Method for manufacturing copper PCB (Printed Circuit Board) circuit
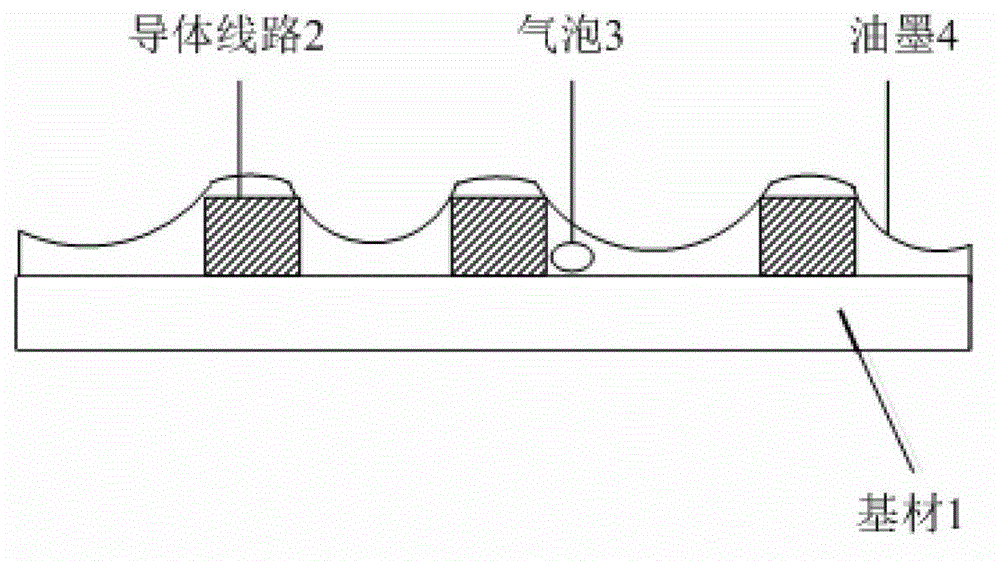
A technology for making PCB boards and circuits. It is used in the manufacture of printed circuits, removal of conductive materials by chemical/electrolytic methods, and printed circuits. It can solve problems such as cracked substrates, ink accumulation on both sides of the circuit, and threats to the reliability of PCB boards.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
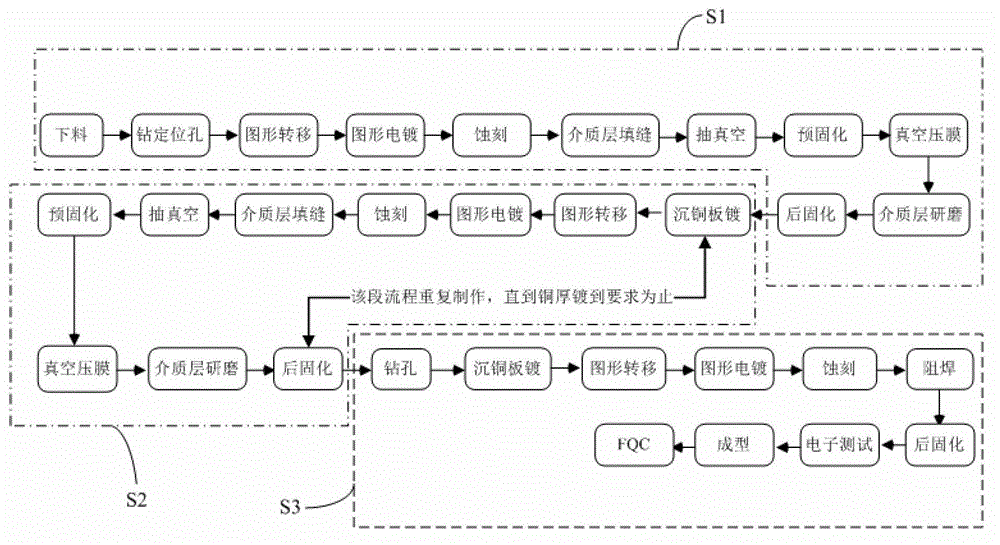
[0028] In order to make the content of the present invention clearer and easier to understand, the content of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments and accompanying drawings.
[0029] The present invention fills the medium layer ink with similar or the same expansion coefficient (CTE) as the epoxy plate between the lines by screen printing layer by layer, ensuring that there is no air in the filled ink and that it is very tightly combined with the substrate and the line wall, so as to achieve reduction The purpose of the drop between the base material and the copper surface. In addition, solder resist printing can be performed when the remaining copper thickness is normal (for example, when the predetermined copper thickness is reached).
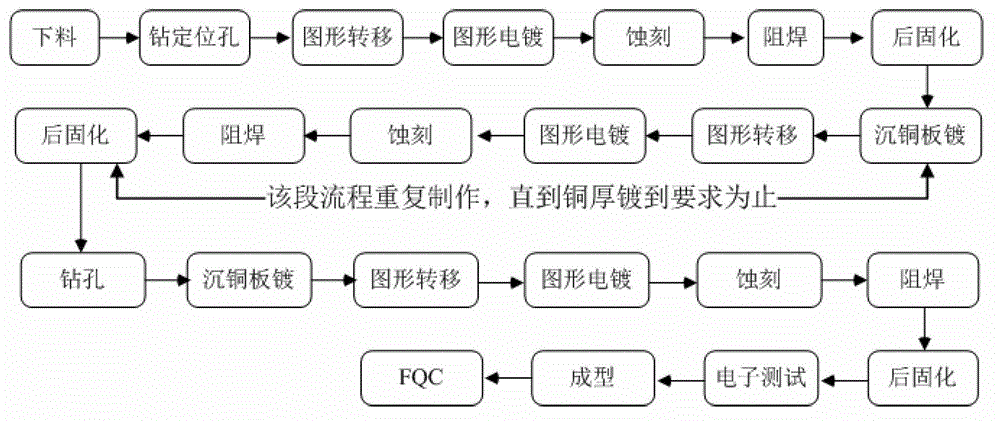
[0030] Specifically, image 3 It schematically shows the flow of the method for fabricating thick copper PCB board circuit according to the embodiment of the present invention. The...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com