Superframe-based low-energy-consumption media access control method in wireless body area network
A media access control and wireless body area network technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of short communication distance, limit sensor node energy and cache, and cannot guarantee time slot utilization, so as to reduce energy consumption and communication loss Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
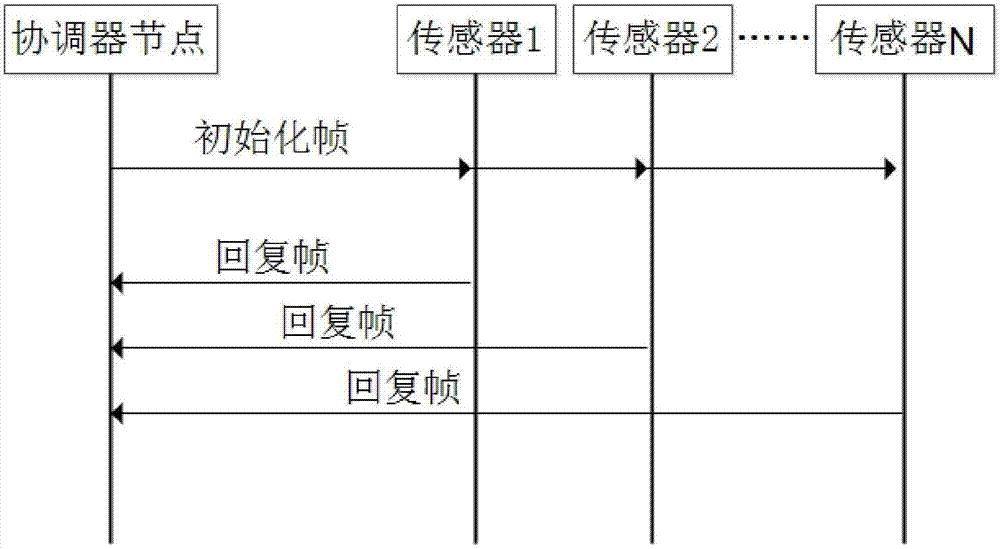
[0040] The embodiments of the present invention are further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings: this embodiment is implemented on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation methods and specific operating procedures are provided, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following the embodiment.
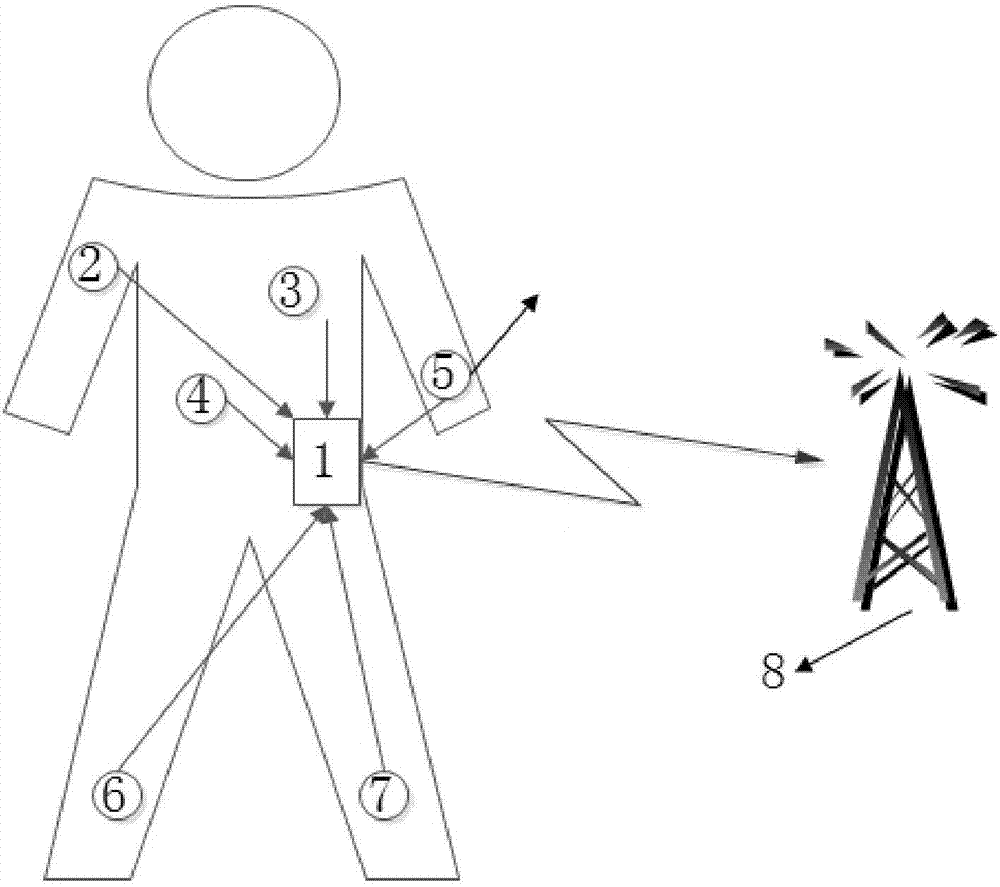
[0041] Take wireless body area network sign medical monitoring as an example, such as figure 1 As shown in the example, the star network topology centered on the personal terminal (coordinator) in this example. These include various medical sensor nodes. Node 1 is a personal terminal (coordinator), node 2 is a blood pressure sensor, node 3 is an ECG signal sensor, node 4 is a body temperature sensor, node 5 is a pulse sensor, nodes 6 and 7 are acceleration sensors, and node 8 is a public network connection sensor. entry point. The system consists of two layers. The first layer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com