Selective cardiac-magnetic signal averaging method in signal noise suppression
A signal noise and magnetic signal technology, applied in the field of signal selective averaging, can solve the problems of signal distortion, high complexity, low efficiency, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding signal distortion and high flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
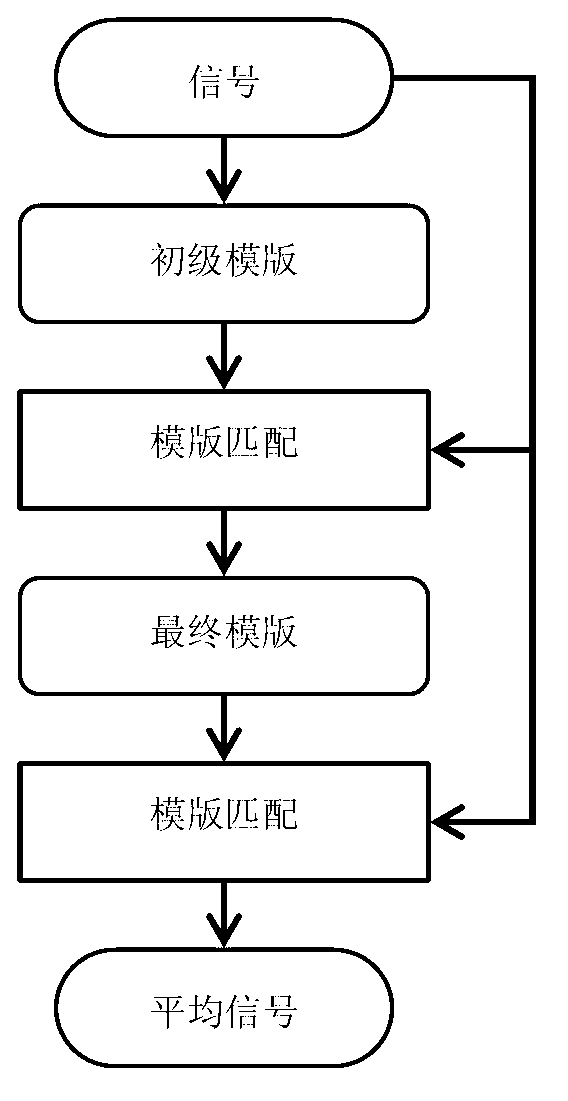
[0032] figure 1 Algorithm flow chart of the selective averaging method: firstly, the primary template signal is obtained by performing full average processing on the magnetic signal to be processed; secondly, the template matching is performed by using the MCD method, and the similarity coefficient between the template signal and the magnetic signal to be processed is calculated; The cycles that meet the set threshold conditions are averaged to obtain the final template; then the final template is matched with the signal to be tested using the MCD method to obtain the qualified cycles; finally, the selected signal cycles are averaged to obtain a selective average signal.
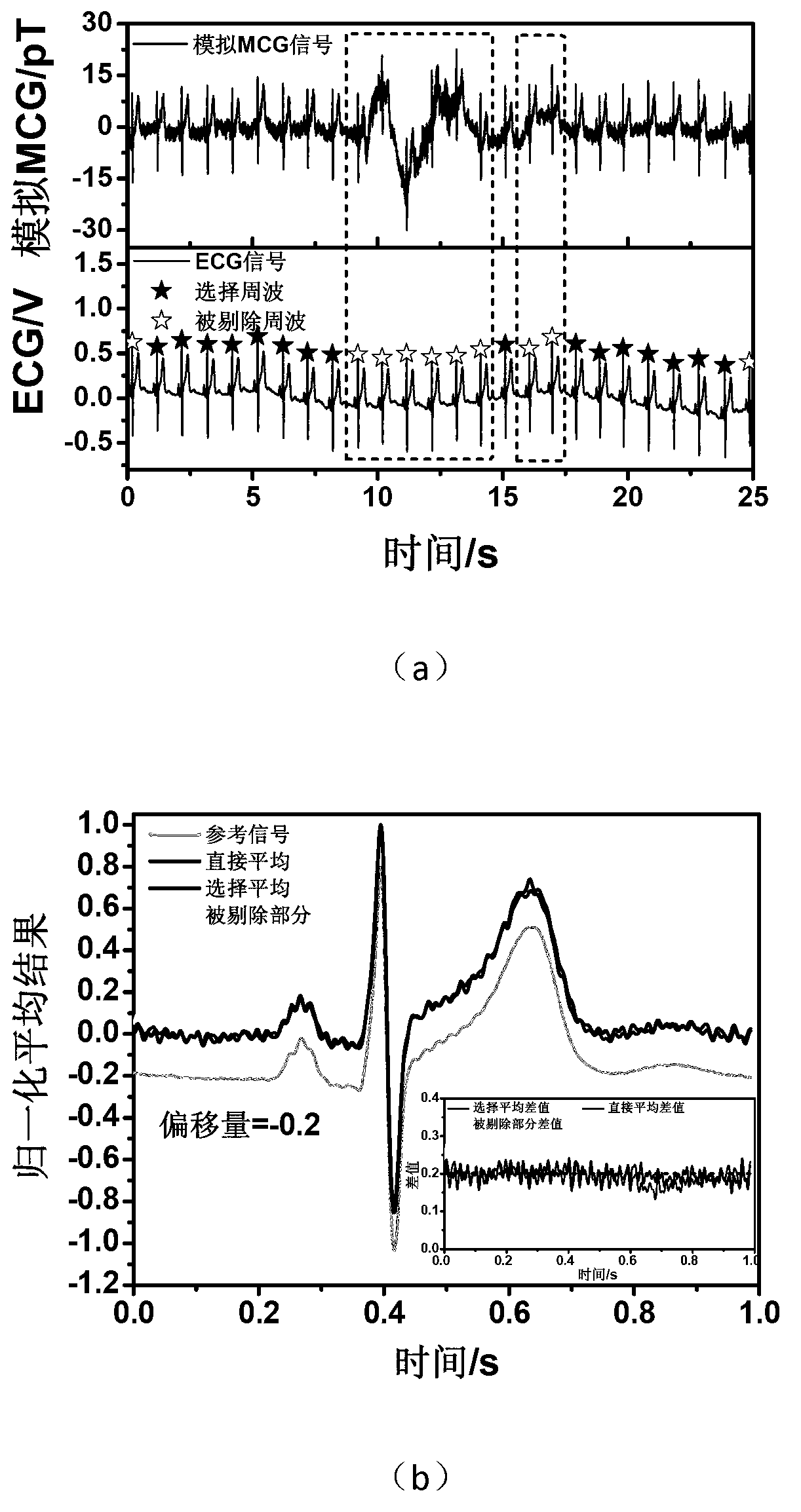
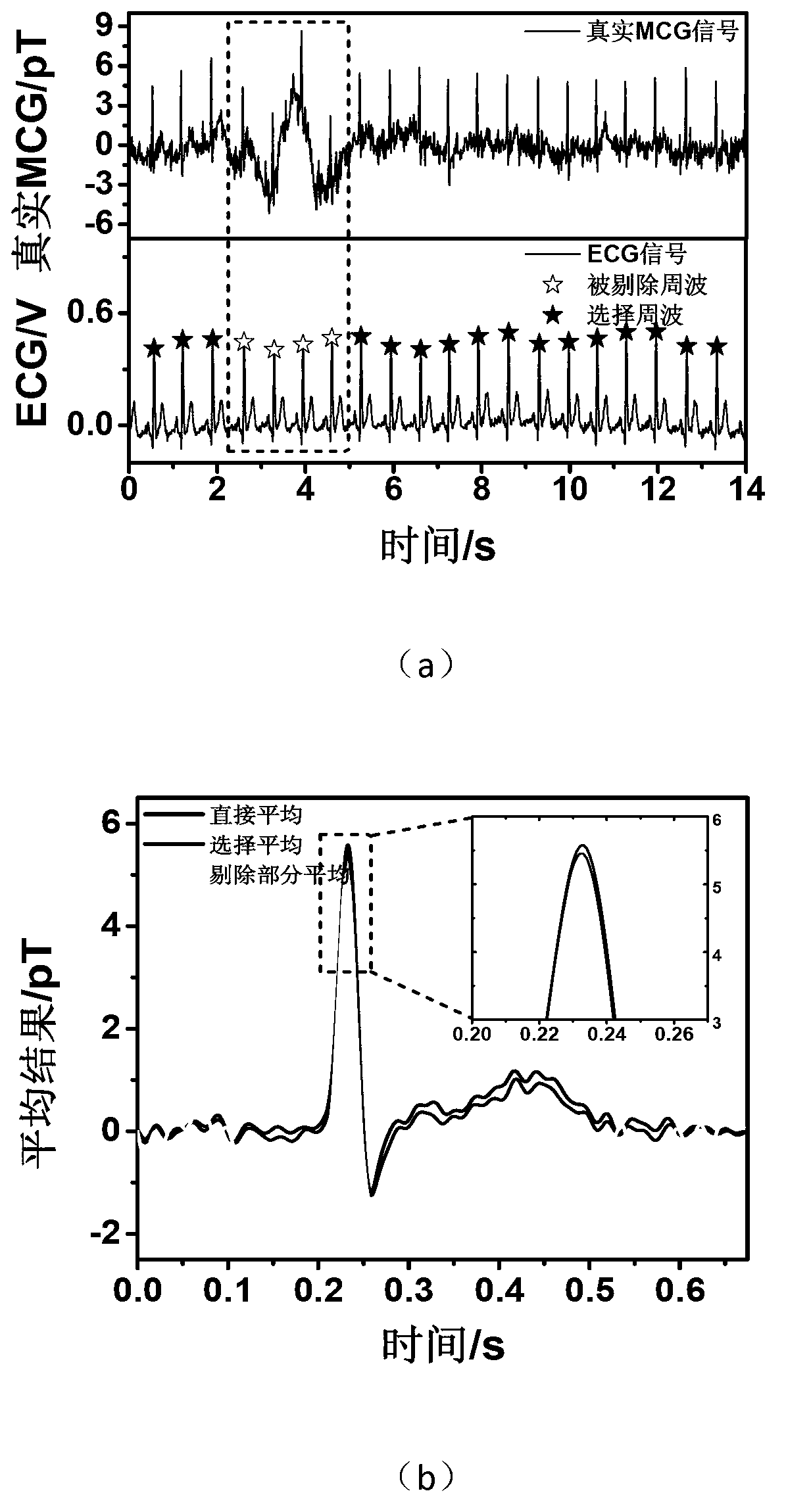
[0033] figure 2 Select an example of averaging for the simulated magnetic signal: use the electrocardiographic signal to drive a small coil to simulate the magnetic signal, and collect the simulated magnetic signal through the acquisition system. figure 2 (a) is the identification of the interference cycle...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The specific steps of signal selective averaging method of the present invention are:
[0038] 1. Find the R peak of the reference ECG signal corresponding to the electrocardiogram signal to be processed, and use it as a benchmark for signal segmentation, divide the electrocardiogram signal to be processed into individual cycles, and judge the edge data segments at both ends of the signal , discarding incomplete cycles.
[0039] 2. Carry out coherent averaging on all independent magnetic cycles of the heart, that is, superimpose and average corresponding points, and use the averaged result as a primary template.
[0040] 3. Compare each independent cardiomagnetic cycle with the primary template, calculate the similarity coefficient, and obtain a set of similarity coefficient sequences; set a reasonable threshold, compare the similarity coefficient sequence with the threshold, and judge the cycle that does not meet the threshold condition as Bad signals are discarded. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com