Device and method for quick online fault detection of high voltage thyristor valve block
A high-voltage thyristor valve, fault detection technology, applied in the direction of testing dielectric strength, circuit breaker testing, etc., can solve the problems of complex detection circuit structure, slow response speed, difficult to operate, etc. Fast, reliable results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
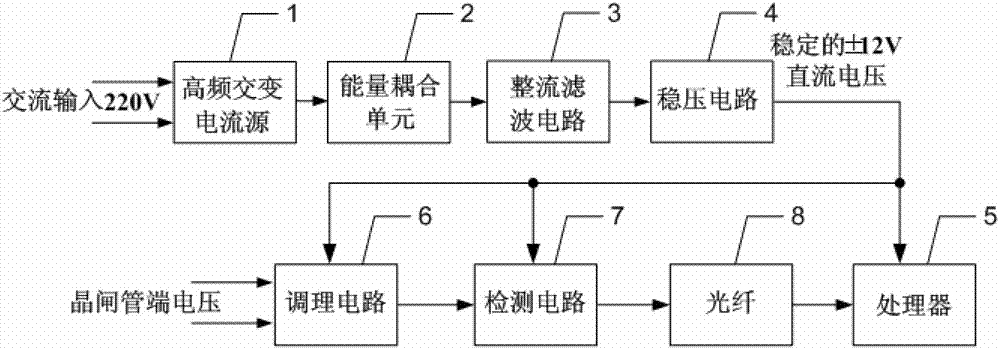
[0039] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 with Image 6 Describe this embodiment, the high-voltage thyristor valve group fast online fault detection device described in this embodiment, it includes a high-frequency alternating current source 1, an energy coupling unit 2, a rectification filter circuit 3, a voltage stabilizing circuit 4, a processor 5, a conditioning Circuit 6, detection circuit 7 and optical fiber 8,
[0040] The output end of the high-frequency alternating current source 1 is connected to the input end of the energy coupling unit 2, the output end of the energy coupling unit 2 is connected to the AC input end of the rectification filter circuit 3, and the DC output end of the rectification filter circuit 3 is connected to the voltage stabilizing circuit 4 is connected to the input end, and the output end of the voltage stabilizing circuit 4 is connected to the DC power supply end of the processor 5, the conditioning circuit ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
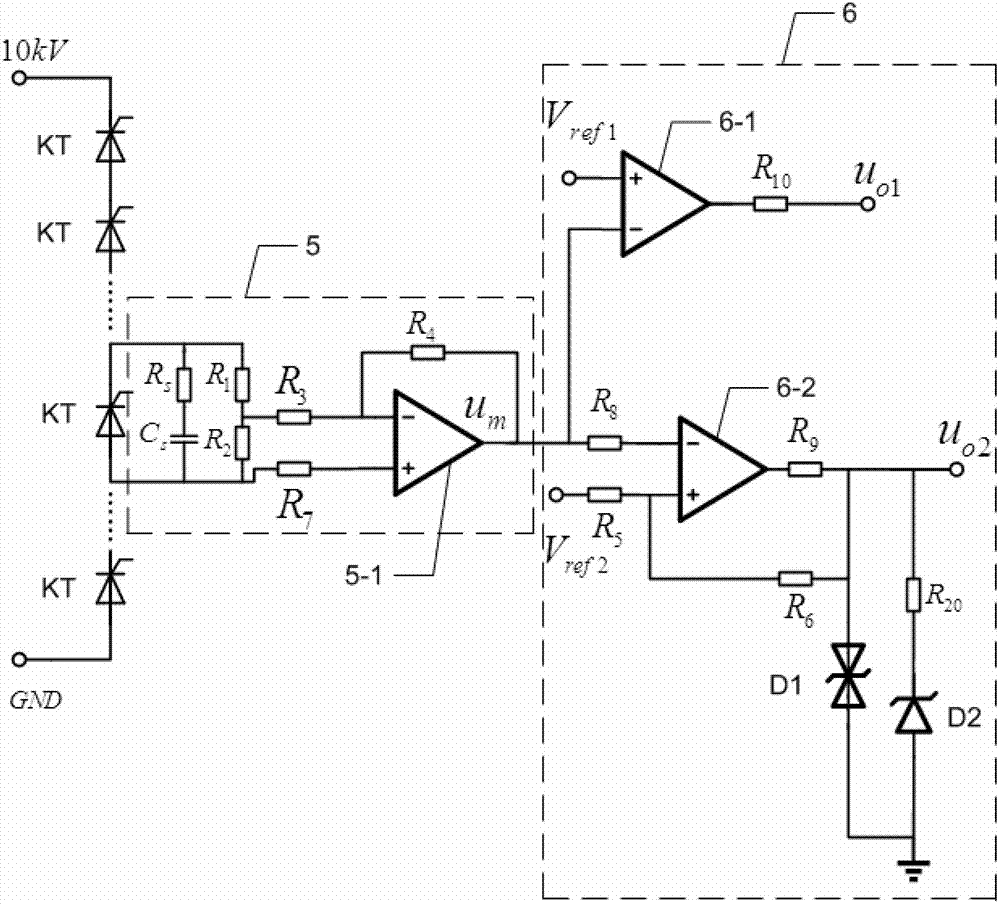
[0045] Specific implementation mode two: this implementation mode will further illustrate the first implementation mode, and the conditioning circuit 6 includes an amplifier 6-1, a resistor R 1 , resistance R 2 , resistance R 3 , resistance R 4 , resistance R 7 , resistance R S and capacitance C S ,
[0046] Resistance R S and capacitance C S Connect in parallel to both ends of the thyristor to be detected in the high-voltage thyristor valve group after being connected in series;
[0047] Resistance R 1 and resistor R 2 connected in parallel with resistor R S and capacitance C S Both ends of the series branch;
[0048] Resistance R 1 and resistor R 2 The junction point with the resistor R 3 Connected to one end of the resistor R 3 The other end of is connected with the inverting input end of amplifier 6-1;
[0049] Resistance R 1 and resistor R 2 The resistance R of the series branch 2 side with resistor R 7 Connected to one end of the resistor R 7 The ot...
specific Embodiment approach 3
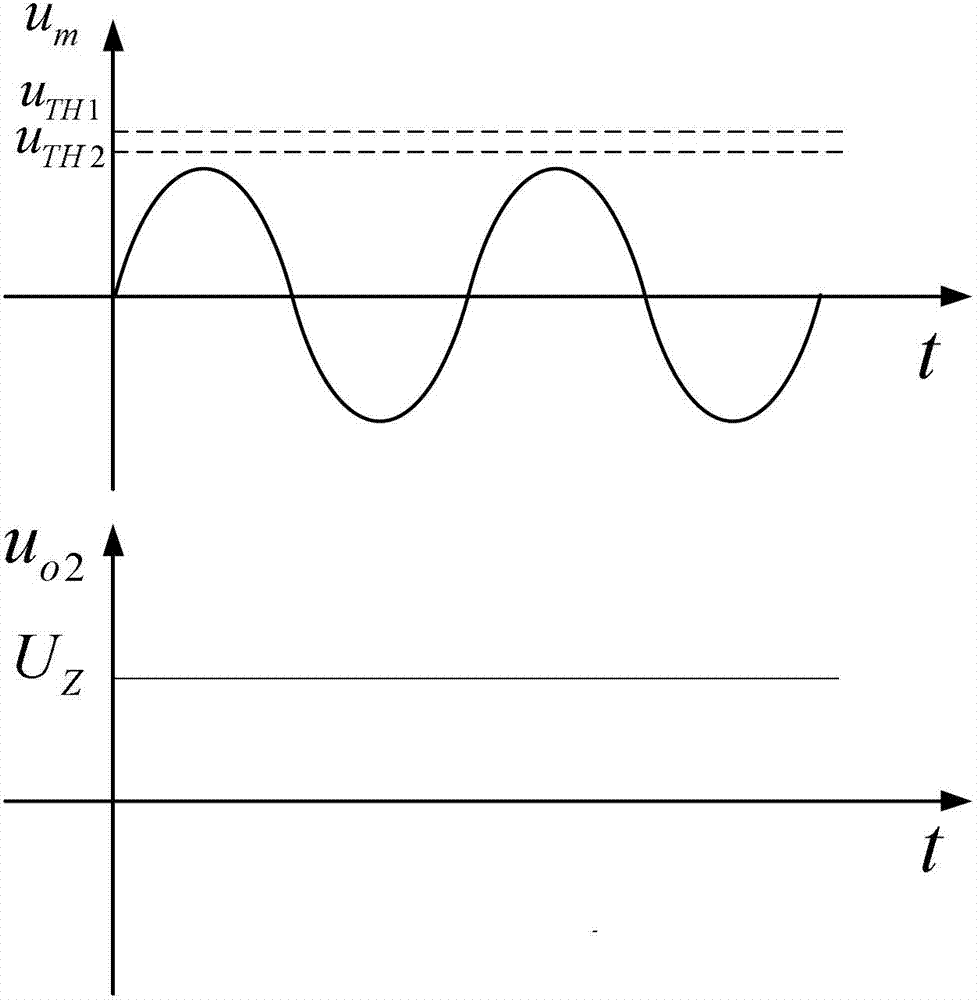
[0051] Specific embodiment three: this embodiment will further illustrate embodiment one or two, the detection circuit 7 includes a single-limit comparator 7-1, a hysteresis comparator 7-2, a resistor R 5 , resistance R 6 , resistance R 8 , resistance R 9 , resistance R 10 , resistance R 20 , bidirectional Zener diode D1 and Zener diode D2,
[0052] The output terminal of the amplifier 6-1 is connected with the inverting input terminal of the single-limit comparator 7-1, and the non-inverting input terminal of the single-limit comparator 7-1 is connected with the reference voltage V ref1 , the output terminal of the single-limit comparator 7-1 and the resistor R 10 Connected to one end of the resistor R 10 The other end of the first monitoring voltage u o1 ;
[0053] The output of amplifier 6-1 is also connected with resistor R 8 Connected to one end of the resistor R 8 The other end of is connected with the inverting input end of hysteresis comparator 7-2,
[0054]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com