Structure-based dependency graph node similarity concurrent computation method
A parallel computing and similarity technology, applied in computing, image data processing, image data processing, etc., can solve the problems of increased computing time for similarity diffusion, increased computational complexity, and failure to meet needs, so as to improve accuracy and reduce complexity The effect of degree and computation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] 101: The CPU end reads multiple story texts as the host end, establishes a graph model, and obtains the first adjacency matrix W of the graph;
[0045] The nodes in the graph represent the words in the story, and the edges between the nodes represent the similarity between the nodes. According to the first similarity measurement rule, the edge relationship between the words in the story and the words between the stories is established in the graph model, and the obtained The first adjacency matrix W of the graph.
[0046] Wherein, the first similarity measurement rule is set according to the needs in practical applications, for example: the similarity measurement between words in the story consists of the frequency of occurrence of word A, the frequency of occurrence of word B, and the co-occurrence of word A and word B and The number of times the distance between two words is less than the preset value is jointly determined; the similarity measure of words between stor...
Embodiment 2
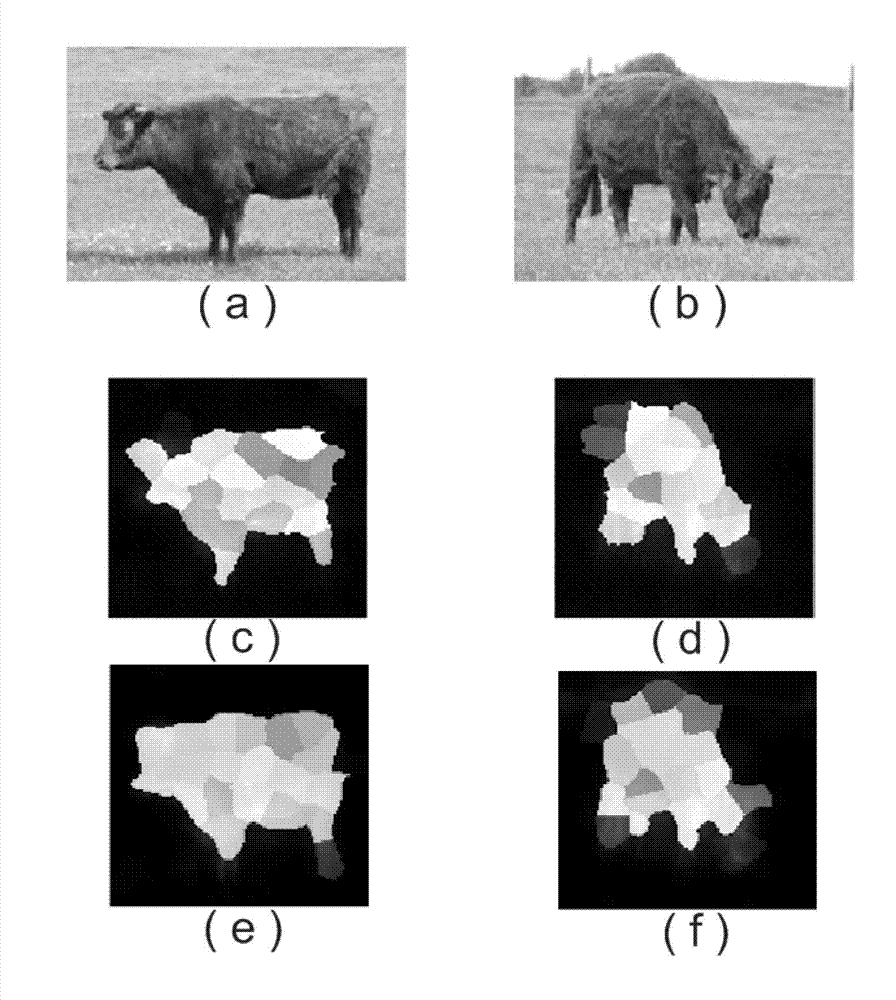
[0060] 201: The CPU side acts as the host side to input multiple images, establish a graph model, and obtain the second adjacency matrix W and transition matrix T of the graph;
[0061] The nodes in the graph represent the superpixels in the image, and the edges between nodes represent the similarity between nodes, and according to the second similarity measurement rule, the superpixels in an image and the superpixels in different images are compared Establish the edge relationship in the graph model, and finally calculate the second adjacency matrix W, and calculate the transfer matrix T from the second adjacency matrix W, and read in the algorithm parameter constant attenuation factor C and error err.
[0062] Among them, the second similarity measurement rule is set according to the needs in practical applications, for example: calculate and obtain a region descriptor for each superpixel, calculate the similarity between two pairs of superpixels in the image through the regi...
Embodiment 3
[0083] When the scale of the graph is large and sparse, in order to increase the speed of calculating the second adjacency matrix, the method may also calculate the second adjacency matrix through step 302 .
[0084] 301: The CPU side acts as the host side to input multiple images, establish a graph model for them, obtain the second adjacency matrix W and transition matrix T of the graph, and store the transition matrix T in a CRS (Compressed Row Storage) structure as sparse matrix;
[0085] This storage form uses contiguous memory locations to store the following vectors: the val row array stores the non-zero matrix elements in row-major order, the col array stores the column index of each element in the val array, and the rowptr vector stores the index of the beginning row in the val array Element ordinal.
[0086] The nodes in the graph represent the superpixels in the image, and the edges between nodes represent the similarity between nodes, and according to the second si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com