radius of curvature of surface 11 and the distance from the beam waist to the apex of the surface. The specific calculation process is as follows:
[0056]
[0057]
[0058]
[0059]
[0060]
[0061] In the formula, ω is the beam section radius of the laser, and its subscript number (such as "11") represents the number of the surface, and the subscript " x ( y )" represents the slow axis (fast axis) direction, that is ω 11y is the beam section radius in the fast axis direction on the surface 11. ω 0 is the beam wais...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Embodiment 2 This embodiment adopts the above second implementation scheme and image 3 The lens shown is realized.
[0076] In this embodiment, the fast axis direction surface 21 y The calculation method of the radius of curvature is the same as in Example 1, namely r 21y = r 11y =0.715mm, d 0 =2.145mm, slow axis direction surface 21 x is flat. The light beam in the direction of the slow axis is collimated and passes through the surface 22 x to fulfill. Lens thickness and surface 22 x The formula for determining the radius of curvature is as follows:
[0077]
[0078]
[0079]
[0080] In this example, ω 11x =0.197mm, ω 12x =0.5mm, θ x =5 0 , n 0 =1, n =1.5, calculated d glass =5.206mm, r 22x =2.864mm.
[0081] The above parameters d 0 , d glass , r 21y、 r 22x As an initial parameter, the specific optimization process is similar to Embodiment 1, and the surface parameters of the two surfaces of the lens are obtained as follow...
Embodiment 3
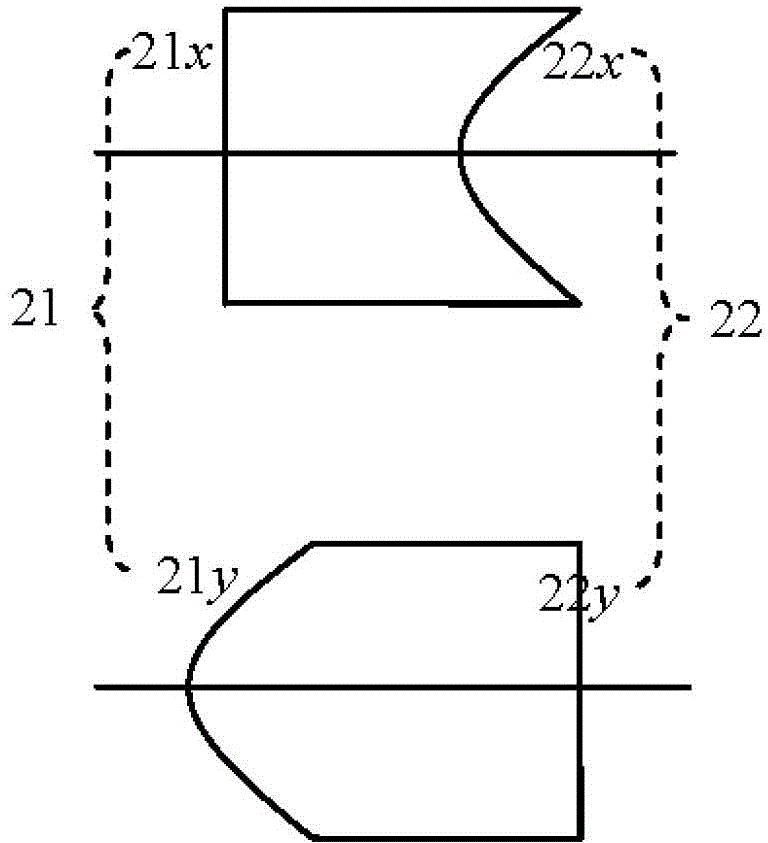
[0085] Embodiment 3 This embodiment adopts the above third implementation scheme and Figure 4 The lens shown is realized.
[0086] In this embodiment, the first surface 31 of the first lens is the same as the first surface 11 of the first lens in Embodiment 1, namely r 31 = r 11 =0.715mm, d 0 =2.145mm. The formula for calculating the distance between the second surface 34 of the second lens in the direction of the slow axis and the first surface 35 of the third lens is as follows:
[0087]
[0088] In the formula, d 34-35 is the distance between the focal coincidence position between the surface 34 and the surface 35 and the surface 34 . The thickness of the first lens d 1 =5mm, second lens thickness d 1 =3mm, the distance between the first lens and the second lens is d 32-33 =2mm. Concrete optimization process is similar to embodiment 1, and the parameters of three lens surfaces that obtain are as follows:
[0089]
[0090] Using POP to analyze the opt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com