Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of the same
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device components, etc., can solve problems such as increased resistance and decreased yield, and achieve the effect of increased yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0021] 1. First Embodiment (Structure of Semiconductor Device)
[0022] 2. First Embodiment (Manufacturing method in which the first wiring exposed at the bottom of the previously formed large-diameter recess is covered with a small-diameter resist pattern)
[0023] 3. Second embodiment (manufacturing method in which etching is stopped midway so that the unetched thicknesses above the first wiring and the second wiring are uniform)
[0024] 4. Third Embodiment (Manufacturing Method Using Interlayer Insulator Film as Etching Stopper to Stop Etching Halfway)
[0025] 5. Fourth Embodiment (Manufacturing Method of Filling a Filling Member into a Concavity Formed by Stopping Etching Halfway)
no. 5 approach
[0026] 6. Fifth Embodiment (Manufacturing Method of Remaining Resist Material for Covering Second Wiring in Previously Formed Small-diameter Recess)
[0027] 7. Sixth embodiment (manufacturing method in which etching is stopped midway so that the unetched thicknesses above the first wiring and the second wiring are uniform)
[0028] 8. Seventh Embodiment (Manufacturing method in which etching is stopped halfway to make unetched thicknesses above first wiring and second wiring uniform and a hard mask is used)
[0029] It should be noted that similar components in the respective embodiments and modifications are denoted by the same reference numerals, and repeated descriptions are omitted.
[0030]
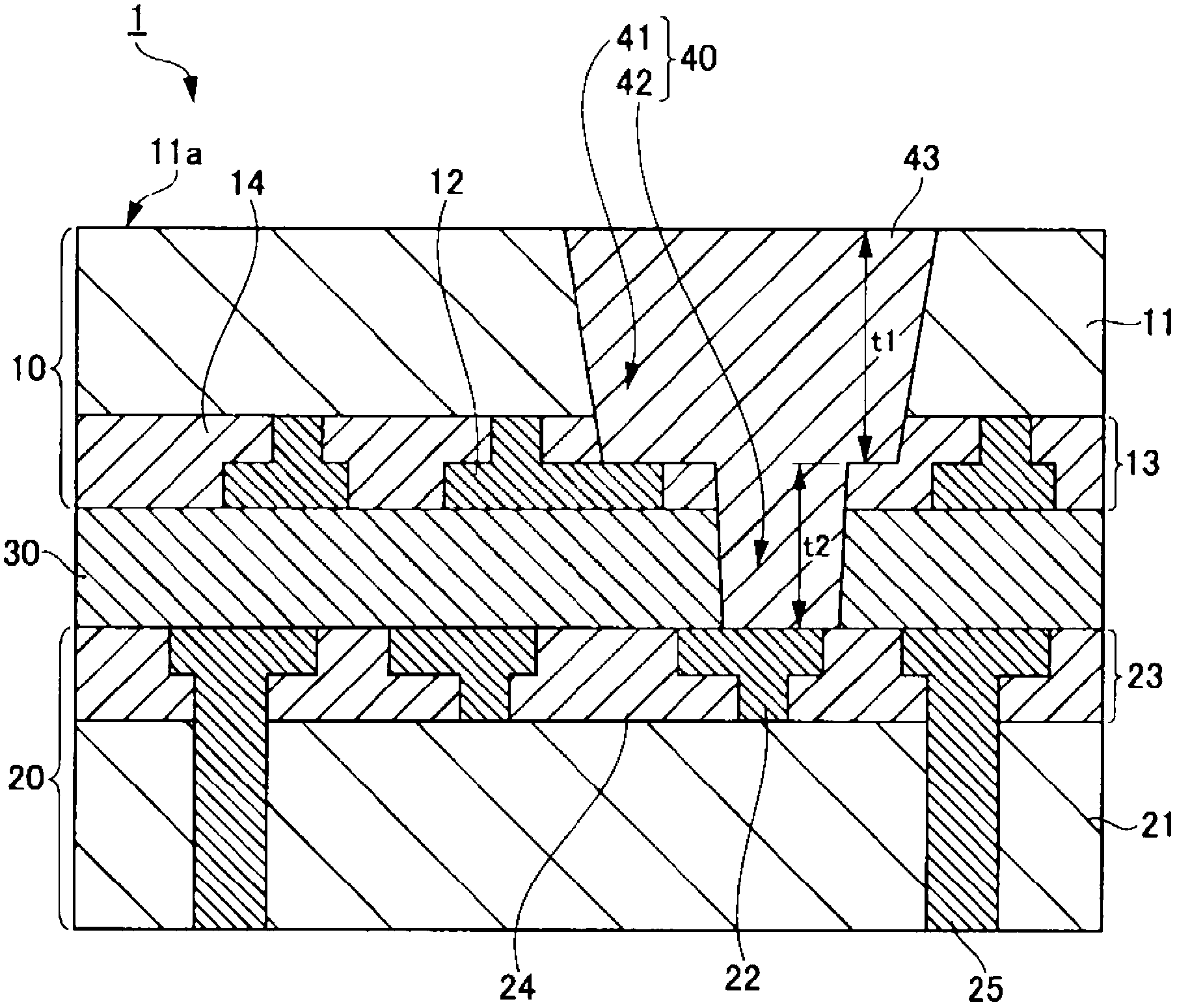
[0031] figure 1 is a cross-sectional view of main components of the semiconductor device of the first embodiment. Next, the semiconductor device of the first embodiment will be described in detail based on the cross-sectional view of the main components.
[0032] figure 1 The ...
Embodiment approach
[0053]
[0054] Below, refer to Figure 2A ~ Figure 2G The cross-sectional step diagrams shown illustrate the method of manufacturing the semiconductor device 1 of the first embodiment described above.
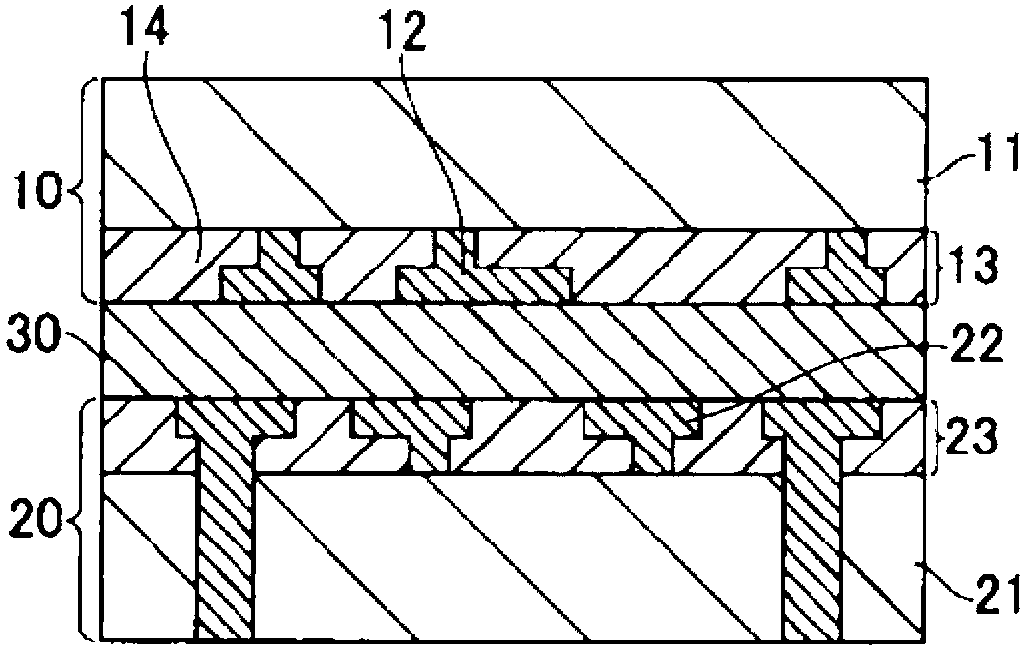
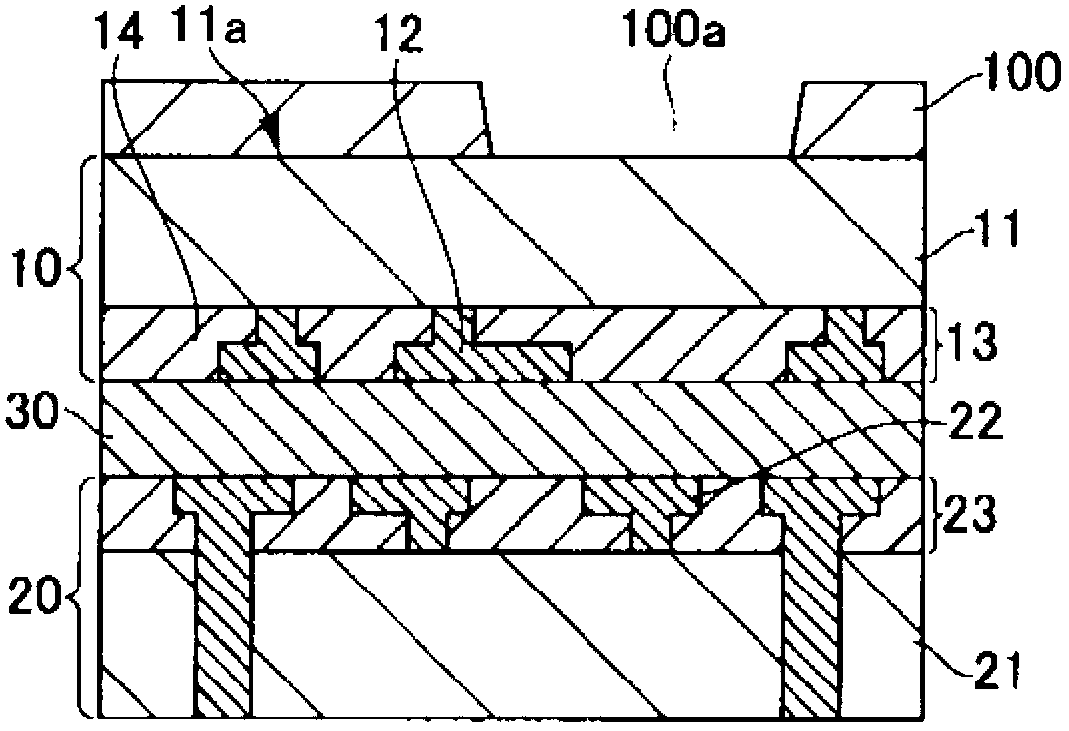
[0055] Such as Figure 2A As shown, a first substrate 10 and a second substrate 20 are manufactured. The wiring layer 13 including the first wiring 12 is provided on one main surface side of the semiconductor layer 11 of the first substrate 10 . The wiring layer 23 including the second wiring 22 is provided on one main surface side of the semiconductor layer 21 of the second substrate 20 . The first substrate 10 and the second substrate 20 are bonded together through the bonding portion 30 interposed between the wiring layer 13 and the wiring layer 23, and thus a bonded substrate is manufactured.
[0056] It should be noted that the steps up to this point are not specifically limited, and the steps can be carried out using usual techniques. The step of forming connection...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com