Cladding material for insulated substrates
A technology of insulating substrates and cladding materials, which is applied in the directions of welding/cutting media/materials, applications, household appliances, etc., and can solve problems such as the inability to install semiconductor components
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
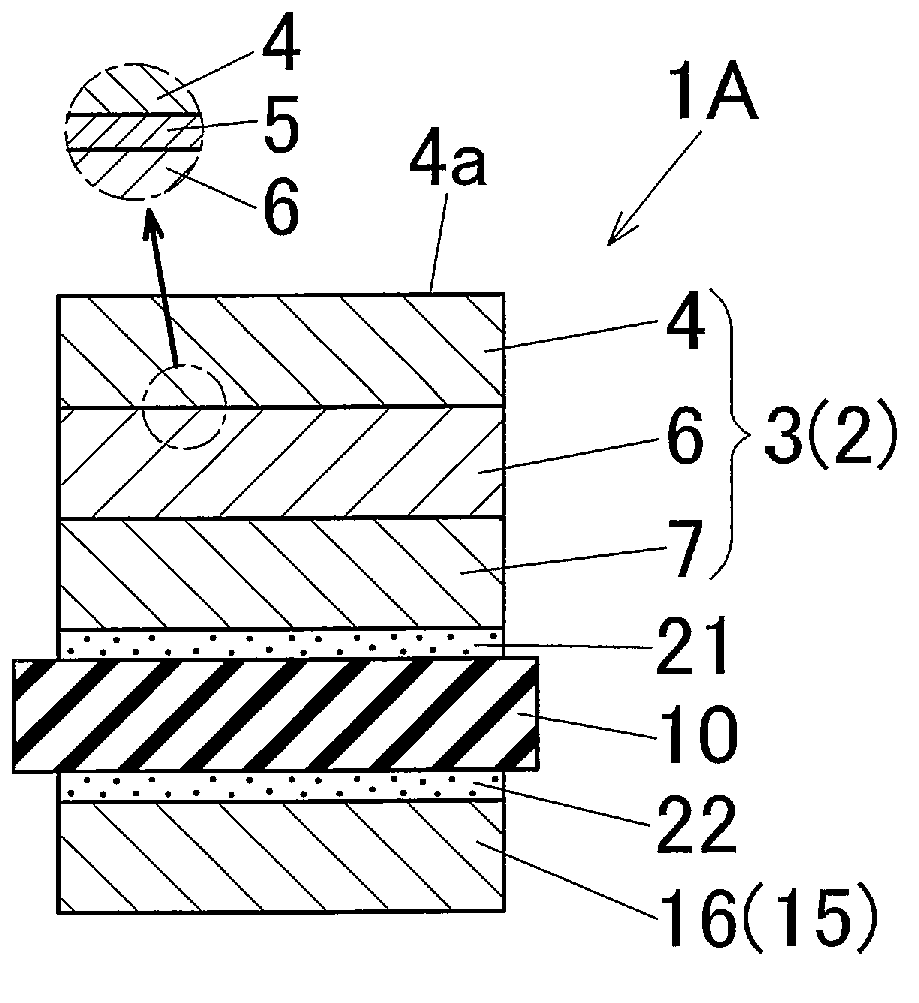
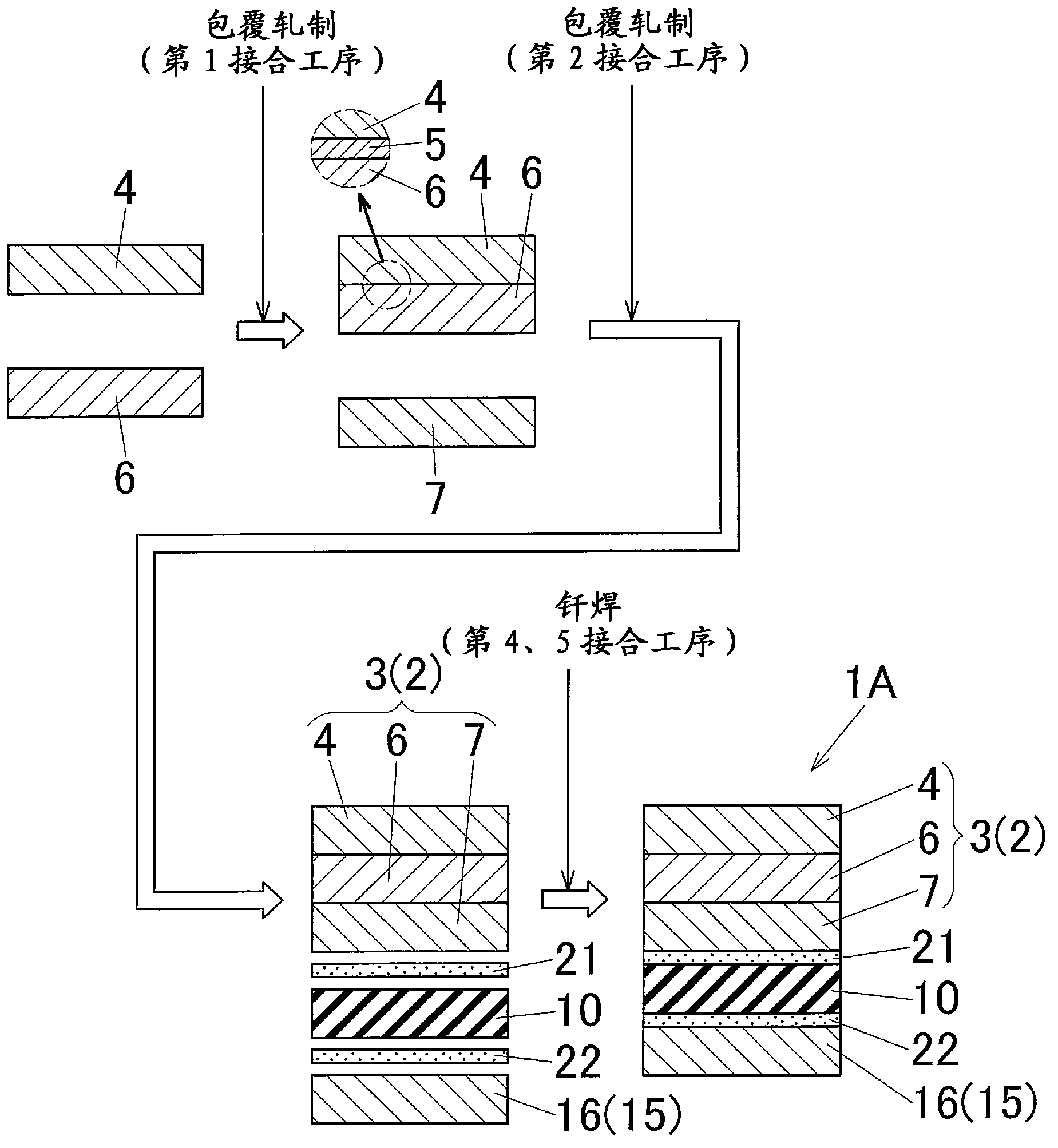
[0198] In this Example 1, a figure 2 and the insulating substrate 1A of the above-mentioned first embodiment shown in 3. Its production method is as follows.
[0199] The lower plate is prepared as the Ni layer 4, the Ti layer 6, the first Al layer 7, the ceramic layer 10, and the third Al layer 16, respectively.
[0200] Ni layer 4: a pure Ni plate with a length of 25 mm x a width of 25 mm x a thickness of 50 μm
[0201] Ti layer 6: a pure Ti plate with a length of 25 mm x a width of 25 mm x a thickness of 200 μm
[0202] The first Al layer 7: a pure Al plate with a length of 25 mm x a width of 25 mm x a thickness of 600 μm
[0203] Ceramic layer 10: AlN plate of 25 mm in length x 25 mm in width x 600 μm in thickness
[0204] The third Al layer 16: a pure Al plate with a length of 25 mm x a width of 25 mm x a thickness of 600 μm.
[0205] The purity of the Ni plate forming the Ni layer 4 is JIS (Japanese Industrial Standard) Class 1. The purity of the Ti plate forming ...
Embodiment 2
[0211] In this Example 2, a Figure 5 The insulating substrate 1B of the above-mentioned second embodiment is shown. Its production method is as follows.
[0212] Lower plates were prepared as Ni layer 4 , Ti layer 6 , first Al layer 7 , second Al layer 8 , ceramic layer 10 , and third Al layer 16 .
[0213] Ni layer 4: a pure Ni plate with a length of 25 mm x a width of 25 mm x a thickness of 20 μm
[0214] Ti layer 6: a pure Ti plate with a length of 25 mm x a width of 25 mm x a thickness of 20 μm
[0215] The first Al layer 7: a pure Al plate with a length of 25 mm x a width of 25 mm x a thickness of 40 μm
[0216] The second Al layer 8: a pure Al plate with a length of 25 mm x a width of 25 mm x a thickness of 600 μm
[0217] Ceramic layer 10: AlN plate of 25 mm in length x 25 mm in width x 600 μm in thickness
[0218] The third Al layer 16: a pure Al plate with a length of 25 mm x a width of 25 mm x a thickness of 600 μm.
[0219] The purity of the Ni plate forming ...
Embodiment 3
[0225] In this Example 3, the same method as in Example 2 above was produced Figure 5 The insulating substrate 1B of the above-mentioned second embodiment is shown. Its production method is as follows.
[0226] Lower plates were prepared as Ni layer 4 , Ti layer 6 , first Al layer 7 , second Al layer 8 , ceramic layer 10 , and third Al layer 16 .
[0227] Ni layer 4: a pure Ni plate with a length of 25 mm x a width of 25 mm x a thickness of 15 μm
[0228] Ti layer 6: a pure Ti plate with a length of 25 mm x a width of 25 mm x a thickness of 15 μm
[0229] The first Al layer 7: an Al plate with a length of 25 mm x a width of 25 mm x a thickness of 100 μm
[0230] The second Al layer 8: a pure Al plate with a length of 25 mm x a width of 25 mm x a thickness of 600 μm
[0231] Ceramic layer 10: AlN plate of 25 mm in length x 25 mm in width x 600 μm in thickness
[0232] The third Al layer 16: a pure Al plate with a length of 25 mm x a width of 25 mm x a thickness of 600 μm....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com