Charging device and charging method
A charging device and charging electrode technology, applied in circuit devices, battery circuit devices, secondary battery charging/discharging, etc., to achieve the effects of less power consumption, small size, and wide voltage regulation range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
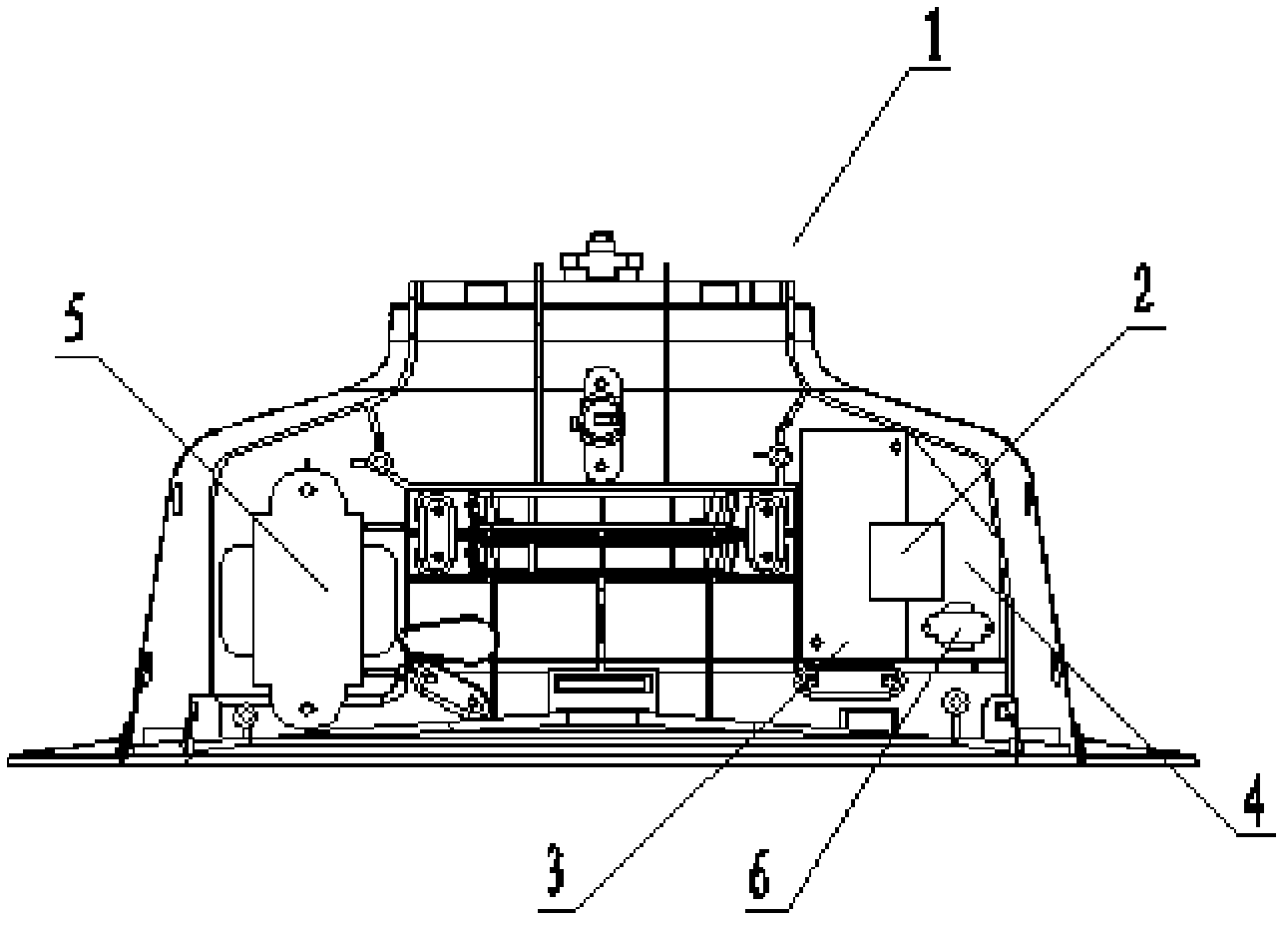
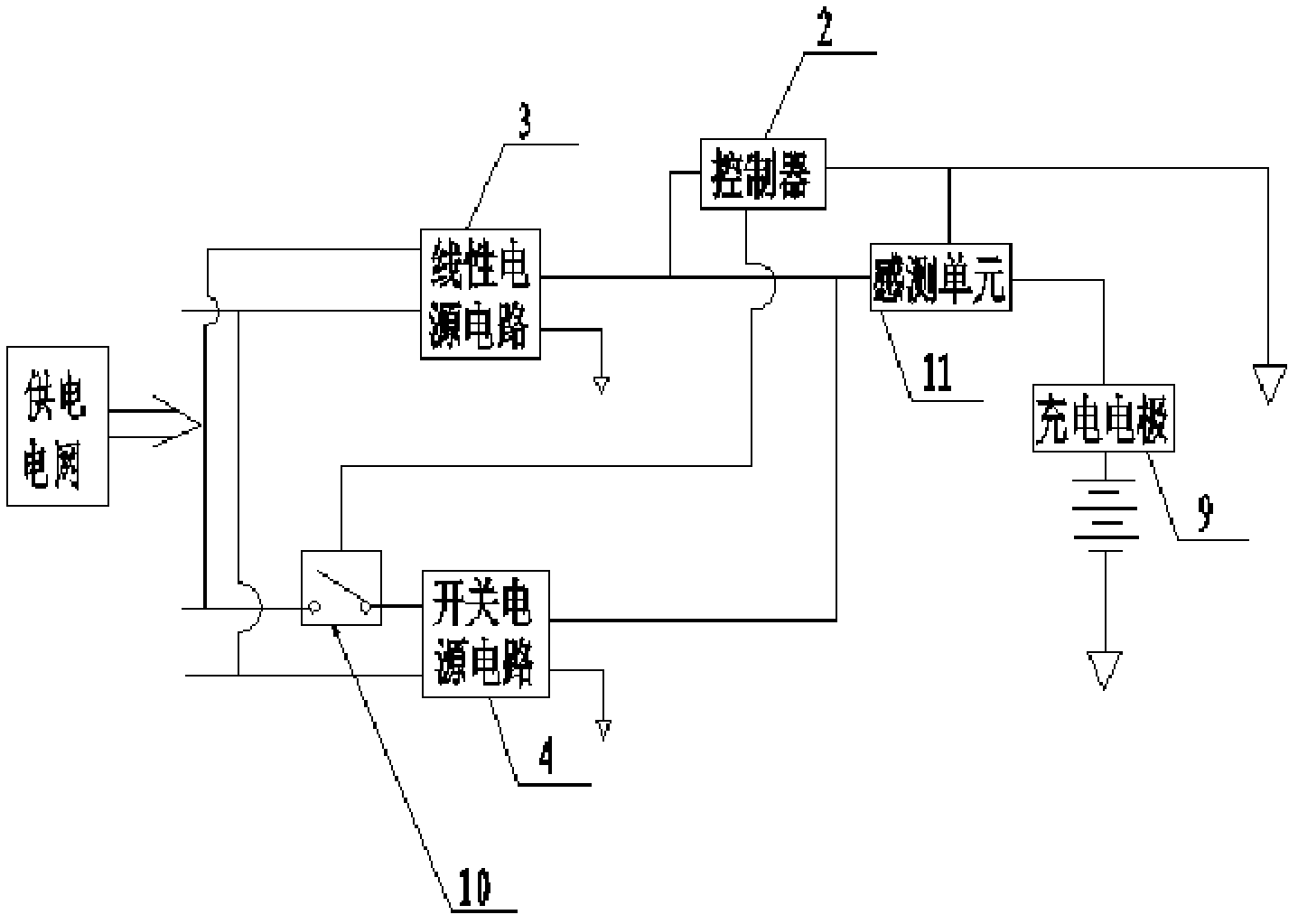
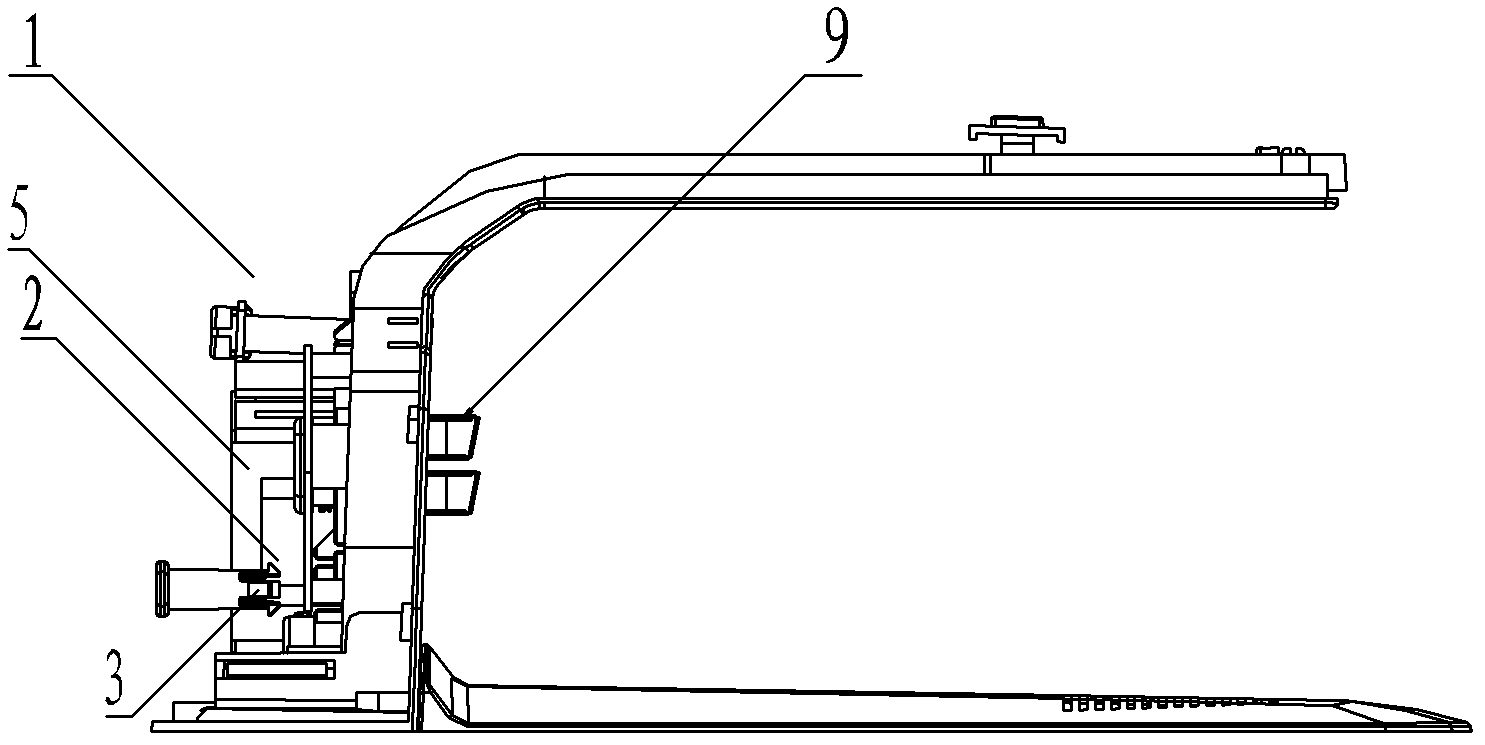
[0046] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 , Figure 6 As shown, the charging device 1 includes a controller 2, a linear power supply circuit 3 and a charging electrode 9. The charging device 1 also includes a switching power supply circuit 4 connected in parallel with the linear power supply circuit 3. The input and output terminals of the switching power supply circuit 4 are respectively Connected with the first switch 10 and the charging electrode 9, the switching power supply circuit 4 is provided with an inverter 6, which is also called a high-frequency transformer, and its function is to convert direct current into alternating current.
[0047] The output end of the linear power supply circuit 3 is connected to the controller 2, and the linear power supply circuit 3 is provided with a linear transformer 5; the controller 2 controls the connection and disconnection of the switching power supply circuit 4 through the first switch 10.
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0061] In Embodiment 2, the components, circuit connections and working principles included in the charging device 1 are basically the same as those in Embodiment 1. The difference between the two is that in Embodiment 2, the charging device 1 is also provided with a second switch (not shown in the figure), the output end of the linear power supply circuit 3 is connected to the charging electrode 9 through the second switch; when the controller 2 turns off the first switch 10, the second switch is closed.
[0062] The significance of adding the second switch is that when the storage battery of the electric device 7 is fully charged, if the electric device 7 does not need to be put into work immediately, the first switch 10 can be disconnected by the controller 2, and the second switch is closed, thereby The linear power supply circuit 3 supplementally charges the electric device 7 by way of trickle charging, so as to maintain the full power state of the electric device 7 . And...
Embodiment 3
[0066] The difference between this embodiment and embodiments 1 and 2 lies in the connection relationship between the sensing unit and other components. Specifically, in this embodiment, the sensing unit is only connected to the controller 2 and not connected to the charging electrode 9 . Specifically, when the sensing unit adopts an electromagnetic sensor or a magnetic induction sensor, the sensing unit may not be connected to the charging electrode 9 .
[0067] For example, a magnetic signal transmitter can be arranged near the docking electrode 8 of the electrical device 7, and when the docking electrode 8 of the electrical device 7 is docked with the charging electrode 9 of the charging device 1, the magnetic signal sensor can sense the corresponding magnetic signal, and send the sensing signal to the controller 2, and the controller 2 controls the first switch 10 to turn off according to the sensing signal.
[0068] As another example, an electromagnetic sensor can also ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com