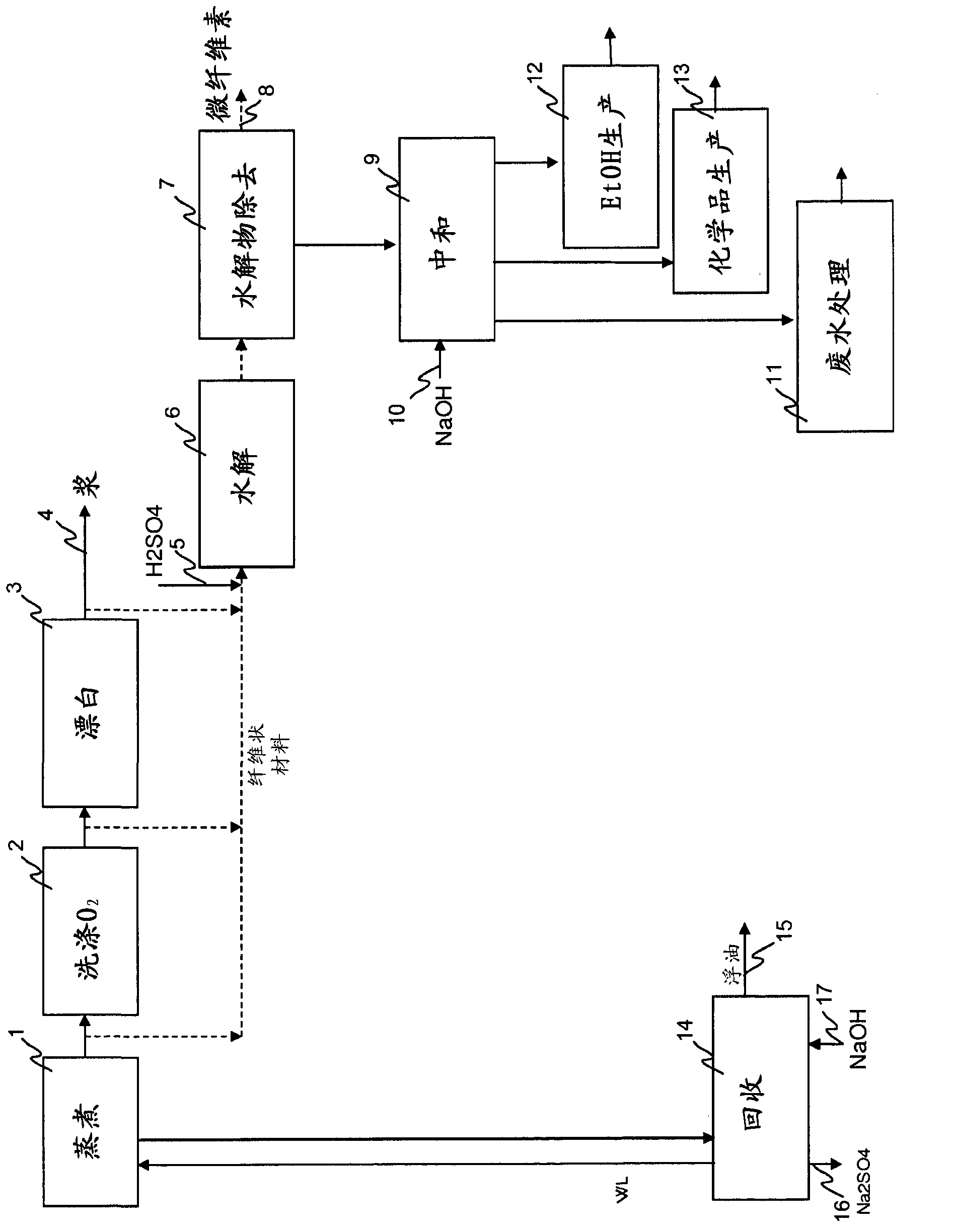
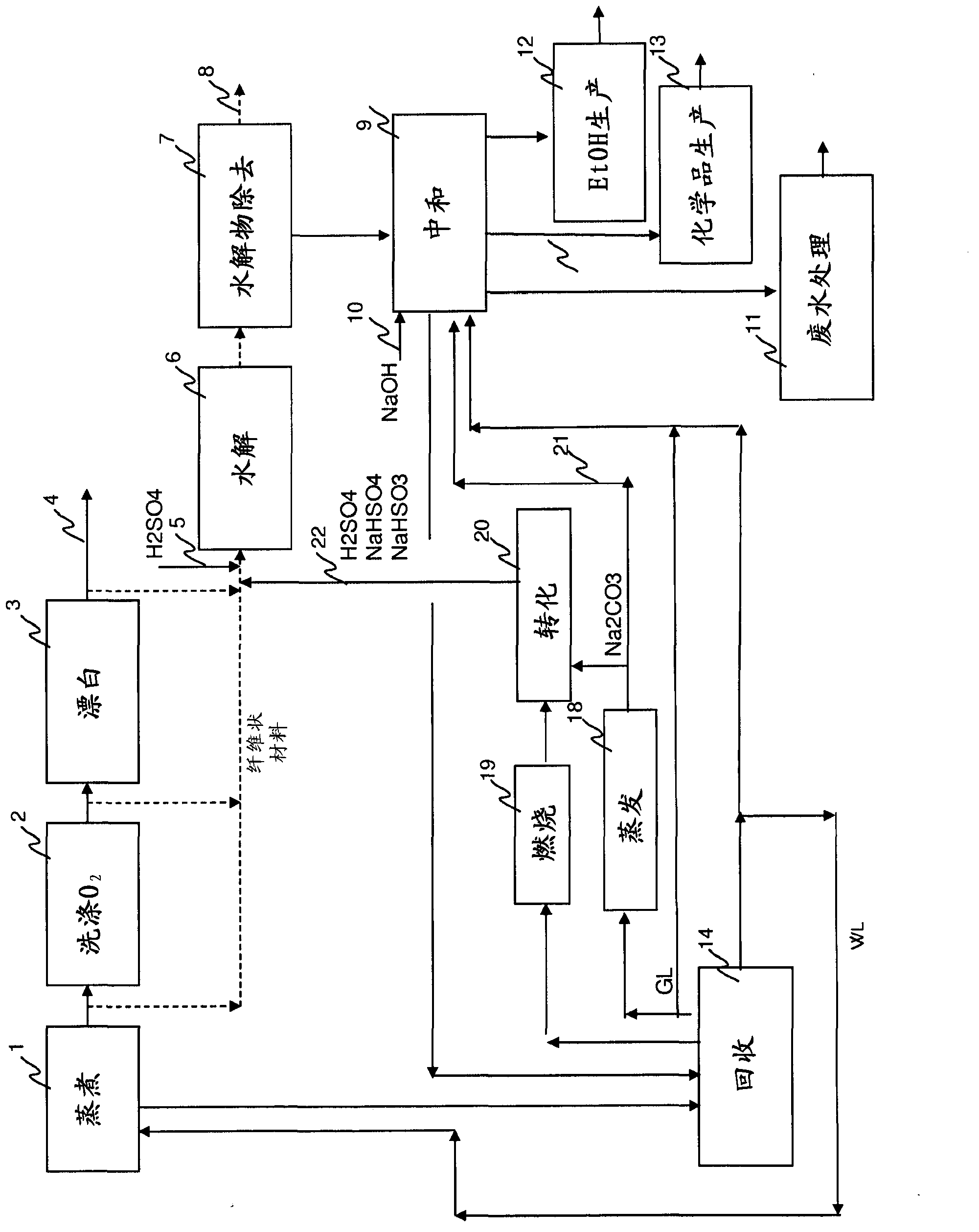
A novel method to produce microcellulose
A technology of microcellulose and cellulose, applied in the new field of production of microcellulose, can solve the problems of inefficient and expensive alternatives, and achieve the effect of controlling particle size distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0092] Example 1 Acid hydrolysis of completely white pulp, acid dosage (of dry pulp) 0.5%, cooking temperature 160°C
[0093] Using fully bleached softwood pulp, a series of hydrolysis experiments were carried out. The pulp was baled sheets (dry matter 92.4%). The procedure of Experiment 1-1 is described below. All experiments were performed in a similar manner.
[0094] Pulp chips 324.7 g (bundled sheets, dry matter 92.4%, dry pulp 300 g) were placed in the autoclave unit of the air-bath-cooker. Premix sulfuric acid 15.3ml (concentration 1mol / l, absolute sulfuric acid amount 1.50g) and water 660ml, and add to the pulp tablet. The consistency of this mixture is 30%. The sulfuric acid dosage of the pulp (absolute acid of the dried pulp) was 0.5%.
[0095] The autoclave unit was closed and heating started. The digester was first heated to 80°C in 20 minutes and then the heating section was started. The mixture was heated to 160°C at a rate of 2°C / min. When the temperatur...
Embodiment 2
[0100] Example 2 Acid hydrolysis of fully bleached pulp, acid dosage 1.5%, cooking temperature 160°C
[0101]Using fully bleached softwood pulp at 10% humidity, a series of hydrolysis experiments were carried out. The parameters and results of Example 2 are listed in Table 2.
[0102] Table 2
[0103] experiment
[0104] The particle size distribution curves are similar to those of Example 1. The results show that microcellulose with an average particle size below 20 microns can be produced without the need for mechanical treatment. The results showed that the particle size decreased slightly with increasing cooking time, but the yield decreased significantly. Compared with Example 1, the average particle size is lower, but the yield is also lower.
Embodiment 3
[0105] Example 3 Acid hydrolysis of fully bleached pulp, acid dosage 0.5%, cooking temperature 175°C
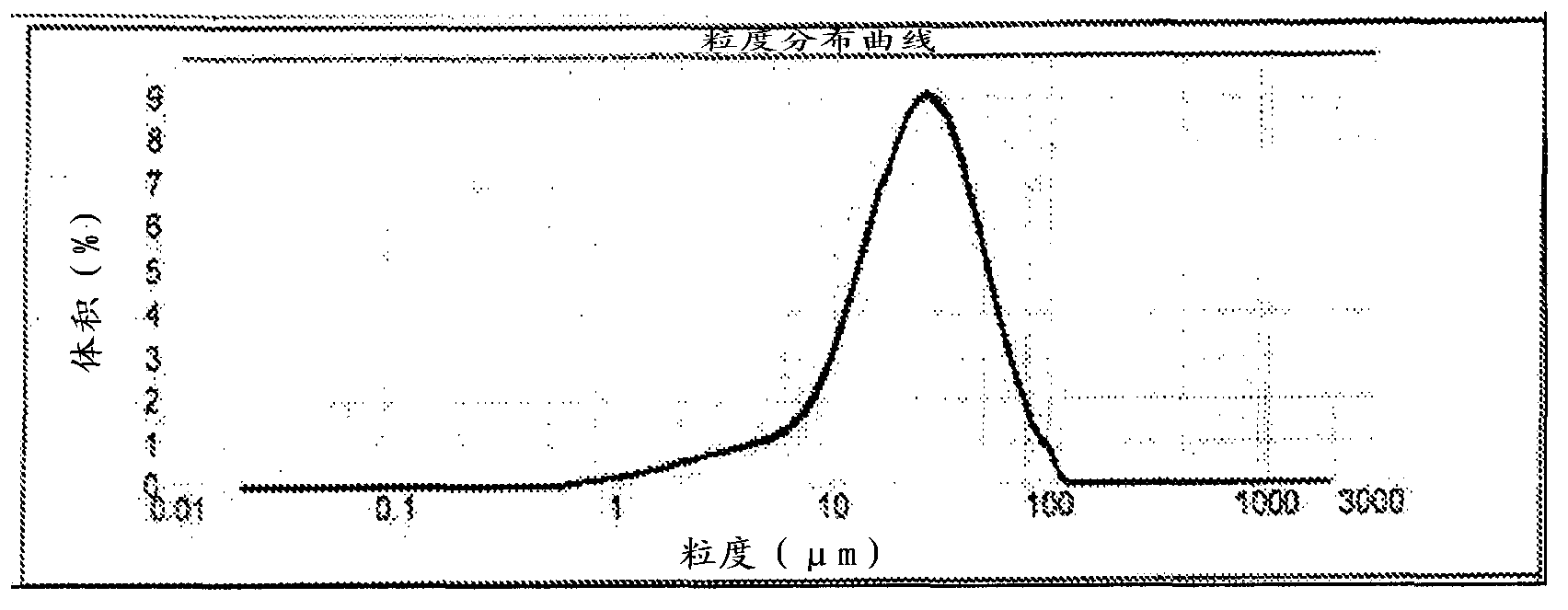
[0106] Using fully bleached softwood pulp at 10% humidity, a series of hydrolysis experiments were carried out. Table 3 lists the parameters and results of Example 3. exist Figure 4 The particle size distribution curve of Experiment 3-1 is listed in .
[0107] table 3
[0108] experiment
[0109] The results in Table 3 show that microcellulose with an average particle size of about 20 microns can be produced in good yields using a cooking time of 30 minutes or less. With a cooking time of 90 minutes, a reduced process yield was observed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com