Protein sequence with enterocyte protective function and application thereof
A technology of intestinal epithelial cells and protein sequences, which can be used in medical preparations containing active ingredients, peptide/protein components, digestive system, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1, inhibiting the adhesion of EIEC / EPEC to NCM460 cells
[0020] For experimental methods, please refer to the literature: Liu Z, Shen T, Zhang P, Ma Y, Qin H, Lactobacillus plantarum surface layer adhesive protein protects intestinal epithelial cells against tight junction injury induced by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, Mol Biol Rep , 2011; 38(5): 3471-3480
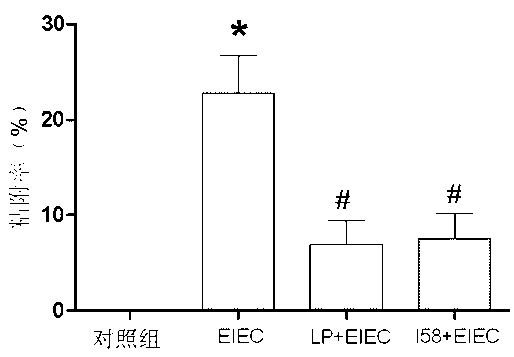
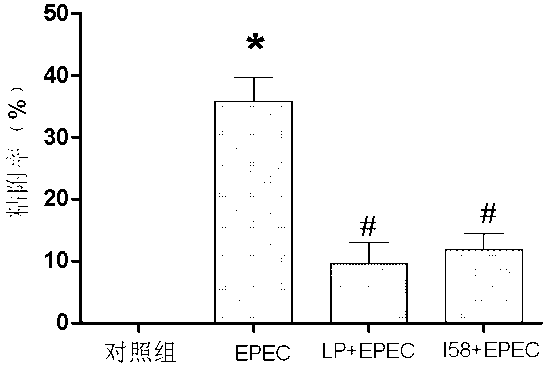
[0021] As shown in Figure 1, the adhesion rate of EIEC to NCM460 cells was 15%-28%, and the adhesion rate of EPEC to NCM460 cells was 20%-45%. However, when the protein sequence (I58) of the present invention was pretreated (I58+EIEC, I58+EPEC), the adhesion rates of EIEC and EPEC were significantly reduced, both falling below 10%. Compared with pretreatment with Lactobacillus plantarum (LP+ EIEC, LP+EPEC) are similar, or even better.
[0022] However, after adding anti-MIMP (anti-I158) to block its effect, the protective effect of the protein sequence of the present invention disappeared (P<0.05...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2, Inhibition of EIEC / EPEC-induced decrease in NCM460 cell permeability (TER)
[0024] Test method reference: Qin H, Zhang Z, Hang X, Jiang Y. L., Plantarum prevents enteroinvasive Escherichia coli-induced tight junction proteins changes in intestinal epithelial cells, BMC Microbiol , 2009; 9: 63
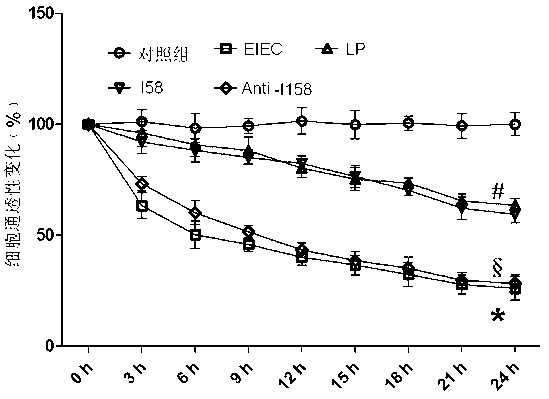
[0025] The experimental results shown in Figure 2 showed that after EIEC / EPEC intervention, the TER value of NCM460 cells was significantly decreased compared with the control group (P Figure 2A , Figure 2B ), but after I58 pretreatment, the TER value of NCM460 cells increased significantly. After 24 hours, the permeability of EIEC to NCM460 cells increased from about 25% to about 65-70%, and the permeability of EPEC to NCM460 cells increased from 30 % rises to about 70~75%, which is similar to the effect of direct use of Lactobacillus plantarum (LP).
[0026] However, after adding anti-MIMP (anti-I158) to block its effect, the protective effect of the protein s...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3, reducing the destructive effect of EIEC / EPEC on tight junction protein (TJ) and F-actin
[0028] Test method reference: Qin H, Zhang Z, Hang X, Jiang Y. L., plantarum prevents enteroinvasive Escherichia coli-induced tight junction proteins changes in intestinal epithelial cells, BMC Microbiol , 2009; 9: 63
[0029] As shown in Figure 3, fluorescence staining showed that the expression of TJ-related proteins in the control group showed that the fluorescence was distributed along the cell membrane with clear boundaries and a network structure. After EIEC / EPEC infected Caco-2 cells, the fluorescence distribution among the cells was obviously scattered and the intensity was weakened. The gap between cells increases, and the fluorescence intensity of TJ-related proteins is significantly improved after I58 pretreatment, and the distribution along the cell membrane is clearer, similar to the effect of using Lactobacillus plantarum (LP). IF method for F-actin det...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com